Abstract
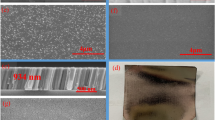
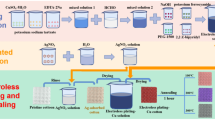
Double-layer Fe73.5Si15.5B7Cu1Nb3/Cu composite strips were prepared by depositing copper films on the surface of Fe73.5Si15.5B7Cu1Nb3 amorphous strips using magnetron sputtering. The structure of Fe73.5Si15.5B7Cu1Nb3 amorphous strips and the double-layer composite strips before and after annealing was performed by X-ray diffraction. The electrical and magnetic properties of the composite strips were tested by Hall effect tester and impedance analyzer, respectively. Furthermore, the shielding effectiveness (SE) of the composite strips before and after annealing against electromagnetic waves in the range of 1–9 GHz was measured by vector network analyzer. The results show that the SE of amorphous strips annealed at 320 °C is better than that of 380 °C and 440 °C. The composite strip depositing copper film for 20 min and then annealed at 320 °C for 30 min has the highest SE of about 110.1 dB at 6.7 GHz, which is 28 dB higher than that of Fe73.5Si15.5B7Cu1Nb3 amorphous strips. Due to the addition of the conductivity (σ) of the strips sputtered copper film, the ability of this strip to reflect electromagnetic waves is improved. After annealing, the effective permeability of FeSiBCuNb/Cu composite strips increases, so the magnetic loss also increases.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this manuscript (and its supplementary information files) or can be available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Z. Ma, J. Li, J. Zhang et al., Ultrathin, flexible, and high-strength Ni/Cu/metallic glass/Cu/Ni composite with alternate magneto-electric structures for electromagnetic shielding. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 81, 43–50 (2021)
D.O. Carpenter, Human disease resulting from exposure to electromagnetic fields1. Rev. Environ. Health 28(4), 159–172 (2013)
R. Stam, S. Yamaguchi-Sekino, Occupational exposure to electromagnetic fields from medical sources. Ind. Health 56(2), 96–105 (2018)
G. Redlarski, B. Lewczuk, A. Żak, et al., The influence of electromagnetic pollution on living organisms: historical trends and forecasting changes. BioMed Res. Int. (2015).
P. Kumar, U.N. Maiti, A. Sikdar et al., Recent advances in polymer and polymer composites for electromagnetic interference shielding: review and future prospects. Polym. Rev. 59(4), 687–738 (2019)
S.H. Lee, S. Yu, F. Shahzad et al., Highly anisotropic Cu oblate ellipsoids incorporated polymer composites with excellent performance for broadband electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Sci. Technol. 144, 57–62 (2017)
J.H. Park, J.W. Lee, H.J. Choi et al., Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of sputtered NiFe/Cu multi-layer thin film at high frequencies. Thin Solid Films 677, 130–136 (2019)
O.A. Testov, A.E. Komlev, K.G. Gareev et al., Providing a specified level of electromagnetic shielding with nickel thin films formed by DC magnetron sputtering. Coatings 11(12), 1455 (2021)
H. Zhao, L. Hou, Y. Lu, Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness and serviceability of the multilayer structured cuprammonium fabric/polypyrrole/copper (CF/PPy/Cu) composite. Chem. Eng. J. 297, 170–179 (2016)
M.H. Al-Saleh, G.A. Gelves, U. Sundararaj, Copper nanowire/polystyrene nanocomposites: lower percolation threshold and higher EMI shielding. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 42(1), 92–97 (2011)
D.X. Yan, H. Pang, B. Li et al., Structured reduced graphene oxide/polymer composites for ultra-efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Func. Mater. 25(4), 559–566 (2015)
Z. Wang, B. Mao, Q. Wang et al., Ultrahigh conductive copper/large flake size graphene heterostructure thin-film with remarkable electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness. Small 14(20), 1704332 (2018)
G.M. Weng, J. Li, M. Alhabeb et al., Layer-by-layer assembly of cross-functional semi-transparent MXene-carbon nanotubes composite films for next-generation electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28(44), 1803360 (2018)
J. Zhang, J. Li, G. Tan et al., Thin and flexible Fe–Si–B/Ni–Cu–P metallic glass multilayer composites for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9(48), 42192–42199 (2017)
J. Luo, L. Wang, X. Huang et al., Mechanically durable, highly conductive, and anticorrosive composite fabrics with excellent self-cleaning performance for high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11(11), 10883–10894 (2019)
I.R. Radulescu, L. Surdu, B. Mitu et al., Conductive textile structures and their contribution to electromagnetic shielding effectiveness. Industria Textila. 71(5), 432–437 (2020)
B. Zhao, C.B. Park, Tunable electromagnetic shielding properties of conductive poly (vinylidene fluoride)/Ni chain composite films with negative permittivity. J. Mater. Chem. C 5(28), 6954–6961 (2017)
S. Li, Z. Xu, Y. Dong et al., Ni@ nylon mesh/PP composites with a novel tree-ring structure for enhancing electromagnetic shielding. Compos Part A 131, 105798 (2020)
F. Shahzad, M. Alhabeb, C.B. Hatter et al., Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes). Science 353(6304), 1137–1140 (2016)
A. Iqbal, F. Shahzad, K. Hantanasirisakul et al., Anomalous absorption of electromagnetic waves by 2D transition metal carbonitride Ti3CNTx (MXene). Science 369(6502), 446–450 (2020)
H. Zhao, Y. Huang, Y. Han et al., Flexible and lightweight porous polyether sulfone/Cu composite film with bidirectional differential structure for electromagnetic interference shielding and heat conduction. Chem. Eng. J. 440, 135919 (2022)
O. Gutfleisch, M.A. Willard, E. Brück et al., Magnetic materials and devices for the 21st century: stronger, lighter, and more energy efficient. Adv. Mater. 23(7), 821–842 (2011)
J. Lee, Y. Liu, Y. Liu et al., Ultrahigh electromagnetic interference shielding performance of lightweight, flexible, and highly conductive copper-clad carbon fiber nonwoven fabrics. J. Mater. Chem. C. 5(31), 7853–7861 (2017)
X. Ma, Q. Zhang, Z. Luo et al., A novel structure of ferro-aluminum based sandwich composite for magnetic and electromagnetic interference shielding. Mater. Des. 89, 71–77 (2016)
F. Qin, H.X. Peng, Ferromagnetic microwires enabled multifunctional composite materials. Prog. Mater Sci. 58(2), 183–259 (2013)
Z. Stokłosa, J. Rasek, P. Kwapuliński et al., Magnetic, electrical and plastic properties of Fe76Nb2Si13B9, Fe75Ag1Nb2Si13B9 and Fe75Cu1Nb2Si13B9 amorphous alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 509(37), 9050–9054 (2011)
J. Xu, Y. Yang, Q. Yan et al., Softening and magnetic properties of ultrahigh Fe content FeSiBCuPC nanocrystalline alloy induced by low-pressure stress annealing. Scr. Mater. 179, 6–11 (2020)
M. Yu, C. Yang, X. Bian et al., Application of Fe78Si9B13 amorphous particles in magnetorheological fluids. RSC Adv. 6(27), 22511–22518 (2016)
B.F. Zou, T.D. Zhou, J. Hu, Effect of amorphous evolution on structure and absorption properties of FeSiCr alloy powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 335, 17–20 (2013)
Y. Yang, M. Li, Y. Wu et al., Nanoscaled self-alignment of Fe3O4 nanodiscs in ultrathin rGO films with engineered conductivity for electromagnetic interference shielding. Nanoscale 8(35), 15989–15998 (2016)
L.D.L.S. Valladares, D.H. Salinas, A.B. Dominguez et al., Crystallization and electrical resistivity of Cu2O and CuO obtained by thermal oxidation of Cu thin films on SiO2/Si substrates. Thin Solid Films 520(20), 6368–6374 (2012)
B. Zhao, X. Guo, W. Zhao et al., Facile synthesis of yolk–shell Ni@ void@ SnO2 (Ni3Sn2) ternary composites via galvanic replacement/Kirkendall effect and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. Nano Res. 10(1), 331–343 (2017)
X. Lyu, Z. Yang, M. Li et al., Facile chemical synthesis of amorphous FeB alloy nanoparticles and their superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 126, 143–149 (2019)
P. Liu, Y. Wang, G. Zhang, et al., Hierarchical engineering of double‐Shelled nanotubes toward hetero‐interfaces induced polarization and microscale magnetic interaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022: 2202588.
P. Liu, S. Gao, G. Zhang et al., Hollow engineering to Co@ N-doped carbon nanocages via synergistic protecting-etching strategy for ultrahigh microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31(27), 2102812 (2021)
P. Liu, T. Gao, W. He et al., Electrospinning of hierarchical carbon fibers with multi-dimensional magnetic configurations toward prominent microwave absorption. Carbon 202, 244–253 (2023)
H. Xu, G. Zhang, Y. Wang et al., Heteroatoms-doped carbon nanocages with enhanced dipolar and defective polarization toward light-weight microwave absorbers. Nano Res. 15(10), 8705–8713 (2022)
H. Xu, G. Zhang, Y. Wang et al., Size-dependent oxidation-induced phase engineering for MOFs derivatives via spatial confinement strategy toward enhanced microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 14, 102 (2022)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52071089) and Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2019B030302010).
Funding
Funding was provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 52071089).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, WX and YY; methodology, WX, JQ, and YZ; experiments, WX, GZ and YZ; characterization, WX, HO, HZ and YW; writing—original draft preparation, WX and YY; writing—review and editing, WX and YY; supervision, YY; project administration, WX; funding acquisition, YY All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, W., Qi, J., Zhang, Y. et al. Effect of annealing treatment on electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of double-layer FeSiBCuNb/Cu composite strips. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 376 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09740-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09740-2