Abstract
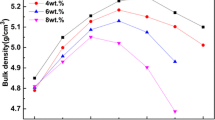
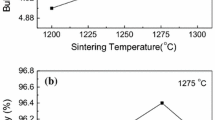
Glass additive SrO–B2O3–ZnO (SBZ) is used to decrease the sintering temperature of 0.8Ba0.2Sr0.8TiO3–0.2Bi(Mg0.5Zr0.5)O3 (BST-BMZ) ceramic and improve ceramic energy storage performance. The effects of glass content on the sintering temperature, crystal structure, microstructure, dielectric property, and energy storage performance of BST-BMZ ceramics are investigated. Benefiting from the good wetting behavior of SBZ glass melt and BST-BMZ ceramic, the addition of SBZ glass on the BST-BMZ matrix facilitates achievement of low temperature sintering process, and the sintering temperature reduces from 1300 ºC to 1100 ºC for BST-BMZ + 2 wt% SBZ ceramic. While, the decrease of average grain size and superior densification resulting from the low sintering temperature, are also beneficial to the high breakdown strength. The BST-BMZ + 2 wt% SBZ ceramic achieves the optimum comprehensive properties with the maximum energy storage density of 2.13 J/cm3 and the remarkable efficiency of 94.1%. The addition of SBZ glass reduces the sintering temperature of BST-BMZ ceramic and improves the energy storage performance. The results indicate that the BST-BMZ + 2 wt% SBZ ceramic is a potential dielectric material for multilayer ceramic capacitors.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and analysed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
F.Z. Yao, Q.B. Yuan, Q. Wang, H. Wang, Multiscale structural engineering of dielectric ceramics for energy storage applications: from bulk to thin films. Nanoscale 12, 17165–17184 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NR04479B
J. Jiang, X.J. Meng, L. Li, S. Guo, M. Huang, J. Zhang, J. Wang, X.H. Hao, H.G. Zhu, S.T. Zhang, Ultrahigh energy storage density in lead-free relaxor antiferroelectric ceramics via domain engineering. Energy. Storage. Mater 43, 383–390 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2021.09.018
L.L. Li, B. Zhou, H.B. Yuan, F. Wen, Z. Xu, G.F. Wang, Effect of BaTiO3 particles with different shape on electrical properties of (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 piezoceramics. Ceram. Int. 45, 1960–1968 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.10.090
W.W. Ping, W.F. L, S.T. L, Enhanced energy storage property in glass-added Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3-0.15(Ba0.7Ca0.3)TiO3 ceramics and the charge relaxation. Ceram. Int. 45, 11388–11394 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.03.003
P.Y. Zhao, Z.M. Cai, L.W. Wu, C.Q. Zhu, L.T. Li, X.H. Wang, Perspectives and challenges for lead-free energy-storage multilayer ceramic capacitors. 10, 1153–1193 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40145-021-0516-8
S.N. Das, Relaxor (Pb0.7Bi0.3)(Mg0.231Nb0.462Fe0.3)O3 electronic compound for magnetoelectric field sensor applications. J. Appl. Phys. 128, 114101 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0014110
M.J. Pan, C.A. Randall, A brief introduction to ceramic capacitors. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag 26, 44–50 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/MEI.2010.5482787
Y. Wang, Z.Y. Shen, Y.M. Li, Z.M. Wang, W.Q. Luo, Y. Hong, Optimization of energy storage density and efficiency in BaxSr1-xTiO3 (x ≤ 0.4) paraelectric ceramics. Ceram. Int. 41, 8252–8256 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.02.126
M.S. Zeng, J.S. Liu, H.Q. Li, S.R. Zhang, W.L. Zhang, High energy storage efficiency and fast discharge property of temperature stabilized Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3-Bi(Mg0.5Ti0.5)O3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 48, 23518–23526 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.04.348
C.L. Diao, H.X. Liu, H. Hao, M.H. Cao, Z.H. Yao, Effect of SiO2 additive on dielectric response and energy storage performance of Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 42, 12639–12643 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.04.169
Z. Song, H.X. Liu, M.T. Lanagan, S.J. Zhang, H. Hao, M.H. Cao, Z.H. Yao, Z.X. Fu, K. Huang, Thermal annealing effects on the energy storage properties of BST ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 100, 3550–3557 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.14903
Z. Song, H.X. Liu, S.J. Zhang, Z.J. Wang, Y.T. Shi, H. Hao, M.H. Cao, Z.H. Yao, Z.Y. Yu, Effect of grain size on the energy storage properties of (Ba0.4Sr0.6)TiO3 paraelectric ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34, 1209–1217 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2013.11.039
Z.J. Wang, M.H. Cao, Z.H. Yao, Z. Song, G.Y. Li, W. Hu, H. Hao, H.X. Liu, Dielectric relaxation behavior and energy storage properties in SrTiO3 ceramics with trace amounts of ZrO2 additives. Ceram. Int. 40, 14127–14132 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.05.147
Z.H. Yao, Q. Luo, G.F. Zhang, H. Hao, M.H. Cao, H.X. Liu, Improved energy-storage performance and breakdown enhancement mechanism of Mg-doped SrTiO3 bulk ceramics for high energy density capacitor applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. El 28, 11491–11499 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6945-z
W. Wang, L.Y. Zhang, C. Li, D.O. Alikin, V.Y. Shur, X.Y. Wei, F. Gao, H.L. Du, L. Jin, Effective strategy to improve energy storage properties in lead-free (Ba0.8Sr0.2)TiO3-Bi(Mg0.5Zr0.5)O3 relaxor ferroelectric ceramics. Chem. Eng. J. 446, 137389 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.137389
X.W. Jiang, H. Hao, S.J. Zhang, J.H. Lv, M.H. Cao, Z.H. Yao, H.X. Liu, Enhanced energy storage and fast discharge properties of BaTiO3 based ceramics modified by Bi(Mg1/2Zr1/2)O3. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 39, 1103–1109 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.11.025
A. Zed, S.J. Milne, Temperature-stable dielectric properties from – 20 ºC to 430 ºC in the system BaTiO3-Bi(Mg0.5Zr0.5)O3. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34, 3159–3166 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2014.04.047
A. Young, G. Hilmas, S.C. Zhang, R.W. Schwartz, Effect of liquid-phase sintering on the breakdown strength of barium titanate. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 90, 1504–1510 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2007.01637.x
Y.R. Wang, Y.P. Pu, Y.F. Cui, Y. Shi, H.Y. Zheng, Enhanced energy storage density of Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3 ceramics with additive of Bi2O3-B2O3-ZnO glass. Mater. Lett. 201, 203–206 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.05.007
P. Tripathi, P. Kumari, V.K. Mishra, R. Singh, S.P. Singh, D. Kumar, Effect of PbO-B2O3-BaO-SiO2 glass additive on dielectric properties of Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3 ceramics for radio-frequency applications. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 127, 60–67 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2018.12.006
X. Chen, Y. Tang, X.K. Bo, J. Song, J.Z. Luo, Microstructures and energy storage properties of Sr0.5Ba0.5Nb2O6 ceramics with SrO–B2O3–SiO2 glass addition. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. El 29, 17563–17570 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9858-6
H.Y. Wang, M.H. Cao, M. Liu, H. Hao, Z.H. Yao, H.X. Liu, Enhanced energy storage properties of fine-crystalline Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3 ceramics by coating powders with B2O3–Al2O3–SiO2. J. Alloy Compd. 826, 153891 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.153891
T. Wang, L. Jin, L.L. Shu, Q.Y. Hu, X.Y. Wei, Energy storage properties in Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3 ceramics with addition of semi-conductive BaO-B2O3-SiO2-Na2CO3-K2CO3 glass. J. Alloy Compd. 617, 399–403 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.08.038
H.J. Lee, S.W. Kim, S.S. Ryu, Sintering behavior of aluminum nitride ceramics with MgO-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 glass additive. Int. J. Refract. Met. H 53, 46–50 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2015.04.013
P.S. Anjana, M.T. Sebastian, Microwave dielectric properties and low-temperature sintering of cerium oxide for LTCC applications. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 96–104 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2008.02756.x
A.I. Borhan, M. Gromada, G.G. Nedelcu, L. Leontie, Influence of (CoO, CaO, B2O3) additives on thermal and dielectric properties of BaO-Al2O3-SiO2 glass-ceramic sealant for OTM applications. Ceram. Int. 42, 10459–10468 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.03.199
J. Song, L. Han, T.Y. Liu, Q. Feng, Z.W. Luo, A.X. Lu, Microstructures and energy storage properties of BSN ceramics with crystallizable glass addition. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. El 29, 5934–5943 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8566-6
H.B. Yang, F. Yan, Y. Lin, T. Wang, Enhanced energy storage properties of Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3 lead-free ceramics with Bi2O3-B2O3-SiO2 glass addition. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38, 1367–1373 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.11.058
Z.Y. Shen, Y. Wang, Y.X. Tang, Y.Y. Yu, W.Q. Luo, X.C. Wang, Y.M. Li, Z.M. Wang, F.S. Song, Glass modified barium strontium titanate ceramics for energy storage capacitor at elevated temperatures. J. Materiomics 5, 641–648 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2019.06.003
H.T. Yu, L. He, M.S. Zeng, J.S. Liu, E.Z. Li, X.H. Zhou, S.R. Zhang, Low temperature sintering of Zn1.8SiO3.8 dielectric ceramics containing 3ZnO-2B2O3 glass. Mater. Lett. 179, 150–153 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.05.091
Q.Y. Hu, T. Wang, L.Y. Zhao, L. Jin, Z. Xu, X.Y. Wei, Dielectric and energy storage properties of BaTiO3-Bi(Mg1/2Ti1/2)O3 ceramic: influence of glass addition and biasing electric field. Ceram. Int. 43, 35–39 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.08.005
L.M. Chen, X.H. Hao, Q.W. Zhang, S.L. An, Energy-storage performance of PbO-B2O3-SiO2 added (Pb0.92Ba0.05La0.02)(Zr0.68Sn0.27Ti0.05)O3 antiferroelectric ceramics prepared by microwave sintering method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. El 27, 4534–4540 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4328-5
S.N. Das, S.K. Pradhan, S. Bhuyan, R.N.P. Choudhary, Capacitive, resistive and conducting characteristics of bismuth ferrite and lead magnesium niobate based relaxor electronic system. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. El 28, 18913–18928 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7845-y
S.N. Das, S. Pradhan, S. Bhuyan, R.N.P. Choudhary, P. DAS, Modification of relaxor and impedance spectroscopy properties of lead magnesium niobate by bismuth ferrite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. El 46, 1637–1649 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-5207-9
G. Liu, Y. Wang, G.Y. Han, J.H. Gao, L.J. Yu, M.Y. Tang, Y. Li, J.Z. Hu, L. Jin, Y. Yan, Enhanced electrical properties and energy storage performances of NBT-ST Pb-free ceramics through glass modification. J. Alloy Compd. 836, 154961 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154961
T. Wei, K. Liu, P.Y. Fan, D.J. Lu, B.H. Ye, C.R. Zhou, H.B. Yang, H. Tan, D. Salamon, B. Nan, H.B. Zhang, Novel NaNbO3-Sr0.7Bi0.2TiO3 lead-free dielectric ceramics with excellent energy storage properties. Ceram. Int. 47, 3713–3719 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.09.228
T. Wu, Y.P. Pu, T.T. Zong, P. Gao, Microstructures and dielectric properties of Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3 ceramics with BaO-TiO2-SiO2 glass-ceramics addition. J. Alloy Compd. 584, 461–465 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.09.072
Z.Y. Shen, Y.M. Li, W.Q. Luo, Z.M. Wang, X.Y. Gu, R.H. Liao, Structure and dielectric properties of NdxSr1-xTiO3 ceramics for energy storage application. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. El 24, 704–710 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-012-0798-2
Z.Y. Shen, Y.Y. Yu, Y. Wang, L. Zhang, W.Q. Luo, Z.M. Wang, Y.M. Li, Reduced high temperature dielectric loss in BSB glass modified Ba0.3Sr0.7TiO3 ceramics for energy storage. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. El 29, 1093–1097 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8010-3
L.T. Yang, X. Kong, F. Li, H. Hao, Z.X. Cheng, H.X. Liu, J.F. Li, S.J. Zhang, Perovskite lead-free dielectrics for energy storage applications. Prog Mater. Sci. 102, 72–108 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2018.12.005
G. Liu, Y. Li, B. Guo, M.Y. Tang, Q. Li, J. Dong, L.J. Yu, K. Yu, Y. Yan, D.W. Wang, L.Y. Zhang, H.B. Zhang, Z.B. He, L. Jin, Ultrahigh dielectric breakdown strength and excellent energy storage performance in lead-free barium titanate-based relaxor ferroelectric ceramics via a combined strategy of composition modification, viscous polymer processing, and liquid-phase sintering. Chem. Eng. J. 398, 125625 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125625
H.S. Wang, Y.C. Liu, T.Q. Yang, S.J. Zhang, Ultrahigh energy-storage density in antiferroelectric ceramics with field-induced multiphase transitions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1807321 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201807321
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by HX and PL. Revised it critically for important intellectual content by JL and MZ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by HX and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Liu, J., Luo, P. et al. Low temperature sintering and energy storage properties of 0.8Ba0.2Sr0.8TiO3–0.2Bi(Mg0.5Zr0.5)O3 ceramic with additive of SrO–B2O3–ZnO glass. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1048 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10352-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10352-7