Abstract
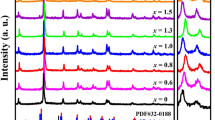
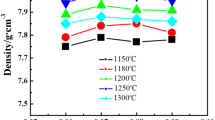
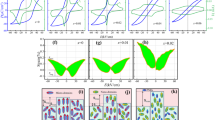
Piezoelectric materials are widely used in the direction of sensors. PZT-based ceramics are very suitable for precision sensors. However, due to the low Curie temperature, the application temperature range of the material is relatively narrow. Here we show a high-performance material 0.6PZT–0.4PNN. In this case, a morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) region was artificially designed in the 0.6Pb(ZrxTi1−x)O3–0.4Pb(Ni1/3Nb2/3)O3 (x = 0.35–0.41) ceramics to develop high-performance piezoelectric compositions which could cofire with low-cost Ag/Pd inner electrode by 0.2wt% Li2CO3 addition. The ceramic composition at x = 0.39 near MPB possess exceptional properties with high piezoelectric coefficient d33 ∼ 611 pC/N, planar electromechanical coupling coefficient kp ∼ 53.5%, low mechanical quality factor Qm ∼ 64.5 piezoelectric strain of 0.17%, and suitable Curie temperature Tc ∼ 191 °C, respectively. The fact that d33 was detected close to Tc, and no noticeable change below 6.6% in cycling stability was observed at 20 kV/cm means a robust temperature-independence and fatigue reliability of the piezoelectric ceramics. Thus, this research provides a novel high-piezoelectricity configuration with elemental regulation, comparable to the commercial PZTs.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
L. Bian, X. Qi, K. Li et al., High-performance [001] c‐textured PNN‐PZT relaxor ferroelectric ceramics for electromechanical coupling devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30(25), 2001846 (2020)
X. Niu, W. Jia, S. Qian et al., High-performance PZT-based stretchable piezoelectric nanogenerator. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7(1), 979–985 (2018)
B.S. Kim, J.H. Ji, J.H. Koh, Improved strain and transduction values of low-temperature sintered CuO-doped PZT-PZNN soft piezoelectric materials for energy harvester applications. Ceram. Int. 47(5), 6683–6690 (2021)
W. Gu, B. Zhao, B. Yang et al., Achieving superior electrical properties of PZT-PNN piezoelectric ceramics through low-temperature sintering with PbO-CuO eutectic additives. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 42(9), 3831–3840 (2022)
S. Yang, J. Li, Y. Liu et al., Textured ferroelectric ceramics with high electromechanical coupling factors over a broad temperature range. Nat. Commun. 12(1), 1414 (2021)
X. Gao, J. Wu, Y. Yu et al., Giant piezoelectric coefficients in relaxor piezoelectric ceramic PNN-PZT for vibration energy harvesting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28(30), 1706895 (2018)
F. Fan, W. Tang, Z. Wang, Flexible nanogenerators for energy harvesting and self-powered electronics. Adv. Mater. 28(22), 4283–4305 (2016)
R. Gao, X. Chu, Y. Huan et al., A study on (K, Na) NbO3 based multilayer piezoelectric ceramics micro speaker. Smart Mater. Struct. 23(10), 105018 (2014)
B. Gao, Z. Yao, D. Lai et al., Unexpectedly high piezoelectric response in Sm-doped PZT ceramics beyond the morphotropic phase boundary region. J. Alloys Compd. 836, 155474 (2020)
H. Zhu, D. Zheng, X. Wang et al., Effects of Ta2O5 addition on relaxation behavior and electric properties of PMS-PNN-PZT ceramics. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29(19), 16864–16871 (2018)
M. Khacheba, N. Abdessalem, A. Hamdi et al., Effect of acceptor and donor dopants (Na, Y) on the microstructure and dielectric characteristics of high Curie point PZT-modified ceramics. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31(1), 361–372 (2020)
S.R. Shannigrahi, F.E.H. Tay, K. Yao et al., Effect of rare earth (La, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Dy, Er and Yb) ion substitutions on the microstructural and electrical properties of sol–gel grown PZT ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 24(1), 163–170 (2004)
N. Luo, Q. Li, Z. Xia, Effect of Pb(Fe1/2Nb1/2)O3 modification on dielectric and piezoelectric properties of Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3–PbZr0.52Ti0.48O3 ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 46(9), 1333–1339 (2011)
Z. Lin, Z. Zhu, Z. Yao et al., Piezoelectric response and cycling fatigue resistance of low-temperature sintered PZT-based ceramics. Materials 16(4), 1679 (2023)
Z. Du, C. Zhao, H.C. Thong et al., Effect of MnCO3 on the electrical properties of PZT-based piezoceramics sintered at low temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 801, 27–32 (2019)
J. Luo, J. Qiu, K. Zhu et al., Effects of the calcining temperature on the piezoelectric and dielectric properties of 0.55PNN–0.45PZT ceramics. Ferroelectrics 425(1), 90–97 (2011)
H. Wang, F. Zhang, Y. Chen et al., Giant piezoelectric coefficient of PNN-PZT-based relaxor piezoelectric ceramics by constructing an R-T MPB. Ceram. Int. 47(9), 12284–12291 (2021)
S.H. Lee, S.H. Jun, H.E. Kim et al., Fabrication of porous PZT-PZN piezoelectric ceramics with high hydrostatic figure of merits using camphene-based freeze casting. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 90(9), 2807–2813 (2007)
S. Lee, S. Lee, C. Yoon et al., Low-temperature sintering of MnO2-doped PZT-PZN piezoelectric ceramics. J. Electro Ceram. 18, 311–315 (2007)
D. Wang, Q. Zhao, M. Cao et al., Dielectric, piezoelectric, and ferroelectric properties of Al2O3 and MnO2 modified PbSnO3–PbTiO3–Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3 ternary ceramics. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 210(7), 1363–1368 (2013)
Z. Zhang, J. Xu, L. Yang et al., Design and comparison of PMN-PT single crystals and PZT ceramics based medical phased array ultrasonic transducer. Sens. Actuators A-Physical. 283, 273–281 (2018)
H. Ying, G. Ding, J. Zhao et al., Properties of PSN-PZT piezoelectric ceramic powder prepared by fast solid-phase reaction method. Mater. Today Commun. 35, 106086 (2023)
J. Ye, G. Ding, X. Wu et al., Development and performance research of PSN-PZT piezoelectric ceramics based on road vibration energy harvesting technology. Mater. Today Commun. 34, 105135 (2023)
Z. Zhu, B. Li, G. Li et al., Microstructure and piezoelectric properties of PMS-PZT ceramics. Mater. Sci. Engineering: B 117(2), 216–220 (2005)
Z. Zhu, N. Zheng, G. Li et al., Dielectric and electrical conductivity properties of PMS-PZT ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 89(2), 717–719 (2006)
M.S. Yoon, H.M. Jang, Relaxor-normal ferroelectric transition in tetragonal-rich Field of Pb(Ni1/3Pb2/3)O3–PbTiO3–PbZrO3 system. J. Appl. Phys. 77(8), 3991–4001 (1995)
H. Chen, J. Xing, J. Xi et al., Origin of high piezoelectricity in low-temperature sintering PZT-based relaxor ferroelectric ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 860, 157930 (2021)
Y. Yue, Q. Zhang, R. Nie et al., Influence of sintering temperature on phase structure and electrical properties of 0.55Pb(Ni1/3Nb2/3)O3–0.45Pb(Zr0.3Ti0.7)O3 ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 92, 123–128 (2017)
R. Cao, G. Li, J. Zeng et al., The piezoelectric and dielectric properties of 0.3Pb (Ni1/3Nb2/3) O3–xPbTiO3–(0.7 − x)PbZrO3 ferroelectric ceramics near the morphotropic phase boundary. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93(3), 737–741 (2010)
G. Robert, D. Damjanovic, N. Setter, Temperature dependence of piezoelectric properties for relaxor-ferroelectric solid solutions undergoing a rhombohedral to tetragonal phase transition. Ferroelectrics. 224(1), 97–104 (1999)
S. Chandarak, M. Unruan, A. Prasatkhetragarn et al., Structural investigation of PZT-PNN and PZT-PZN probed by synchrotron X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Ferroelectrics 455, 117–122 (2013)
C.-H. Nam, H.-Y. Park, Low-temperature sintering and piezoelectric properties of 0.65Pb(Zr1 – xTix)O3–0.35Pb(Ni0.33Nb0.67)O3 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 3442–3448 (2011)
T. Pu, H. Chen, J. Xing et al., High piezoelectricity of low-temperature sintered Li2CO3-added PNN-PZT relaxor ferroelectrics. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 33(8), 4819–4830 (2022)
J. Zhang, Y. Zhang, Z. Yan et al., Fabrication and performance of PNN-PZT piezoelectric ceramics obtained by low-temperature sintering. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 27, 359–365 (2020)
A.C. Caballero, E. Nieto, P. Duran et al., Ceramic-electrode interaction in PZT and PNN–PZT multilayer piezoelectric ceramics with Ag/Pd 70/30 inner electrode. J. Mater. Sci. 32, 3257–3262 (1997)
M. Ghasemifard, S.M. Hosseini, A.K. Zak et al., Microstructural and optical characterization of PZT nanopowder prepared at low temperature. Phys. E: Low-Dimen. Syst. Nanostruct. 41(3), 418–422 (2009)
S. Wang, L. Li, X. Wang, Low-temperature firing and microwave dielectric properties of MgNb2 – xVx/2O6–1.25x ceramics. Ceram. Int. 48(1), 199–204 (2022)
C. Vakifahmetoglu, L. Karacasulu, Cold sintering of ceramics and glasses: a review. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 24(1), 100807 (2020)
N.J. Donnelly, T.R. Shrout, C.A. Randall, The role of Li2CO3 and PbO in the low-temperature sintering of Sr, K, Nb (SKN)‐doped PZT. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92(6), 1203–1207 (2009)
C. Huang, K. Cai, Y. Wang et al., Revealing the real high temperature performance and depolarization characteristics of piezoelectric ceramics by combined in situ techniques. J. Mater. Chem. C 6(6), 1433–1444 (2018)
S. Yasuyoshi, T. Hisaaki, T. Toshihiko et al., Lead-free piezoceramics. Nature 432(7013), 84–87 (2004)
Funding
This work was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of China (51872213), Sanya Science and Education Innovation Park of Wuhan University of Technology (2021KF0014), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2022B1515120041 and 2022A1515010073).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by PS, ZZ and ZY. Supervision, project administration, funding acquisition were performed by ZY, MC, HH, and HL. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflicts of interest to this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, P., Zhu, Z., Yao, Z. et al. Piezoelectric enhancement of 0.6Pb(Zr,Ti)O3–0.4Pb(Ni1/3Nb2/3)O3 ceramics with artificial MPB engineering. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 58 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11778-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11778-9