Abstract
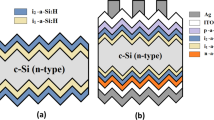
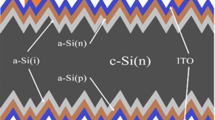
The postdeposition microwave heating treatment is carried out on the n-type crystalline silicon with bifacial deposited intrinsic hydrogenated amorphous silicon layers (i/c-Si/i) used as a precursor for amorphous silicon/crystalline silicon heterojunction (SHJ) solar cells. The passivation of i/c-Si/i heterostructure was improved significantly in 5 s microwave processing and two cycles of this processing later it could be stabilized. The results of FTIR show that the hydrogen within (i)a-Si:H layer is released rapidly during the process and the microstructure factor R* continues to decrease versus the processing time. An appropriate amount of hydrogen atoms released from Si–H bonds (especially weak bonds) move to the interface to saturate the dangling bonds favoring the passivation performance but excessive hydrogen release from the layers could lead to extremely poor passivation. The SHJ solar cell with a microwave-treated precursor of i/c-Si/i achieved an improved efficiency of 1.6%abs corresponding to the reference cell and improved surface passivation quality is the main reason for the efficiency gain, while the efficiency of the cells with the other two microwave-treated precursors of i/c-Si/i/p and n/i/c-Si/i/p increased by 1.1%abs and decreased by 0.7%abs, respectively, which may due to the difference in temperature rise during the processing. In addition, the cell with the microwave-treated precursor of i/c-Si/i shows a greater degradation of about 0.4%abs after storage in the N2 atmosphere for 312 h, while the cells with the other two precursors show good stability. It indicates that weak bonds formed by dopant atoms with hydrogen may be broken and released during the process, which may play an important facilitator role in the mechanism of degradation after the SHJ solar cells are fabricated.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
M. Tanaka, M. Taguchi, T. Matsuyama, T. Sawada, S. Tsuda, S. Nakano, H. Hanafusa, Y. Kuwano, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 31, 3518 (1992)
M. Taguchi, A. Terakawa, E. Maruyama, M. Tanaka, Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 13, 481 (2005)
X. Ru, M. Qu, J. Wang, T. Ruan, M. Yang, F. Peng, W. Long, K. Zheng, H. Yan, X. Xu, Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 215, 110643 (2020)
S. De Wolf, C. Ballif, M. Kondo, Phys. Rev. B 85, 113302 (2012)
Y. Liu, Y. Li, Y. Wu, G. Yang, L. Mazzarella, P. Procel-Moya, A.C. Tamboli, K. Weber, M. Boccard, O. Isabella, X. Yang, B. Sun, Mater. Sci. Eng. 142, 100579 (2020)
H. Lin, M. Yang, X. Ru, G. Wang, S. Yin, F. Peng, C. Hong, M. Qu, J. Lu, L. Fang, C. Han, P. Procel, O. Isabella, P. Gao, Z. Li, X. Xu, Nat. Energy 8, 789 (2023)
S. De Wolf, M. Kondo, Appl. Phy Lett. 90, 042111 (2007)
S. De Wolf, S. Olibet, C. Ballif, Appl. Phy Lett. 93, 032101 (2008)
A. Descoeudres, L. Barraud, S. De Wolf, B. Strahm, D. Lachenal, C. Guérin, Z.C. Holman, F. Zicarelli, B. Demaurex, J. Seif, J. Holovsky, C. Ballif, Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 123506 (2011)
M. Mews, T.F. Schulze, N. Mingirulli, L. Korte, Appl. Phy Lett. 102, 122106 (2013)
E. Kobayashi, S. De Wolf, J. Levrat, G. Christmann, A. Descoeudres, S. Nicolay, M. Despeisse, Y. Watabe, C. Ballif, Appl. Phy Lett. 109, 153503 (2016)
S. Bao, L. Yang, J. Huang, Y. Bai, J. Yang, J. Wang, L. Lu, L. Feng, X. Bai, F. Ren, D. Li, H. Jia, J. Mater. Sci. 32, 4045 (2021)
T.F. Schulze, H.N. Beushausen, T. Hansmann, L. Korte, B. Rech, Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 182108 (2009)
H. Sai, H.-J. Hsu, P.-W. Chen, P.-L. Chen, T. Matsui, Phys. Status Solidi 218, 2000743 (2021)
A.A. Langford, M.L. Fleet, B.P. Nelson, W.A. Lanford, N. Maley, Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 45, 13367 (1992)
Q. Zeng, G. Guo, Z. Meng, L. Gao, H. Meng, L. Zhou, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 154, 107192 (2023)
A. Richter, S.W. Glunz, F. Werner, J. Schmidt, A. Cuevas, Phys. Rev. B 86, 165202 (2012)
S. Bernardini, M.I. Bertoni, Phys. Status Solidi 216, 1800705 (2018)
T.F. Schulze, H.N. Beushausen, C. Leendertz, A. Dobrich, B. Rech, L. Korte, Appl. Phy Lett. 96, 252102 (2010)
T. Matsui, H. Sai, K. Saito, M. Kondo, Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 21, 1363 (2013)
T. Ruan, M. Qu, J. Wang, Y. He, X. Xu, C. Yu, Y. Zhang, H. Yan, J. Mater. Sci. 30, 13330 (2019)
L. Zhao, H. Diao, X. Zeng, C. Zhou, H. Li, W. Wang, Physica B 405, 61 (2010)
S. Kim, V.A. Dao, C. Shin, J. Cho, Y. Lee, N. Balaji, S. Ahn, Y. Kim, J. Yi, Thin Solid Films 521, 45 (2012)
Funding
The authors of the present contribution gratefully acknowledge the support of the present work by the Key R&D Plan of Jiangxi Province, China under Project No.20213AAE02012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qingguo Zeng: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing—Original draft, Data Curation, Writing—Review & Editing. Longwei Li: Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis. Hongchen Meng: Investigation, Resources. Xiaoyuan Wu: Investigation, Data Curation. Xiuqin Wei: Data curation, Writing—review & editing. Lang Zhou: Supervision, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Writing—review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Q., Li, L., Meng, H. et al. A study on the improvement of amorphous silicon/crystalline silicon heterojunction solar cells by microwave processing. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 476 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12241-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12241-z