Abstract
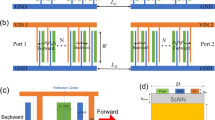
With the development of information technology, surface acoustic wave (SAW) devices are strongly required to exhibit higher integration, and lower insertion loss, as well as complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS), processes compatibility. Aluminum nitride (AlN) is an excellent piezoelectric material that is compatible with CMOS processes; however, the insertion loss for AlN/Si SAW devices is high under conventional interdigital transducers (IDT) structure. In this work, AlN piezoelectric film-based floating electrode unidirectional transducers (FEUDT) structures are developed, and its propagation characteristics are simulated with the help of finite-element method (FEM). By Fourier transforming the corresponding time response, the insertion loss of the devices is calculated to be − 15.52 (forward) and − 22.94 dB (backward). According to simulation structure, FEUDT and IDT-structured devices with 3.6 μm wavelength are fabricated by electron beam lithography, and operating frequency of both devices reached 1.4 GHz, which is basically consistent with simulation results, and insertion loss of floating electrode unidirectional transducers structures is about 11 dB lower than that of conventional structure.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
D.C. Malocha, Acoustoelectric amplifier model using coupling of modes and charge control analysis. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 68(8), 2794–2803 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TUFFC.2021.3073892
Y. Zhu, G. Fan, L. Huang et al., Integrated acousto-optic interaction at ultrahigh frequencies. Opt. Commun. 497, 1–5 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2021.127174
K.S. Pasupuleti, M. Reddeppa, D.J. Nam et al., Boosting of NO2 gas sensing performances using GO-PEDOT: PSS nanocomposite chemical interface coated on langasite-based surface acoustic wave sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 344, 1–12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130267
Y. Wang, C. Xu, D. Mei et al., Tunable patterning of microscale particles using a surface acoustic wave device with slanted-finger interdigital transducers. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 22, 331–343 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A2000501
K. Länge, B.E. Rapp, M. Rapp, Surface acoustic wave biosensors: a review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 391, 1509–1519 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-1911-5
Z. Lu, S. Fu, Z. Chen et al., High-frequency and high-temperature stable surface acoustic wave devices on ZnO/SiO2/SiC structure. J. Phys. D 53(30), 1–21 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/ab8324
Y. Liu, Y. Cai, Y. Zhang et al., Materials, design, and characteristics of bulk acoustic wave resonator: a review. Micromachines. 11(7), 630–656 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070630
L. Wei, X. Kuai, Y. Bao, J. Wei et al., The recent progress of MEMS/NEMS resonators. Micromac-hines 12(6), 724 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060724
M.Z. Aslam, V. Jeoti, S. Karuppanan, A.F. Malik et al., FEM analysis of sezawa mode SAW sensor for VOC based on CMOS compatible AlN/SiO2/Si multilayer structure. Sensors 18(6), 1687 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061687
A.A.M. Ralib, A.N. Nordin, A.Z. Alam et al., Piezoelectric thin films for double electrode CMOS MEMS surface acoustic wave (SAW) resonator. Microsyst. Technol. 21, 1931 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2319-0
G. Bu, D. Ciplys, M. Shur et al., Surface acoustic wave velocity in single-crystal AlN substrates. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 53(1), 251–254 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/TUFFC.2006.1588412
K. Li, F. Wang, M. Deng et al., Microstructure and bending piezoelectric characteristics of AlN film for high-frequency flexible SAW devices. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 32, 13146–13155 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05830-9
B. Fu, F. Wang, R. Cao et al., Optimization of the annealing process and nanoscale piezoelectric properties of (002) AlN thin films. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 28, 9295–9300 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6666-3
W. Wang, P.M. Mayrhofer, X. He et al., High performance AlScN thin film-based surface acoustic wave devices with large electromechanical coupling coefficient. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105(13), 133502 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4896853
W.B. Wang, Y.Q. Fu, J.J. Chen et al., AlScN thin film-based surface acoustic wave devices with enhanced microfluidic performance. J. Micromech. Microeng. 26(7), 1–8 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/26/7/075006
E. Dai, Technique for low-loss and wideband surface acoustic wave filters. Electron. Lett. 36(22), 1904–1905 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1049/el:20001305
K. Yamanouchi, H. Furuyashiki, New low-loss SAW filter using internal floating electrode reflection types of single-phase unidirectional transducer. Electron. Lett. 20(24), 989–990 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1049/el:19840672
K. Yamanouchi, H. Furuyashiki, S.A.W. Low-Loss, Filter using internal reflection types of new single-phase unidirectional transducer. Electron. Lett. 20(20), 819–821 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1049/el:19840557
P.V. Wright, The natural single-phase unidirectional transducer: a new low-loss SAW transducer. Ultrason. Symp. IEEE (1985). https://doi.org/10.1109/ULTSYM.1985.198478
K. Hanma, B.J. Hunsinger, A triple transit suppression technique. Ultrason. Symp. IEEE (1976). https://doi.org/10.1109/ULTSYM.1976.196692
T. Kodama, H. Kawabata, Y. Yasuhara, H. Sato, Design of low-loss SAW filters employing distributed acoustic reflection transducers. Ultrason. Symp. IEEE (1986). https://doi.org/10.1109/ULTSYM.1986.198710
C.S. Hartmann, B.P. Abbott, Overview of design challenges for single phase unidirectional SAW filters. Ultrason. Symp. IEEE (1989). https://doi.org/10.1109/ULTSYM.1989.66963
H. Nakamura, T. Yamada, T. Igaki, K. Nishimura, T. Ishizaki, K. Ogawa, A practical SPUDT design for SAW filters with different-width split-finger interdigital transducers. Ultrason. Symp. IEEE. (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/ULTSYM.2000.922517
F. Huang, Possible design procedure for low-loss 180 degrees reflecting arrays in SAW devices. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 35(1), 57–60 (1988). (414 8)
J.X. Zhai, C. Chen, Low-loss floating electrode unidirectional transducer for SAW sensor. Acoust. Phys. 65(2), 178–184 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S106377101902012X
S. Maouhoub, Y. Aoura, A. Mir, FEM simulation of Rayleigh waves for SAW devices based on ZnO/AlN/Si. Microelectron. Eng. 136, 22–25 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2015.03.042
D.S. Ballantine Jr., R.M. White, S.J. Martin et al., Acoustic wave sensors: Theory, design and physico-chemical applications[M], vol. 63 (Elsevier, Asterdam, 1996), pp.79–79
L.L. Brizoual, O. Elmazria, FEM modeling of AlN/diamond surface acoustic waves device. Diam. Relat. Mater. 16(4–7), 987–990 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2007.01.002
M. Takeuchi, K. Yamanouchi, Coupled mode analysis of SAW floating electrode type unidirectional transducers. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 40(6), 648–658 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1109/58.248207
S. Menzel, M. Pekarčikova, M. Hofmann et al., Material transport in Al-metallizations of power-loaded SAW structures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 252(1), 215–217 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2005.02.020
I.Y. Huang, C.Y. Lin, J.W. Lan, Improving thin-film zinc-oxide surface acoustic wave device insertion loss using a grooved reflective grating structure. J. Micro Nanolithogr MEMS MOEMS 12(1), 1–10 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JMM.12.1.013019
D. Wang, Y. Chen, Z. Yao et al., The design of silicon substrate AlN ellipse IDT structure SAW filter. Chin. J. Sens. Actuators 26(12), 1691–1694 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2013.12.013
L. Wang, S. Chen, J. Zhang et al., Enhanced performance of 17.7 GHz SAW devices based on AlN/diamond/Si layered structure with embedded nanotransducer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 111(25), 253502 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5006884
Y. Ai, S. Yang, Z. Cheng et al., Enhanced performance of AlN SAW devices with wave propagation along the <11–20> direction on c-plane sapphire substrate. J. Phys. D 52(21), 215103 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/ab0bf6
W. Wang, P.M. Mayrhofer, X. He et al., High performance AlScN thin film based surface acoustic wave devices with large electromechanical coupling coefficient. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 133502 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4896853
Funding
This work was supported by Science and Technology Planning Project of Tianjin City (20ZYQCGX00070), Open project of state Key Laboratory of Functional Materials for Information (SKL202007), the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin City (18JCzDJC30500 and 18JCYBJC85700), Research and Development Program in Significant Area of Guangdong Province (2020B0101040002), Tianjin Enterprise Science and Technology Commissioner Project (19JCTPJC56200), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62001326).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by LL, FW, KL, and KZ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by LL, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. LL, KL, KZ, FW, and YH: Conceptualization, DK, KH: Methodology, YX, ZS, LQ: Formal analysis and investigation, LL, KL: Writing—original draft preparation, LL, KZ, FW: Writing—review and editing, KZ, FW, YH: Funding acquisition DS: Resources, KZ: Supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Wang, F., Li, K. et al. Effect of interdigital transducers structure on insertion loss of high-frequency surface acoustic wave devices. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 22017–22026 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08993-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08993-1