Abstract
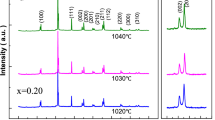
Li2Mg3Ti0.91(Al0.5Nb0.5)0.09O6-based microwave dielectric ceramics with high dielectric constant, quality-factor and temperature stability were prepared by conventional solid-state reaction method. Influence of Zn2+ dopant on structures and microwave dielectric properties of Li2Mg3Ti0.91(Al0.5Nb0.5)0.09O6 ceramics were investigated by X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. The X-ray diffraction results showed that no new phase was produced with the zinc addition before y = 0.08, above that some ZnTiO3 peaks with very low intensity appear in the low-angle region of the diffraction pattern. The results of the scanning electronic microscope confirmed that Zn2+ doping helped grains growth, reduced grain boundaries and made grains distribution uniform. All of these improvements have led to great dielectric constant (εr), superior quality factor (Q×f) and outstanding temperature coefficient of resonance frequency (τf). A microwave dielectric ceramic based on Li2Mg3Ti0.91(Al0.5Nb0.5)0.09O6 with optimum Zn2+ content sintered at optimum temperature, exhibiting better comprehensive dielectric properties: εr = 14.51, Q×f = 158,120 GHz, τf = −13.0 ppm/°C.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data was used for the research described in the article. The data that has been used is confidential. Data will be made available on request.
References
Z.F. Fu, P. Liu, J.L. Ma, X.M. Chen, H.W. Zhang, New high Q low-fired Li2Mg3TiO6 microwave dielectric ceramics with rock salt structure. Mater. Lett. 164, 436–439 (2016)
H. Xie, Microwave dielectric properties of low loss Li2(Mg0.95A0.05)3TiO6 (A = Ca2+, Ni2+, Zn2+, Mn2+) ceramics system. J. Alloys Compd. 689(25), 246–249 (2016)
Z.X. Fang, B. Tang, F. Si, S. Zhang, Temperature stable and high-Q microwave dielectric ceramics in the Li2Mg3 – xCaxTiO6 system (x = 0.00-0.18). Ceram. Int. 43(2), 1682–1687 (2017)
H.L. Pan, Y.X. Mao, Y.K. Yang, Y.W. Zhang, H.T. Wu, Crystal structure, Raman spectra, infrared spectra and microwave dielectric properties of Li2Mg3Ti1 – x(Mg1/3Ta2/3)xO6 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.2) solid solution ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 105, 296–305 (2018)
H.L. Pan, Y.W. Zhang, H.T. Wu, Crystal structure, infrared spectroscopy and microwave dielectric properties of ultra low-loss Li2Mg3Ti0.95(Mg1/3Sb2/3)0.05O6 ceramic. Ceram. Int. 44, 3464–3468 (2018)
P. Zhang, H. Xie, Y.G. Zhao, M. Xiao, Synthesis and microwave dielectric characteristics of high-Q Li2MgxTiO3 + x ceramics system. Mater. Res. Bull. 98, 160–165 (2018)
F. Zhao, Z.X. Yue, Y.C. Zhang, Z.L. Gui, L.T. Li, Microstructure and microwave dielectric properties of Ca[Ti1 – x(Mg1/3Nb2/3)x]O3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 25(14), 3347–3352 (2005)
J.J. Bian, X.H. Zhang, Structural evolution, grain growth kinetics and microwave dielectric properties of Li2Ti1 – x(Mg1/3Nb2/3)xO3. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38(2), 599–604 (2018)
G.H. Chen, H.R. Xu, C.L. Yuan, Microstructure and microwave dielectric properties of Li2Ti1 – x(Zn1/3Nb2/3)xO3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 39(5), 4887–4892 (2013)
H.T. Chen, B. Tang, P. Fan, M. Wei, S.R. Zhang, Phase evolution and microwave dielectric properties of Ca0.61Nd0.26Ti1– x(Al1/2Nb1/2)xO3 ceramics (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.2). Ceram-Silikaty. 61(1), 1–5 (2017)
T.W. Zhang, R.Z. Zuo, J. Zhang, Structure, microwave dielectric properties, and low-temperature sintering of acceptor/donor codoped Li2Ti1 – x(Al0.5Nb0.5)xO3 Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 99, 825–832 (2015)
E.Z. Li, X. Yang, H.C. Yang, H.Y. Yang, H.B. Sun, Y. Yuan et al., Crystalstructure, microwave dielectric properties and low temperature sintering of (Al0.5Nb0.5) 4+ co-substitution for Ti4+ of LiNb0.6Ti0.5O3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 45, 5418–5424 (2019)
Z.F. Fu, J.L. Ma, X.S. Zhang, B. Wang, The effect of sintering agents on the sinterability and dielectric properties of Li2Mg3TiO6 ceramics. Ferroelectr 510(1), 50–55 (2017)
J. Liang, W.Z. Lu, J.M. Wu, J.G. Guan, Microwave dielectric properties of Li2TiO3 ceramics sintered at low temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 176(2), 99–102 (2011)
Y.W. Tseng, J.Y. Chen, Y.C. Kuo, C.L. Huang, Low-loss microwave dielectrics using rock salt oxide Li2MgTiO4. J. Alloy Compd. 509(33), L308–L310 (2011)
R.D. Shannon, Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomie distances in halides and chaleogenides. Acta Crystallogr. A32(5), 751–767 (1976)
M. Tabuchi, K. Ado, H. Kobayashi, I. Matsubara, H. Kageyama, M. Wakita et al., Magnetic properties of metastable lithium iron oxides obtained by solvothermal/hydrothermal reaction. J. Solid State Chem. 141(2), 5541–5561 (1998)
N.E. Brese, M. O’Keeffe, Bond-valence parameters for solids. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B: Struct. Sci. 47, 192–197 (1991)
H.L. Pan, L. Cheng, H.T. Wu, Relationships between crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of Li2(Mg1 – xCox)3TiO6 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.4) ceramics. Ceram. Int. 43, 15018–15026 (2017)
E.S. Kim, C.J. Jeon, P.G. Clem, Effects of Crystal structure on the microwave Dielectric Properties of ABO4 (A = ni, mg, Zn and B = Mo, W) Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95(9), 1–5 (2012)
N.X. Xu, J.H. Zhou, H. Yang, Q.L. Zhang, M.J. Wang, L. Hu, Structural evolution and microwave dielectric properties of MgO-LiF co-doped Li2TiO3 ceramics for LTCC applications. Ceram. Int. 40(9B), 15191–15198 (2014)
T.Y. Qin, C.W. Zhong, Y. Qin, B. Tang, S.R. Zhang, Low-temperature sintering mechanism and microwave dielectric properties of ZnAl2O4-LMZBS composites. J. Alloys Compd. 797, 744–753 (2019)
L.X. Zhang, L. Gan, H.Y. Cheng, S.F. Yuan, S.B. An, J. Jiang et al., Crystal structure, Raman spectra analysis and microwave dielectric properties optimization of (Ca0.22Li0.39Sm0.39)TiO3 ceramics doped with SmAlO3. J. Alloys Compd. 817, 152708–152714 (2020)
R.D. Shannon, Dielectric polarizabilities of ions in oxides and fluorides. J. Appl. Phys. 73, 348–366 (1993)
W.M. Robertson, G. Arjacalingam, S.L. Shinde, Microwave dielectric measurements of zirconia-alumina ceramic composites – A text of the clausius-mossotti mixture equations. J. Appl. Phys. 70(12), 7648–7650 (1991)
E. Talebian, M. Talebian, A general review on the derivation of Clausius-Mossotti relation. Optik. 12(416), 2324–2326 (2013)
H.L. Pan, H.T. Wu, Crystal structure, infrared spectra and microwave dielectric properties of new ultra low-loss Li6Mg7Ti3O16 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 43(16), 14484–14487 (2017)
E.S. Kim, B.S. Chun, R. Freer, R.J. Cernik, Effects of packing fraction and bond valence on microwave dielectric properties of A2+B6+O4 (A2+: ca, Pb, Ba; B6+: Mo, W) ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 30(7), 1731–1736 (2010)
M. Xiao, Q.Q. Gu, Z.Q. Zhou, P. Zhang, Study of the microwave dielectric properties of (La1 – xSmx)NbO4 (x = 0-0.10) ceramics via bond valence and packing fraction. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 100, 3952–3960 (2017)
H.J. Jo, E.S. Kim, Effect of Sn4+ substitution on microwave dielectric properties of (Mg0.95Ni0.05)(Ti1 – xSnx)O3 ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 67, 221–225 (2015)
J.M. Li, Y.X. Han, T. Qiu, C.G. Jin, Effect of bond valence on microwave dielectric properties of (1-x)CaTiO3-x(Li0.5La0.5)TiO3 ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 47(9), 2375–2323 (2012)
E.S. Kim, K.H. Yoon, Effect of nickel on microwave dielectric properties of Ba(Mg1/3Ta2/3O3. J. Mater. Sci. 29, 830–834 (1994)
C.L. Huang, M.H. Weng, H.L. Chen, Effects of additives on microstructure and microwave dielectric properties of (Zr, Sn)TiO4 ceramics. Mater. Chem. Phys. 71, 17–22 (2001)
E.S. Kim, W. Choi, Effect of phase transition on the microwave dielectric properties of BiNbO4. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26(10–11), 176 (2006)
E.S. Kim, D.H. Kang, Relationships between crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of (Zn1/3B2/35+)xTi1–xO2 (B 5+= nb, Ta) ceramics. Ceram. Int. 34(4), 883–888 (2008)
J.C. Phillips, J.A. Vechten, Dielectric classification of crystal structures, ionization potentials, and band structures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 22(14), 705–708 (1969)
B.F. Levine, Bond susceptibilities and ionicities in complex crystal structures. J. Chem. Phys. 59(3), 1463–1486 (1973)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support from Suzhou Boom High Purity Materials Technology Co. Ltd and Sichuan Mianyang Weiqi Electronic Technology Co., Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study concept and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were carried out by HJ, TG, JG, HF, and TY. The first draft of the manuscript was written by HJ. The study was supervised by HY. All the authors have commented on previous versions of the manuscript. Final draft read and approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jing, H., Gou, T., Gao, J. et al. Effect of Zn2+ doping Li2Mg3Ti0.91(Al0.5Nb0.5)0.09O6 on structures and microwave dielectric properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 626 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10040-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10040-6