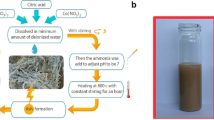
Abstract
Water contamination by toxic metals is an endless global environmental threat to human health, thus imperative to develop efficient multifunctional materials for water monitoring and remediation. Among the heavy metals, Pb(II) is among the most used and persistent pollutants that drastically affect the working ecosystem. Nonetheless, the evolution of inexpensive functional materials for the effective removal of heavy metals remains a prohibited challenge. In this work, the use of Nickel ferrite (NF) and Nickel ferrite/rGO (NG) nanocomposite for the adsorption of lead from an aqueous solution is examined. The physicochemical characterizations confirm the formation of magnetic nanoparticles with an average crystallite size of 35 and 30 nm and with a specific surface area of 59 and 110.9 m2/g for NF and NG. The magnetic measurements of NF and NG indicate multi-domain nanostructure with a saturation magnetization of 44.29 and 21.3 emu/g. Batch adsorption studies have been performed to determine the effect of pH, initial Pb(II) concentration, and the adsorbent dose on the removal performance of Pb(II) by NF and NG. The results prove that upon the addition of rGO to nickel ferrite nanoparticles, NG exhibits a maximum adsorption capacity of 390 mg/g under optimum conditions (pH = 6, T = 25 °C, [Pb(II)] = 20 mg/mL, [NG] = 15 mg). The adsorption kinetics of Pb(II) onto NF and NG obey the pseudo-second-order kinetic model with an R2 value of 0.999 and 0.999, which is higher than the pseudo-first model and Elovich models. The adsorption isothermal findings indicate that the Langmuir model perfectly fits the experimental data than Freundlich, Temkin and Redlich-Peterson isotherm models, which illustrates the monolayer adsorption process for both NF and NG. The thermodynamic study elucidates that the adsorption of Pb(II) onto NF and NG is endothermic. NG nanocomposite can be easily recovered while maintaining a relatively high adsorption capacity of 85% after four continuous cycles. This study demonstrates the effectiveness of NG nanosorbent for removing lead residues that help in assessing other toxic heavy metals contaminants in wastewater.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing are not applicable to this article as no datasets were analysed during the current study.
References
H. Khurshid, M.R.U. Mustafa, M.H. Isa, Adsorption of chromium, copper, lead and mercury ions from aqueous solution using bio and nano adsorbents: a review of recent trends in the application of AC BC nZVI and MXene. Environ. Res. 212, 113138 (2022)
V.-P. Dinh, D.-K. Nguyen, T.-T. Luu, Q.-H. Nguyen, L.A. Tuyen, D.D. Phong, H.A.T. Kiet, T.-H. Ho, T.T.P. Nguyen, T.D. Xuan, P.T. Hue, N.T.N. Hue, Adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by pomelo fruit peel-derived biochar. Mater. Chem. Phys. 285, 126105 (2022)
H. Li, Q. Jiang, J. Zhang, Y. Wang, Y. Zhang, Synchronization adsorption of Pb(II) and Ce(III) by biochar supported phosphate-doped ferrihydrite in aqueous solution: Adsorption efficiency and mechanism. Coll. Surf. A. Physiochem. Eng. Asp. 648, 129230 (2022)
M. Govarthanan, C.-H. Jeon, W. Kim, Synthesis and characterization of lanthanum- based metal organic framework decorated polyaniline for effective adsorption of lead ions from aqueous solutions. Environ. Pollut. 303, 119049 (2022)
A.-M. Georgescu, F. Nardou, V. Zichil, I.D. Nistor, Adsorption of lead(II) from aqueous solutions onto Cr-pillared clays. Appl. Clay Sci. 152, 44 (2018)
V.-P. Dinh, N.-C. Le, L.A. Tuyen, N.Q. Hung, V.-D. Nguyen, N.T. Nguyen, Insight into adsorption mechanism of lead(II) from aqueous solution by chitosan loaded MnO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 207, 294–302 (2018)
A. Bashir, L.A. Malik, S. Ahad, T. Manzoor, M.A. Bhat, G.N. Dar, A.H. Pandith, Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous system by ion-exchange and biosorption methods. Environ. Chem. Lett. 17, 729–754 (2019)
M.C. Benalia, L. Youcef, M.G. Bouaziz, S. Achour, H. Menasra, Removal of heavy metal from industrial wastewater by chemical precipitation: mechanisms and sludge characterization. Arab J. Sci. Eng. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05525-7
K.C. Khulbe, T. Matsuura, Removal of heavy metals and pollutants by membrane adsorption techniques. Appl. Water Sci. 8, 19 (2018)
T.-T. Luu, V.-P. Dinh, Q.-H. Nguyen, N.-Q. Tran, D.-K. Nguyen, T.-H. Ho, V.-D. Nguyen, D.-X. Tran, H.A.T. Kiet, Pb(II) adsorption mechanism and capability from aqueous solution using red mud modified by chitosan. Chemosphere 287, 132279 (2022)
F. Boudrahem, F. Aissani-Benissad, A. Soualah, Adsorption of lead(II) from aqueous solution by using leaves of date trees as an adsorbent. J. Chem. Eng. Data 56, 1804–1812 (2011)
B. Liu, S. Gai, Y. Lan, K. Cheng, F. Yang, Metal-based adsorbents for water eutrophication remediation: a review of performances and mechanisms. Environ. Res. 212, 113353 (2022)
M. Sajid, M. Asif, N. Baig, M. Kabeer, I.I. Mohammad, AW, Carbon nanotubes-based adsorbents: properties, functionalization, interaction mechanisms and applications in water purification. J. Water Process Eng. 47, 102815 (2022)
M. Adel, M.A. Ahmed, A.A. Mohamed, A facile and rapid removal of cationic dyes using hierarchically porous reduced graphene oxide decorated with manganese ferrite. FlatChem 26, 100233 (2021)
V. Nithya Priya, M. Rajkumar, J. Mobika, S.P.L. Sibi, Adsorption of As (V) ions from aqueous solution by carboxymethyl cellulose incorporated layered double hydroxide/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites: Isotherm and kinetic studies. Environ. Technol. Innov. 26, 102268 (2022)
T. Tatarchuk, M. Liaskovska, V. Kotsyubynsky, M. Bououdina, Green synthesis of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles using Cydonia oblanga extract: structural and mössbauer studies. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 672, 54–66 (2019)
T. Tatarchuk, M. Myslin, I. Lapchuk, A. Shyichuk, A.P. Murthy, R. Gargula, P. Kurzydto, B.F. Bogacz, A.T. Pedziwiatr, Magnesium- zinc ferrites as magnetic adsorbents for Cr(VI) and Ni(II) ions removal: Cation distribution and antistructure modeling. Chemosphere 270, 129414 (2021)
H. Qin, Y. He, P. Xu, D. Huang, Z. Wang, H. Wang, Z. Wang, Y. Zhao, Q. Tian, C. Wang, Spinel ferrites (MFe2O4): Synthesis, improvement and catalytic application in environment and energy field. Adv. Coll. Interface Sci. 294, 102486 (2021)
T. Tatarchuk, N. Danyliuk, V. Kotsyubynsky, A. Shumskaya, E. Kaniukov, A.A. Ghfar, M. Naushad, A. Shyichuk, Eco-friendly synthesis of cobalt-zinc ferrites using quince extract for adsorption and catalytic applications: an approach towards environmental remediation. Chemosphere 294, 133565 (2022)
T. Tatarchuk, A. Shyichuk, Z. Sojka, J. Gryboś, M. Naushad, V. Kotsyubynsky, M. Kowalska, S. Kwiatkowska- Marks, N. Danyliuk, Green synthesis, structure, cations distribution and bonding characteristics of superparamagnetic cobalt-zinc ferrites nanoparticles for Pb(II) adsorption and magnetic hyperthermia applications. J. Mol. Liq. 328, 115375 (2021)
A. Kumar, H.K. Rathore, D. Sarkar, A. Shukla, Nanostructured transition metal oxides and their composites for supercapacitors. Electrochem. Sci. Adv. 2, 1–42 (2021)
K. Kaviyarasu, C.M. Magdalene, D. Jayakumar, Y. Samson, A.K.H. Bashir, M. Maaza, D. Letsholathebe, A.H. Mahmoud, J. Kennedy, High performance of pyrochlore like Sm2Ti2O7 heterojunction photocatalyst for efficient degradation of rhodamine-B dye with wastewater under visible light irradiation. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 32(2), 1516–1522 (2020)
C.M. Magdalene, K. Kaviyarasu, N. Matinise, N. Mayedwa, N. Mongwaketsi, D. Letsholathebe, G.T. Mola, N. AbdullahAI- Dahabi, M.V. Arasu, M. Henini, J. Kennedy, M. Maaza, B. Jeyaraj, Evaluation of La2O3 garlanded ceria heterostructured binary metal oxide nanoplates for UV/visible light-induced removal of organic dye from urban wastewater. S Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 26, 49–60 (2018)
S. Panimalar, S. Logambal, R. Thambidurai, C. Inmozhi, R. Uthrakumar, A. Muthukumaran, R.A. Rasheed, M.K. Gatasheh, A. Raja, J. Kennedy, K. Kaviyarasu, Effect of Ag doped MnO2 nanostructures suitable for wastewater treatment and other environmental pollutant applications. Environ. Res. 205, 112560 (2022)
L.P. Lingamdinne, I.-S. Kim, J.-H. Ha, Y.-Y. Chang, J.R. Koduru, J.-K. Yang, Enhanced adsorption removal of Pb(II) and Cr(III) by using nickel ferrite-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite. Metals 7(22), 1–15 (2017)
S. Kumar, R.R. Nair, P.B. Pillai, S.N. Gupta, M.A.R. Iyengar, A.K. Sood, Graphene oxide- MnFe2O4 Magnetic nanohybrids for efficient removal of lead and arsenic from water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6(20), 17426–17436 (2014)
E.-R. Wang, K.-Y. Shih, Facile microwave hydrothermal synthesis of ZnFe2O4/rGO nanocomposites and their ultra-fast adsorption of methylene blue dye. Materials (Basel) 14(18), 5394 (2021)
S.-S. Wu, D.-H. Lan, X.-W. Zhang, Y. Huang, X.-H. Deng, C.-T. Au, B. Yi, Microwave hydrothermal synthesis, characterization and excellent uranium adsorption properties of CoFe2O4@rGO nanocomposite. J. Cent. South Univ. 28, 1955–1965 (2021)
A. Al-Nafiey, M.H.K. Al-Mamoori, S.M. Alshrefi, A.K. Shakir, R.T. Ahmed, One step to synthesis (rGO/Ni NPs) nanocomposite and using to adsorption dyes from aqueous solution. Mater. Today 19, 94–101 (2018)
B.P. Jacob, A. Kumar, R.P. Pant, S. Singh, E.M. Mohammed, Influence of preparation method on structural and magnetic properties of nickel ferrite nanoparticles. Bull. Mater. Sci. 34(7), 1345–1350 (2011)
P.L. Narayana, L.P. Lingamdinne, R.R. Karri, S. Devanesan, M.S. Alsalhi, N.S. Reddy, Y.-Y. Chang, Predictive capability evaluation and optimization of Pb(II) removal by reduced graphene oxide- based inverse spinel nickel ferrite nanocomposite. Environ Res 204, 112029 (2022)
N.M. Mahmoodi, F. Moghimi, M. Arami, F. Mazaheri, Silk degumming using microwave irradiation as an environmentally friendly surface modification method. Fibers Polym 11(2), 234–240 (2010)
H. Astaraki, S.M. Masoudpanah, S. Alamolhoda, Effects of fuel contents on physiochemical properties and photocatalytic activity of CuFe2O4/reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nanocomposited synthesized by solution combustion method. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 13402–13410 (2020)
A. Shanmugavani, R. Kalai Selvan, S. Layek, C. Sanjeeviraja, Size dependent electrical and magnetic properties of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by the combustion method: Comparison between aspartic acid and glycine as fuels. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 354, 363–371 (2014)
A. El-Maghraby, H.M. Awad, A.M. Naglah, M.S. Refat, H.M. Alkahtani, M.A. Al-Omar, A new comparative study by use of various amino acids as a self-combustion fuel to synthesis nano-ceramic compound at low temperature. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 14(9), 4283–4290 (2017)
C. Yue, W. Yujie, W. Zhang, B. Zhang, Y. Zhang, Z. Liu, Effects of moisture and particle size distribution on flame propagation of L-lysine sulfate powder. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 67, 104244 (2020)
R.R. Nair, B.C.J. Mary, J.J. Vijaya, A. Mustafa, L. Khezami, A. Modwi, M. Ismail, M. Bououdina, O.M. Lemine, Reduced graphene oxide/spinel ferrite nanocomposite as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 28253–28274 (2021)
M. Verma, A. Kumar, K.P. Singh, R. Kumar, V. Kumar, C.M. Srivastava, V. Rawat, G. Rao, S. Kumari, P. Sharma, H. Kim, Graphene oxide-manganese ferrite (GO-MnFe2O4) nanocomposite: One-pot hydrothermal synthesis and its use for adsorptive removal of Pb2+ ions from aqueous medium. J. Mol. Liq. 315, 113769 (2020)
L. Sun, R. Zhang, Z. Wang, L. Ju, E. Cao, Y. Zhang, Structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of NiFe2O4 prepared via sol-gel auto-combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 421, 65–70 (2017)
T. Shanmugavel, S.G. Raj, G.R. Kumar, G. Rajarajan, D. Saravanan, Cost effective preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline nickel ferrites (NiFe2O4) in low temperature regime. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 27(2), 176–181 (2015)
M.M.L. Sonia, S. Anand, M. Vinosel, M.A. Janifer, S. Pauline, A. Manikandan, Effect of lattice strain on structure, morphology and magneto-dielectric properties of spinel NiGdxFe2-xO4 ferrite nano-crystallites synthesized by sol-gel route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 466, 238–251 (2018)
D. Nath, F. Singh, R. Das, X-ray diffraction analysis by Williamson-Hall, Halder-Wagner and size-strain plot methods of CdSe nanoparticles- a comparative study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 239, 122021 (2020)
M.S. Abd El-Sadek, H.S. Wasly, K.M. Batoo, X-ray peak profile analysis and optical properties of CdS nanoparticles synthesized via the hydrothermal method. Appl. Phys. A 125, 283 (2019)
T.C. Paul, J. Podder, Synthesis and characterization of Zn- incorporated TiO2 thin films: impact of crystallite size and X-ray line broadening and bandgap tuning. Appl. Phys. A 125, 818 (2019)
K. Kombaiah, J.J. Vijaya, L.J. Kennedy, K. Kaviyarasu, Catalytic studies of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by conventional and microwave combustion method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 221, 11–28 (2019)
S. Debnath, R. Das, Cobalt doping on nickel ferrite nanocrystals enhances the micro-structural and magnetic properties: shows a correlation between them. J. Alloy Compd. 852, 156884 (2021)
J. Massoudi, M. Smari, K. Khirouni, E. Dhahri, L. Bessais, Impact of particle size on the structural and magnetic properties of superparamagnetic Li-ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 528, 167806 (2021)
E.E. Ateia, R. Ramadan, A.S. Shafaay, Efficient treatment of lead-containing wastewater by CoFe2O4/ graphene nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. A 126, 222 (2020)
T. Tatarchuk, A. Shyichuk, Z. Sokja, J. Gryboś, M. Naushad, V. Kotsyubynsky, M. Kowalska, S. Kwiatkowska-Marks, N. Danyliuk, Green synthesi, structure, cations distribution and bonding characteritics of superparamagnetic cobalt-zinc ferrites nanoparticles for Pb(II) adsorption and magnetic hyperthermia applications. J. Mol. Liq. 328, 115375 (2021)
D. Thatikayala, B. Min, Copper ferrite supported reduced graphene oxide as cathode materials to enhance microbial electrosynthesis of volatile fatty acids from CO2. Sci. Total Environ. 768, 144477 (2021)
B.R. Vergis, R. Hari Krishna, N. Kottam, B.M. Nagabhushana, R. Sharath, B. Darukaprasad, Removal of malachite green from aqueous solution by magnetic CuFe2O4 nano- adsorbent synthesized by one pot solution combustion method. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 8, 1–12 (2018)
P.T.L. Huong, N. Tu, H. Lan, L.H. Thang, N.V. Quy, P.A. Tuan, N.X. Dinh, V.N. Phan, A.-T. Le, Functional manganese ferrite/graphene oxide nanocomposites: effects of graphene oxide on the adsorption mechanisms of organic MB dye and inorganic As(v) ions from aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 8, 12376–12389 (2018)
I.S. Elashmawi, A.M. Ismail, Study of the spectroscopic, magnetic and electrical behavior of PVDF/PEO blend incorporated with nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) nanoparticles. Polym. Bull. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04139-9
A.R. Balakrishna, R.D. James, Design of soft magnetic materials. Npj Comput. Mater. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41524-021-00682-7
K.R.P. Munasir, Synthesis and Characterization of Fe3O4@rGO composite with wet-mixing (ex-situ) process. J. Phys. Conf. Series 1171, 012048 (2018)
S. Nag, A. Roychowdhury, D. Das, S. Mukherjee, Effects of rGO incorporated on structural and magnetic properties of Ni-Zn ferrite nanostructures. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 559, 169507 (2022)
A.R. Kagdi, N.P. Solanki, F.E. Carvalho, S.S. Meena, P. Bhatt, R.C. Pullar, R.B. Jotania, Influence of Mg substitution on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of X-type barium-zinc hexaferrites Ba2Zn2-xMgxFe28O46. J. Alloy. Compd. 741, 377–391 (2018)
H.N. Chaudhari, P.N. Dhruv, C. Singh, S.S. Meena, S. Kavita, R.B. Jotania, Effect of heating temperature on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of Magnesium ferrites prepared in the presence of Solanum Lycopersicum fruit extract. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 18445 (2020)
R.M. Moattari, S. Rahimi, L. Rajabi, A.A. Derakhshan, M. Keyhani, Statistical investigation of lead removal with various functionalized carboxylate ferroxane nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 283, 276–291 (2015)
A. Farooghi, M.H. Sayadi, M.R. Rezaei, A. Allahresani, An efficient removal of lead from aqueous solutions using FeNi3@SiO2 magnetic nanocomposite. Surf. Interfaces 10, 58–64 (2018)
L.P. Lingamdinne, J.R. Koduru, Y.-L. Choi, Y.-Y. Chang, J.-K. Yang, Studies on removal of Pb(II) and Cr(III) using graphene oxide based inverse spinel nickel ferrite nano-composite as sorbent. Hydrometallurgy 165, 64–72 (2016)
R. Jayalakshmi, J. Jeyanthi, K.R.A. Sidhaarth, Versatile application of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for the removal of heavy metals and dyes from aqueous solution. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit Manag. 17, 100659 (2022)
B. Xiang, D. Ling, H. Lou, H. Gu, 3D hierarchical flower-like nickel ferrite/manganese dioxide toward lead(II) removal from aqueous water. J. Hazard Mater. 325, 178–188 (2017)
B. Xiang, D. Ling, F. Gao, H. Lou, H. Gu, Z. Guo, Hexavalent chromium induced tunable surface functionalization of graphite. RSC Adv. 63, 58354–58362 (2016)
R.K. Sharma, A. Puri, Y. Monga, A. Adholeya, Acetoacetanilide-functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles for selective and cyclic removal of Pb2+ ions from different charged wastewaters. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 12888–12898 (2014)
S. Rezania, A. Mojiri, J. Park, N. Nawrot, E. Wojciechowska, N. Marraiki, N.S.S. Zaghloul, Removal of lead ions from wastewater using lanthanum sulfide nanoparticle decorated over magnetic graphene oxide. Environ. Res. 204, 11959 (2022)
S. Kokate, K. Parasuraman, H. Prakash, Adsorptive removal of lead ion from water using banana stem scutcher generated in fiber extraction process. Results Eng. 14, 100439 (2022)
N. Smječanin, D. Bužo, E. Mašić, M. Nuhanović, J. Sulejmanović, O. Azhar, F. Sher, Algae based green biocomposites for uranium removal from wastewater: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 283, 125998 (2022)
O.K. Amadi, C.J. Odidiozor, I.A. Okoro, Sorption kinetic and intraparticle diffusivities of As3+ and Hg2+ detoxification from aqueous solution suing cellulosic biosorbent derived from okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) stems. Int. J. Eng. Inf. Syst. 1(8), 72–85 (2017)
T.C. Egbosiuba, M.C. Egwunyenga, J.O. Tijani, S. Mustapha, A.S. Abdulkareem, A.S. Kovo, V. Kriskstolaityte, A. Veksha, M. Wagner, G. Lisak, Activated multi-walled carbon nanotubes decorated with zero valent nickel nanoparticles for arsenic, cadmium and lead adsorption from wastewater in a batch and continuous flow modes. J. Hazard. Mater. 423, 126993 (2022)
B. Mehdi, H. Belkacemi, D. Brahmi-Ingrachen, L.A. Braham, L. Muhr, Study of nickel adsorption on Nacl-modified natural zeolite using response surface methodology and kinetics modelling. Groundw Sustain. Dev. 17, 100757 (2022)
X. Chen, M.F. Hossain, C. Duan, J. Lu, Y.F. Tsang, M.S. Islam, Y. Zhou, Isotherm models for adsorption of heavy metals from water- A review. Chemosphere 307, 135545 (2022)
L. Wang, F. Fang, J. Liu, J. Beiyuan, J. Cao, S. Liu, Q. Ouyang, Y. Huang, J. Wang, Y. Liu, G. Song, D. Chen, U(VI) adsorption by green and facilely modified Ficus macrocarpa aerial roots: Behavior and mechanism investigation. Sci. Total. Environ. 810, 151166 (2022)
L.G. Bach, T.V. Tran, T.D. Nguyen, T.V. Pham, S.T. Do, Enhanced adsorption of methylene blue onto graphene oxide-doped XFe2O4 (X=Co, Mn, Ni) nanocomposite: kinetic, isothermal, thermodynamic and recyclability studies. Res. Chem. Intermed. 44(3), 1661–1687 (2018)
K.M. Khushboo, K. Jeet, Mechanistic insight into adsorption and photocatalytic potential of magnesium ferrite-bentonite nanocomposite. J Photochem Photobiol A: Chem 425, 113717 (2022)
T. Lei, S.-J. Li, F. Jiang, Z.-X. Ren, L.-L. Wang, X.-J. Yang, L.-H. Tang, S.-X. Wang, Adsorption of cadmium ions from an aqueous solution on a highly stable dopamine-modified magnetic nano-adsorbent. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 14, 352 (2019)
P. Zhao, M. Jian, R. Xu, Q. Zhang, C. Xiang, R. Liu, X. Zhang, H. Liu, Removal of arsenic (III) from water by 2D zeolite imidazolate framework -67 nanosheets. Environ. Sci. Nano 7, 3616–3626 (2020)
Q. Li, R. Li, X. Ma, W. Zhang, B. Sarkar, X. Sun, N. Bolan, Efficient removal of antimonate from water by yttrium-based metal-organic framework: Adsorbent stability and adsorption mechanism investigation. Coll. Surf. A: Physiochem. Eng. Asp 633, 127877 (2022)
H. Li, Y. Yao, J. Chen, C. Wang, J. Huang, J. Du, S. Xu, J. Tang, H. Zhao, M. Huang, Heterogenous activation of peroxymonosulfate by bimetallic MOFs for efficient degradation of phenanthrene: Synthesis, performance, kinetics and mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 259, 118217 (2020)
H.T. Van, L.H. Nguyen, N.V. Dang, H.-P. Chao, Q.T. Nguyen, T.H. Nguyen, T.B.L. Nguyen, D.V. Thanh, H.D. Nguyen, P.Q. Thang, P.T.H. Thanh, V.P. Huang, The enhancement of reactive red 24 adsorption from aqueous solution using agricultural waste- derived biochar modified with ZnO nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 11, 5801 (2021)
A.R.K. Gollakota, V.S. Munagapati, C.-M. Shu, J.-C. Wen, Adsorption of Cr (VI), and Pb(II) from aqueous solution by 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifletrifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide functionalized biomass Hazel Sterculia (Sterculia Foetida L.). J Mol Liq 350, 118534 (2022)
L.P. Lingamdinne, J.R. Koduru, Y.-Y. Chang, S.-H. Kang, J.-K. Yang, Facile synthesis of flowered mesoporous graphene oxide-lanthanum fluoride nanocomposite for adsorptive removal of arsenic. J Mol Liq 279, 32–42 (2019)
F. Liu, W. Zhang, W. Chen, J. Wang, Q. Yang, W. Zhu, J. Wang, One-pot synthesis of NiFe2O4 integrated with EDTA-derived carbon dots for enhanced removal of tetracycline. Chem. Eng. 310, 187–196 (2017)
S. Banerjee, M.C. Chattopadhyaya, Adsorption characteristics for the removal of a toxic dye, tartrazine from aqueous solutions by a low-cost agricultural by-product. Arab. J. Chem. 10(2), S1629–S1638 (2017)
A. Homayonfard, M. Miralinaghi, R.H.S.M. Shirazi, E. Moiri, Efficient removal of cadmium (II) ions from aqueous solution by CoFe2O4/chitosan and NiFe2O4/chitosan composites as adsorbents. Water Sci. Technol. 78(11), 2297–2307 (2018)
T. Jiang, Y.-D. Liang, Y.-J. He, Q. Wang, Activated carbon/NiFe2O4 magnetic composite: a magnetic adsorbent for the adsorption of methyl orange. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 3, 1740–1751 (2015)
L.T.M. Thy, N.T.C. Linh, T.T. Tram, T.H. Tu, L.T. Tai, P.T. Khang, H.H. Nam, N.H. Hieu, M.T. Phong, Fabrication and response surface methodology for the adsorption of nickel ferrite-graphene oxide nanocomposite for the removal of methylene blue from water. J. Nanometer 2021, 4636531 (2021)
R. Nasiri, N. Arsalani, Y. Panahian, One-pot synthesis of novel magnetic three-dimensional graphene/ chitosan/nickel ferrite nanocomposite for lead ions removal from aqueous solution: RSM modelling design. J. Clean. Prod. 201, 507–515 (2018)
C. Santhosh, P. Kollu, S. Felix, V. Velmurugan, S.K. Jeong, A.N. Grace, CoFe2O4 and NiFe2O4@ graphene adsorbents for heavy metal ion- kinetic and thermodynamic analysis. RSC Adv. 5, 28965–28972 (2015)
H. Shekari, M.H. Sayadi, M.R. Rezaei, A. Allahresani, Synthesis of nickel ferrite/titanium oxide magnetic nanocomposite and its use to remove hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions. Surf. Interfaces 8, 199–205 (2017)
L.P. Lingamdinne, Y.-L. Choi, I.-S. Kim, J.-K. Yang, J.R. Koduru, Y.-Y. Chang, Preparation and characterization of porous reduced graphene oxide based inverse spinel nickel ferrite nanocomposite for adsorption removal of radionuclides. J. Hazard Mater. 326, 145–156 (2017)
H. Moustafa, H. Isawi, S.A.M.E. Wahab, Utilization of PVA nano-membrane based synthesized magnetic GO-Ni-Fe2O4 nanoparticles for removal of heavy metals from water resources. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 18, 100696 (2022)
I. Khosravi, M. Eftekhar, Characterization and evaluation catalytic efficiency of NiFe2O4 nano spinel in removal of reactive dye from aqueous solution. Powder Technol. 250, 147–153 (2013)
S.K. Sonar, P.S. Niphadkar, S. Mayadevi, P.N. Joshi, Preparation and characterization of porous fly ash/NiFe2O4 composite: promising adsorbent for the removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 148, 371–379 (2014)
H.-Y. Zhu, R. Jiang, Y.-Q. Fu, R.-R. Li, J. Yao, S.-T. Jiang, Novel multifunctional NiFe2O4/ZnO hybrids for dye removal by adsorption, photocatalysis and magnetic separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 369, 1–10 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Loyola College management, affiliated to University of Madras for presuming the necessary organizational facilities to carry out this research work and IIT Madras, University of Bahrain and Al Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU) Saudi Arabia for providing the characterization facilities.
Funding
The authors received no specific grant from any funding agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BCJ and JJ: designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript; MB: participated in the design and interpretation of data; LJ: revised the manuscript; LK and AM: performed experiments and analysis. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.”
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare relevant to the article's content.
Ethical approval
The authors have agreement with all the copyright rules and ethics in publishing that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mary, B.C.J., Vijaya, J.J., Bououdina, M. et al. Adsorption ability of aqueous lead (II) by NiFe2O4 and 2D- rGO decorated NiFe2O4 nanocomposite. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 845 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10237-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10237-9