Abstract
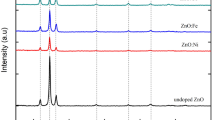
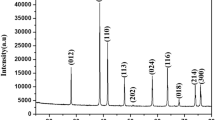
In the present work, we investigated the magneto-optic properties of pure, cobalt-doped, and manganese-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Both pure and doped ZnO nanoparticles are prepared using the co-precipitation method. Examination of X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns confirms the effective substitution of dopants ions (Co2+ and Mn2+) into ZnO hexagonal wurtzite crystal structure. The calculated microstrain and crystallite size values suggest lattice expansion and reduction of particle size to the nano range respectively. Further, a change in the morphology from rounded to the slightly elongated shape of the ZnO nanoparticles was observed with the doping. The absorption spectra showed a minor shift in the optical band gap value from 3.21 to 3.17 eV with doping in the ZnO. Further, the emission spectra of pure ZnO nanoparticles showed strong green emission with color coordinates (0.28, 0.40), and (0.30, 0.40) corresponding to emission wavelengths of 513.14 nm and 592.55 nm respectively. However, this emission gets drastically quenched by Co2+ and Mn2+ ions doping in ZnO. The magnetic properties investigated using a superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) magnetometer exhibited a magnetic behavior change from diamagnetic to ferromagnetic for pure ZnO and doped ZnO nanoparticles respectively. Our study predicts that both cobalt and manganese doping in ZnO change the magnetic behavior of pure ZnO nanoparticles from diamagnetic to ferromagnetic but the emission properties of the pure ZnO also get quenched simultaneously.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author Dr. Ishan Choudhary on reasonable request.
References
L. Zhao, B. Huang, O. Olowolafe, I. Appelbaum, Bottom–up-fabricated oxide–metal–semiconductor spin-valve transistor. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 29(8), 892–894 (2008)
S. Sugahara, M. Tanaka, A spin metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor using half-metallic-ferromagnet contacts for the source and drain. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84(13), 2307–2309 (2004)
I. Choudhary, Deepak, Study on dielectric properties of PVP and Al2O3 thin films and their implementation in low-temperature solution-processed IGZO-based thin-film transistors. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32(6), 7875–7888 (2021)
M.A. Dominguez, J.A. Luna-Lopez, S. Ceron, Low-temperature ultrasonic spray deposited aluminum doped zinc oxide film and its application in flexible Metal-Insulator-Semiconductor diodes. Thin Solid Films 645, 278–281 (2018)
S. Abbas, M. Kumar, J. Kim, All metal oxide-based transparent and flexible photodetector. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 88, 86–92 (2018)
I. Choudhary, D. Deepak, Flexible substrate compatible solution processed P-N heterojunction diodes with indium-gallium-zinc oxide and copper oxide. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 218, 64–73 (2017)
K. Komal, G. Gupta, M. Singh, B. Singh, Improved resistive switching of RGO and SnO2 based resistive memory device for non-volatile memory application. J. Alloys Compd. 923, 166196 (2022)
K.K. Kashyap, L.H.J. Jire, P. Chinnamuthu, A perspective study on Au-nanoparticle adorned TiO2-nanowire for non-volatile memory devices. Mater. Today Commun. 33, 104469 (2022)
D. Kumar, R. Aluguri, U. Chand, T.Y. Tseng, Metal oxide resistive switching memory: materials, properties and switching mechanisms. Ceram. Int. 43, S547–S556 (2017)
K.G. Krishna, S. Parne, N. Pothukanuri, V. Kathirvelu, S. Gandi, D. Joshi, Nanostructured metal oxide semiconductor-based gas sensors: a comprehensive review. Sens. Actuators A 341, 113578 (2022)
Q. Li, W. Zeng, Y. Li, Metal oxide gas sensors for detecting NO2 in industrial exhaust gas: recent developments. Sens. Actuators B 359, 131579 (2022)
A. Singh, S. Sikarwar, A. Verma, B. Chandra Yadav, The recent development of metal oxide heterostructures based gas sensor, their future opportunities and challenges: a review. Sens. Actuators A 332, 113127 (2021)
A. Chatterjee, A.V. Ravindra, G. Kiran Kumar, C. Rajesh, Improvement in the light conversion efficiency of silicon solar cell by spin coating of CuO, ZnO nanoparticles and CuO/ZnO mixed metal nanocomposite material. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 99(9), 100653 (2022)
H.B. Uma, S. Ananda, M.S.V. Kumar, Electrochemical synthesis and characterization of CuO/ZnO/SnO nano photocatalyst: evaluation of its application towards photocatalysis, photo-voltaic and antibacterial properties. Chem. Data Collect. 32, 100658 (2021)
B. Boro, B. Gogoi, B.M. Rajbongshi, A. Ramchiary, Nano-structured TiO2/ZnO nanocomposite for dye-sensitized solar cells application: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 81, 2264–2270 (2018)
A.W. Alshameri, M. Owais, Antibacterial and cytotoxic potency of the plant-mediated synthesis of metallic nanoparticles Ag NPs and ZnO NPs: a review. OpenNano 8, 100077 (2022)
H. Hong et al., Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) exhibit immune toxicity to crucian carp (Carassius carassius) by neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) release and oxidative stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 129, 22–29 (2022)
M. Nagarajan et al., Exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) induces cardiovascular toxicity and exacerbates pathogenesis—role of oxidative stress and MAPK signaling. Chem. Biol. Interact. 351, 109719 (2022)
S. Zeghoud et al., A review on biogenic green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by plant biomass and their applications. Mater. Today Commun. 33, 104747 (2022)
M. Alavi, A. Nokhodchi, Synthesis and modification of bio-derived antibacterial Ag and ZnO nanoparticles by plants, fungi, and bacteria. Drug Discov. Today 26(8), 1953–1962 (2021)
R.S. Rai et al., An eco-friendly approach on green synthesis, bio-engineering applications, and future outlook of ZnO nanomaterial: a critical review. Environ. Res. 221, 114807 (2022)
A. El Golli, M. Fendrich, N. Bazzanella, C. Dridi, A. Miotello, M. Orlandi, Wastewater remediation with ZnO photocatalysts: green synthesis and solar concentration as an economically and environmentally viable route to application. J. Environ. Manag. 286, 112226 (2021)
C.Y. Koo et al., Sol-gel derived Ga-In-Zn-O semiconductor layers for solution-processed thin-film transistors. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 53(1), 218–222 (2008)
K. Nomura, H. Ohta, A. Takagi, T. Kamiya, M. Hirano, H. Hosono, Room-temperature fabrication of transparent flexible thin-film transistors using amorphous oxide semiconductors. Nature 432(7016), 488–492 (2004)
A. Bala, R. Sehrawat, A.K. Sharma, P. Soni, Synthesis and optical properties of polythiophene-capped ZnS/Mn quantum dots. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32(12), 16382–16391 (2021)
M. Ahmad, I. Ahmad, E. Ahmed, M.S. Akhtar, N.R. Khalid, Facile and inexpensive synthesis of Ag doped ZnO/CNTs composite: study on the efficient photocatalytic activity and photocatalytic mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 311, 113326 (2020)
I. Ahmad, M.S. Akhtar, E. Ahmed, M. Ahmad, Aluminium and cerium co-doped ZnO nanoparticles: facile and inexpensive synthesis and visible light photocatalytic performances. J. Rare Earths 39(2), 151–159 (2021)
A. Shukla, V.K. Kaushik, D. Prasher, Growth and characterization of MgxZn1−xO thin films by aerosol-assisted chemical vapor deposition (AACVD). Electron. Mater. Lett. 10(1), 61–65 (2014)
H. Wang et al., Low-temperature facile solution-processed gate dielectric for combustion derived oxide thin film transistors. Rsc Adv. 4(97), 54729–54739 (2014)
Y.S. Rim, H.S. Lim, H.J. Kim, Low-temperature metal-oxide thin-film transistors formed by directly photopatternable and combustible solution synthesis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5(9), 3565–3571 (2013)
I. Choudhary, D. Deepak, Investigation of time-dependent stability and surface defects in sol–gel derived IGZO and IZO thin films. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 100, 132–146 (2021)
N. Kamarulzaman, M.F. Kasim, R. Rusdi, Band gap narrowing and widening of ZnO nanostructures and doped materials. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 10(1), 346 (2015)
L.J. Hoong, Y.C. Keat, A. Chik, T.P. Leng, Band structure and thermoelectric properties of inkjet printed ZnO and ZnFe2O4 thin films. Ceram. Int. 42(10), 12064–12073 (2016)
H. Chen, Y. Qu, L. Sun, J. Peng, J. Ding, Band structures and optical properties of Ag and Al co-doped ZnO by experimental and theoretic calculation. Physica E 114, 113602 (2019)
H. Ohara et al., 4.0-inch active-matrix organic light-emitting diode display integrated with driver circuits using amorphous In-Ga-Zn-oxide thin-film transistors with suppressed variation. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 49(3), 03 (2010)
Y. Nakajima et al., Development of 8-in. oxide-TFT-driven flexible AMOLED display using high-performance red phosphorescent OLED. J. Soc. Inform. Display 22(3), 137–143 (2014)
D. Guruvammal, S. Selvaraj, S. Meenakshi Sundar, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Co doped ZnO DMS nanoparticles by microwave irradiation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 452, 335–342 (2018)
Y. Koseoğlu, Y. Celaleddin Durmaz, R. Yilgin, Rapid synthesis and room temperature ferromagnetism of Ni doped ZnO DMS nanoflakes. Ceram. Int. 40(7), 10685–10691 (2014)
K.C. Sebastian, M. Chawda, L. Jonny, D. Bodas, Structural, magnetic and optical studies of (Zn0.90Co0.05Ni0.05O) DMS. Mater. Lett. 64(20), 2269–2272 (2010)
J. Sahu et al., Defects and oxygen vacancies tailored structural, optical and electronic structure properties of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticle samples probed using soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Vacuum 179, 109538 (2020)
U. Godavarti et al., Precipitated cobalt doped ZnO nanoparticles with enhanced low temperature xylene sensing properties. Physica B 553, 151–160 (2019)
N. Bhakta, P.K. Chakrabarti, Defect induced room temperature ferromagnetism and optical properties of (Co, Y) co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 485, 419–426 (2019)
A.T. Ravichandran, R. Karthick, Enhanced photoluminescence, structural, morphological and antimicrobial efficacy of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by Co-precipitation method. Results Mater. 5, 100072 (2020)
N. Pushpa, M.K. Kokila, Effect of cobalt doping on structural, thermo and photoluminescent properties of ZnO nanopowders. J. Lumin. 190, 100–107 (2017)
S.D. Birajdar, V.R. Bhagwat, A.B. Shinde, K.M. Jadhav, Effect of Co 2+ ions on structural, morphological and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel auto combustion method. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 41, 441–449 (2016)
S. Basu et al., Local structure investigation of cobalt and manganese doped ZnO nanocrystals and its correlation with magnetic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 118(17), 9154–9164 (2014)
G. Clavel, N. Pinna, D. Zitoun, Magnetic properties of cobalt and manganese doped ZnO nanowires. Phys Status Solidi (a) (2007). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.200673025204(1),pp.118-124
D. Sharma, R. Jha, Structural and optical properties of Co-doped ZnO nano-ampoules synthesized by co-precipitation method. Mater. Lett. 190, 9–12 (2017)
A.L. Patterson, The Scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Phys. Rev. 56(10), 978–982 (1939)
R. Udayabhaskar, B. Karthikeyan, Role of micro-strain and defects on band-gap, fluorescence in near white light emitting Sr doped ZnO nanorods. J. Appl. Phys. 116(9), 094310 (2014)
I. Choudhary, R. Shukla, A. Sharma, K.K. Raina, Effect of excitation wavelength and europium doping on the optical properties of nanoscale zinc oxide. J. Mater. Sci. 31(22), 20033–20042 (2020)
S. Saleem et al., Modification in structural, optical, morphological, and electrical properties of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles (NPs) by metal (Ni, Co) dopants for electronic device applications. Arab. J. Chem. 15(1), 103518 (2022)
S. Kumar, T.K. Song, S. Gautam, K.H. Chae, S.S. Kim, K.W. Jang, Structural, magnetic and electronic structure properties of Co doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 66, 76–82 (2015)
A. Mesaros et al., Synthesis, structural and morphological characteristics, magnetic and optical properties of Co doped ZnO nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 40(2), 2835–2846 (2014)
S. Muthukumaran, R. Gopalakrishnan, Structural, FTIR and photoluminescence studies of Cu doped ZnO nanopowders by co-precipitation method. Opt. Mater. 34(11), 1946–1953 (2012)
J. Tauc, Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous Ge and Si. Mater. Res. Bull. 3(1), 37–46 (1968)
D. Raoufi, Synthesis and photoluminescence characterization of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 134, 213–219 (2013)
A. Ghosh, R.N.P.J.J.E.N. Choudhary, Optical emission and absorption spectra of Zn–ZnO core-shell nanostructures. J. Exp. Nanosci. 5, 134–142 (2010)
C.H. Patterson, Role of defects in ferromagnetism in Zn1-xCoxO: a hybrid density-functional study. Phys. Rev. B 74(14), 144432 (2006)
N. Karak, B. Pal, D. Sarkar, T.K. Kundu, Growth of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles by porous alumina assisted sol–gel route: structural optical and magnetic properties. J. Alloys Compd. 647, 252–258 (2015)
S.M. Shah et al., Optical and morphological studies of transition metal doped ZnO nanorods and their applications in hybrid bulk heterojunction solar cells. Arab. J. Chem. 10(8), 1118–1124 (2017)
J. Zhong et al., Ga-doped ZnO single-crystal nanotips grown on fused silica by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83(16), 3401–3403 (2003)
S. Yamamoto, Photoluminescence quenching in cobalt doped ZnO nanocrystals. J. Appl. Phys. 111(9), 094310 (2012)
J.M.D. Coey, M. Venkatesan, C.B. Fitzgerald, Donor impurity band exchange in dilute ferromagnetic oxides. Nat. Mater. 4(2), 173–179 (2005)
N.N. Lathiotakis, A.N. Andriotis, M. Menon, Codoping: a possible pathway for inducing ferromagnetism in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 78(19), 193311 (2008)
A. Ciechan, P. Bogusławski, Theory of the sp–d coupling of transition metal impurities with free carriers in ZnO. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 3848 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This project is supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, India. The authors also acknowledge the Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi, India for helping out with SQUID measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
IC: Experiments, original draft writing, conceptualization, validation, and supervision. RS: Characterization, investigations, review, and editing. SM: Characterization, review, and editing. RM: Methodology, and editing. RD: Data curation, and editing. KR: Experiments. S: Experiments. SS: Experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhary, I., Sehrawat, R., Mehta, S. et al. Photoluminescent and magnetic characteristics of cobalt and manganese doped nanoscale zinc oxide. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1505 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10898-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10898-6