Abstract
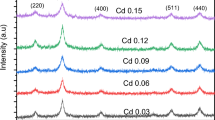
The effect of cerium (Ce3+) on the structural, microstructural, Fourier infrared spectroscopic, electrical, and humidity sensing behavior of CoCr2−xCexO4(CoCrCe) is reported in this paper. To prepare the samples, Solution combustion method using mixture of urea and glucose as a fuel. Samples are sintered for 600 °C for 3 h to get single phase. To analyses the creatinine nature and morphology, samples were characterize X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy. XRD reveals that formation of cubic spinel structures with typical crystallite sizes of less than 10 nm. When Ce3+ ions are replaced by Cr3+ ions, the lattice parameter found decreases from 8.3289 to 8.3163 Å. This is due to the creation of a compressive lattice strain and may be due to the differences between ionic radius of Ce3+ as compared to Cr3+. We discovered the chrommate structure in the absence of impurities by analysing the octahedral and tetrahedral stretching bands using Fourier infrared spectroscopy. Scanning Electron microscopy results reveals that samples exhibits highly porous nature. Elemental analysis were confirms the Ce3+ is present in the samples. All samples subjected to study the humidity sensing studies. The relative humidity influences the resistivity of the surrounding air significantly. We also investigated the relative permittivity characteristics, the conductivity of the samples of interest, and the capacitive sensor’s response time at a fixed frequency of f = 1 kHz. Further, The variation of both relative permittivity and electrical resistivity were strongly depending on humidity. As concentration of Ce3+ increases the permittivity (unit less), Conductivity, electrical capacity(normalized), Response time of capacitive sensor were found increases such as 150, 108 [Ω m], 10, 90 this is may be due to the larger ionic radius of the Ce3+ and also may be high porosity of the samples. Ce3+ at 2 mol% has improved humidity sensing properties as compared to other concentration. We conclude that CoCr1.98Ce0.02O4 be useful for an active material in humidity-sensing devices.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Yamazoe, Y. Shimizu, Humidity sensors: principles and applications. Sens. Actuators 10, 379–398 (1986)
H. Farahani, R. Wagiran, M.N. Hamidon, Humidity sensors principle, mechanism, and fabrication technologies: a comprehensive review. Sensors. 14, 7881–7939 (2014)
M. Pelino, C. Cantalini, M. Faccio, Principles and applications of ceramic humidity sensors. Act. Passiv Electron. Compon. 16, 69–87 (1994)
K. Manjunatha, V. Jagadeesha Angadi, M.C. Oliveira, S.R. de Lazaro, E. Longo, R.A.P. Ribeiro, S.O. Manjunatha, N.H. Ayachit, Towards shape-oriented bi-doped CoCr2O4 nanoparticles from theoretical and experimental perspective: structural, morphological, optical, electrical and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 9, 6452–6469 (2021)
I. Petrila, F. Tudorache, S. Tascu, Micromagnetic investigation of all-optical switching. Phys. Lett. A 377, 1495–1498 (2013)
K. Manjunatha, V. Jagadeesha Angadi, R. Rajaramakrishna, U. Mahaboob, Pasha, Role of 5 mol% Mg–Ni on the structural and magnetic properties of cobalt chromates crystallites prepared by solution combustion technique. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 33, 2861–2866 (2020)
K. Manjunatha, V. Jagadeesha Angadi, K.M. Srinivasamurthy, S. Matteppanavar, V.K. Pattar, Mahaboob Pasha, exploring the structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of 5 Mol% Bi3+-Substituted CoCr2O4 nanoparticles. J. Supercond Nov Magn. 33, 1747–1757 (2020)
I. Petrila, V. Manta, Metropolis Monte Carlo analysis of all-optical switching. Comput. Phys. Commun. 185, 2874–2878 (2014)
I. Petrila, F. Ungureanu, V. Manta, Effects of laser beam modulation on all-optical switching phase diagrams in magneto-optical ultrafast storage device. J. Comput. Electron. 14, 627–633 (2015)
K.K. Bharathi, J.A. Chelvane, G. Markandeyulu, Magnetoelectric properties of Gd and Nd-doped nickel ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 3677–3680 (2009)
S. Chikazumi, Physics of ferromagnetism (Oxford University Press Inc, New York, 1997)
F. Tudorache, I. Petrila, Effects of partial replacement of Iron with Tungsten on microstructure, electrical, magnetic and humidity properties of copper-zinc ferrite material. J. Electron. Mater. 43, 3522–3526 (2014)
K. Wu, Y. Lu, Y. Liu, Y. Liu, M. Shen, M. Debliquy, C. Zhang, Synthesis and acetone sensing properties of copper (Cu2+) substituted zinc ferrite hollow micro-nanospheres. Ceram. Int. 46(18), 28835–28843 (2020)
I. Petrila, F. Tudorache, Influence of partial substitution of Fe3+ with W3+ on the microstructure, humidity sensitivity, magnetic and electrical properties of barium hexaferrite. Superlattices Microstruct. 70, 46–53 (2014)
K. Manjunatha, V. Jagadeesha Angadi, R.A.P. Ribeiro, M.C. Oliveira, S.R. de Lázaro, M.R.D. Bomio, S. Matteppanavar, S. Rayaprol, P.D. Babu, Structural, electronic and magnetic properties of Sc3+ doped CoCr2O4 nanoparticles. New J. Chem. 44, 14246–14255 (2020)
P. Thamilmaran, M. Arunachalam, S. Sankarrajan, K. Sakthipandi, M. Sivabharathy, Structural transition in Gd doped LaCrO3 isovalent by in-situ ultrasonic measurements. Phys. B Condens. Matter 530, 270–276 (2018)
R.R. Kanna, K. Sakthipandi, N. Lenin et al., Neodymium doped on the manganese–copper nanoferrites: analysis of structural, optical, dielectric and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 4473–4486 (2019)
N. Betancur-Granados, O.J. Restrepo-Baena, Flame spray pyrolysis synthesis of ceramic nanopigments CoCr2O4: the effect of key variables. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 37, 5051–5056 (2017)
K. Manjunatha, V.J. Angadi, A.P. Renan, E. Ribeiro, M.C. Longo, R.D. Oliveira, Mauricio, R. Bomio, Sergio, S. de Lazaro, S. Matteppanavar, P.D. Rayaprol, M. Pasha, Structural, electronic, vibrational and magnetic properties of Zn2+ substituted MnCr2O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 502, 166595 (2020)
V. Jagadeesha Angadi, K. Manjunatha, K. Praveena, V.K. Pattar, B.J. Fernandes, S.O. Manjunatha, J. Husain, S.V. Angadi, L.D. Horakeri, K.P. Ramesh, Magnetic properties of larger ionic radii samarium and gadalonium doped manganese zinc ferrite nanoparticles prepared by solution combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 529, 167899 (2021)
P. Pankaj Choudhary, A. Saxena, V.N. Yadav, A. Rai, Mishra, Dielectric and ferroelectric properties of CoCr2O4 nanoceramics. J. Adv. Dielectr. 9, 1950015 (2019)
K. Manjunatha, V.J. Angadi, B.J. Fernandes, K.P. Ramesh, Synthesis and study of structural and dielectric properties of Dy-Ho doped Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles (Intech Open publishers, London, 2021)
V. Jagadeesha Angadi, K. Manjunatha, M. Akyol, A. Ekicibil, S. Matteppanavar, A.V. Pavlenko, S.P. Kubrin, Temperature-dependent dielectric and magnetic properties of scandium-substituted HoFeO3 nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 33, 3525–3534 (2020)
S. Pavithradevi, N. Suriyanarayanan, T. Boobalan, Synthesis, structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of polyol assisted copper ferrite nano particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 137–143 (2017)
K. Ali, J. Iqbal, T. Jan, I. Ahmad, D. Wan, I. Ahmad, Influence of NiO concentration on structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of core/shell CuFe2O4/NiO nanocomposites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 195, 283–294 (2017)
K. Manjunatha, K.M. Srininivasamurthy, C.S. Naveen, Y.T. Ravikiran, E.I. Sitalo, S.P. Kubrin, S. Matteppanavar, N. Sivasankara Reddy, J. Angadi, Observation of enhanced humidity sensing performance and structure, dielectric, optical and DC conductivity studies of scandium doped cobalt chromate. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 17202–17217 (2019)
P. Samoila, T. Slatineanu, P. Postolache, A.R. Iordan, M.N. Palamaru, The effect of chelating/combustion agent on catalytic activity and magnetic properties of Dy doped Ni–Zn ferrite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 136, 241–246 (2012)
R. Sharma, S. Singhal, Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of zinc doped nickel ferrite and their application in photo catalytic degradation of methylene blue. Phys. B 414, 83–90 (2013)
F. Tudorache, I. Petrila, K. Popa, A.M. Catargiu, Electrical properties and humidity sensor characteristics of lead hydroxyapatite material. Appl. Surf. Sci. 303, 175–179 (2014)
F. Tudorache, I. Petrila, P.D. Popa, S. Tascu, Influence of thermal treatment on the structure, humidity sensitivity, electrical and magnetic properties of barium–tungsten ferrite. Compos. B Eng. 51, 106–111 (2013)
I. Petrilaa, F. Tudorache, Effects of sintering temperature on the microstructure, electrical and magnetic characteristics of copper-zinc spinel ferrite with possibility use as humidity sensors. Sens. Actuators: Phys. 332, 113060 (2021)
F. Tudorache, Investigations on microstructure, electrical and magnetic properties of copper spinel ferrite with WO3 addition for applications in the humidity sensors, superlattices and microstructures. Res Data Policy Data Availab Statements 116, 131e140 (2018)
M.-K. Ho, H.-H. Chiu, T.-E. Hsu, B. Chethan, S.-L. Yu, C.-Y. Jheng, C.-E. Chin, R. Selvam, C.-L. Cheng, H. Nagabhushana, K. Manjunatha, Advancing humidity sensing and magnetocaloric properties of spinel structural CoCr2O4 nanoparticles achieved via innovative bismuth doping by combustion synthesis. Mater. Today Chem. 35, 101907 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2024.101907
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their sincere appreciation to the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2024R682), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia for the support.
Funding
This study was supported by Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2024R682), King Saud University, Riyadh Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JAV: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software and Writing—Original Draft preparation and editing, KA: Analysis, NL: Analysis, AHH: Editing, NB: Editing, Conceptualization.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Angadi, V.J., Abdulvakhidov, K., Lyanguzov, N. et al. Cerium doped cobalt chromate for resistive and capacitive humidity sensor applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 420 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12107-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12107-4