Abstract
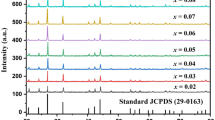
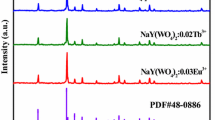
Rare earth-doped phosphor materials have always remained in focus for excellent luminescence properties. Herein we have synthesized Yb3+ and Er3+-doped BaWO4 nanophosphor via facile hydrothermal method with red and green region emissions by 980 nm excitation. Red and green region emissions were observed due to 4F9/2 → 4I15/2 and 2H11/2/4S3/2 → 4I15/2 transitions, respectively, of Er3+, where Yb3+ acts as a sensitizer. The sample characterization was done using X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) techniques. The consequences of different concentrations of activator ion (Er3+) in BaWO4: Yb3+, Er3+ were studied from luminescence perspective in detail. The intensity of overall emission varied with altering the power of excitation that influences the photon transfer pathways. It was found that two-photon processes control both red and green emissions in the upconversion process. Decay behavior for both the emission was investigated. Thus, the tunable photoluminescence property suggests its potential in optoelectronic applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Mahalingam, R. Naccache, F. Vetrone, J.A. Capobianco, Enhancing upconverted white light in Tm3+/Yb33+/Ho3+-doped GdVO4 nanocrystals via incorporation of Li+ ions. Opt. Express. 20, 111–119 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.20.000111
D.R. Kim, S.W. Park, B.K. Moon, S.H. Park, J.H. Jeong, H. Choi, J.H. Kim, The role of Yb3+ concentrations on Er3+ doped SrLaMgTaO6 double perovskite phosphors. RSC Adv. 7, 1464–1470 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA24808J
P. Kumar, B.K. Gupta, New insight into rare-earth doped gadolinium molybdate nanophosphor assisted broad spectral converter from UV to NIR for silicon solar cell. RSC Adv. 5, 24729–24736 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA15383A
T. Li, C.F. Guo, Y.M. Yang, L. Li, N. Zhang, Efficient green up-conversion emission in Yb3+/Ho3+ co-doped CaIn2O4. Acta Mater. 61, 7481–7487 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2013.08.060
O.A. Savchuk, J.J. Carvajal, M.C. Pujol, E.W. Barrera, J. Massons, M. Aguilo, F. Diaz, Ho, Yb:KLu(WO4)2 nanoparticles: A versatile material for multiple thermal sensing purposes by luminescent thermometry. J. Phys. Chem. C 119, 18546–18558 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b03766
P. Kanika, S. Kumar, B.K.G. Singh, A novel approach to synthesis a dual mode luminescent composite pigment for uncloneable high security codes to combat counterfeiting. Chem. A Eur. J. 23, 17144–17151 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201704076
P. Kumar, J. Dwivedi, B.K. Gupta, Highly-luminescent dual mode rare-earth nanorods assisted multi-stage excitable security ink for anti-counterfeiting applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2, 10468–10475 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TC02065K
P. Kumar, S. Singh, B.K. Gupta, Future prospects of luminescent nanomaterials based security ink: From synthesis to anti-counterfeiting applications. Nanoscale 8, 14297–14340 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NR06965C
P. Kumar, K. Nagpal, B.K. Gupta, Unclonable security codes designed from multicolour luminescent lanthanide-doped Y2O3 nanorods for anticounterfeiting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 14301–14308 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b03353
F. Li, L. Li, C. Guo, T. Li, H. Mi, J.H. Jeong, Up-conversion luminescence properties of Yb3+–Ho3+ co-doped CaLa2ZnO5. Ceram. Int. 40, 7363–7366 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.12.080
B. Liu, C. Li, Z. Xie, Z. Hou, Z. Cheng, D. Jin, J. Lin, 808 nm photocontrolled UCL imaging guided chemo/photothermal synergistic therapy with single UCNPs-CuS@PAA nanocomposite. Dalton Trans. 45, 13061–13069 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5DT04857E
Z. Zhang, J. Sheng, M. Zhang, X. Ma, Z. Geng, Z. Wang, Dual-modal imaging and excellent anticancer efficiency of cisplatin and doxorubicin loaded NaGdF4:Yb3+ /Er3+ nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 8, 22216–22225 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA03898H
C. Li, D. Yang, P. Ma, Y. Chen, Y. Wu, Z. Hou, Y. Dai, J. Zhao, C. Sui, J. Lin, Multifunctional upconversion mesoporous silica nanostructures for dual modal imaging and in vivo drug delivery. Small 90, 4150–4159 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201301093
R. Chatterjee, S. Saha, D. Sen, K. Panigrahi, U.K. Ghorai, G.C. Das, K.K. Chattopadhyay, Neutralizing the charge imbalance problem in Eu3+-activated BaAl2O4 nanophosphors: Theoretical insights and experimental validation considering K+ codoping. ACS Omega 3, 788–800 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.7b01525
A. De, A.K. Dey, B. Samanta, U.K. Ghorai, Enhanced red photoluminescence in chain-like SrAl2O4:Eu3+ nanophosphors: utilizing charge compensation by modulating Na+ co-doping concentration. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 8648–8656 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05524-2
H. Wu, J. Yang, X. Wang, S. Gan, L. Li, Solvent directed morphologies and enhanced luminescent properties of BaWO4:Tm3+, Dy3+ for white light emitting diodes. Solid State Sci. 79, 85–92 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2018.02.009
H.L. Li, Z.L. Wang, S.J. Xu, J.H. Hao, Improved performance of spherical BaWO4:Tb3+ phosphors for field-emission displays. J. Electrochem. Soc. 156, J112 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1149/1.3095503
C. He, K. Yang, L. Liu, Z. Si, Preparation and luminescence properties of BaWO4:Yb3+/Tm3+ nano-crystal. J. Rare Earths 31, 790–794 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(12)60359-7
L. Liu, K. Yang, X. Zhang, N. Qi, H. Li, Z. Zuo, Up-conversion luminescence properties of Yb3+ and Ho3+ co-doped Bi3.84W0.16O6.24 powder synthesized by hydrothermal method. J. Rare Earths 30, 1092–1095 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(12)60185-9
J.H. Chung, J.H. Ryu, S.W. Mhin, K.M. Kim, K.B. Shim, Controllable white upconversion luminescence in Ho3+/Tm3+/Yb3+ co-doped CaMoO4. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 3997–4002 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM15332G
W. Gao, H. Zheng, Q. Han, E. He, R. Wang, Unusual upconversion emission from single NaYF4:Yb3+/Ho3+ microrods under NIR excitation. CrystEngComm 16, 6697–6706 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00627E
A. Salah, S.K. El-Mahy, O. El-sayed, I.K. Battisha, Up-conversion behaviors of nano-structure BaTi0.9Sn0.1O3 activated by Er3+/Yb3+ ions. Optik 209, 164571 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164571
K. Janani, S. Ramasubramanian, A.K. Soni, V.K. Rai, P. Thiyagarajan, Luminescence properties of LiYF4:Yb3+, Er3+ phosphors: A study on influence of synthesis temperature and dopant concentration. Optik 169, 147–155 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.05.023
Q. Cheng, J. Sui, W. Cai, Enhanced upconversion emission in Yb3+ and Er3+ codoped NaGdF4 nanocrystals by introducing Li+ ions. Nanoscale 4, 779–784 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C1NR11365H
C.S. Mao, X. Yang, L. Zhao, Simultaneous morphology control and upconversion fluorescence enhancement of NaYF4:Yb, Er crystals through alkali ions doping. Chem. Eng. J. 229, 429–435 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.06.026
X. Chai, J. Li, X. Wang, Y. Li, X. Yao, Color-tunable upconversion photoluminescence and highly performed optical temperature sensing in Er3+/Yb3+ codoped ZnWO4. Opt. Express 24, 22439–22447 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.24.022438
X.N. Chai, J. Li, Y. Zhang, X. Wang, Y. Li, Y. Xi, Bright dual-mode green emission and temperature sensing properties in Er3+/Yb3+ co-doped MgWO4 phosphor. RSC Adv. 6, 64072–64078 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA09656E
B. Samanta, A.K. Dey, P. Bhaumik, S. Manna, A. Halder, D. Jana, K.K. Chattopadhyay, U.K. Ghorai, Controllable white light generation from novel BaWO4:Yb3+/Ho3+/Tm3+ nanophosphor by modulating sensitizer ion concentration. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 1068–1075 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0375-4
A.K. Dey, B. Samanta, P. Bhaumik, S. Manna, A. Halder, T.K. Ghosh, T.K. Parya, U.K. Ghorai, Low-temperature synthesis of thermally stable BaWO4:Yb3+:Ho3+ nanophosphors: Tuning visible emission by controlling activator ion concentration. J. Lumin. 211, 251–257 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2019.03.020
R.D. Shannon, Revised effective ionic radii and systemic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Cryst. A 32, 751–767 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0567739476001551
L. Xu, J. Liu, L. Pei, Y. Xu, Z. Xia, Enhanced up-conversion luminescence and optical temperature sensing in graphitic C3N4 quantum dots grafted with BaWO4:Yb3+, Er3+ phosphors. J. Mater. Chem. C 7, 6112–6119 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TC01351B
N. Dhananjaya, H. Nagabhushana, B.M. Nagabhushana, B. Rudraswamy, Enhanced photoluminescence of Gd2O3:Eu3+ nanophosphors with alkali (M = Li+, Na+, K+) metal ion co-doping Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 86, 8–14 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2011.05.072
B.P. Singh, A.K. Parchur, R.S. Ningthoujam, P.V. Ramakrishna, S. Singh, P. Singh, S.B. Raib, R. Maalej, (2014) Enhanced up-conversion and temperature-sensing behaviour of Er3+ and Yb3+ co-doped Y2Ti2O7 by incorporation of Li+ ions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 22665–22676 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP02949F
R. Chakraborty, A. Maiti, U.K. Ghorai, A.J. Pal, Defect passivation of Mn2+-doped CsPbCl3 perovskite nanocrystals as probed by scanning tunneling spectroscopy: Toward boosting emission efficiencies. ACS Appl. Nano Mater (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.1c01623
Acknowledgements
UKG acknowledges the Teachers Associateship for Research Excellence (TARE) fellowship and research grant (TAR/2018/000763) of SERB, Govt. of India and thanks the TARE project mentor Prof. A. J. Pal, IACS-Kolkata. UKG acknowledges the central DST-FIST program (SR/FST/College-287/2015) for financial support. UKG thanks the DBT Star College Scheme (BT/HRD/11/036/2019) for funding. UKG also acknowledges Science & Technology and Biotechnology Department, Govt. of West Bengal for providing the financial support [199 (Sanc.)/ST/P/S&T/6G-12/2018]. SD acknowledges the SERB for providing financial support (EEQ/2019/000401). SP gratefully thank SERB, Govt. of India for providing the junior research fellowship (JRF). SD and UKG wish to thank Science & Technology and Biotechnology Department, Govt. of West Bengal for providing the financial support (ST/P/S&T/6G-6/2019). AA thanks Science & Technology and Biotechnology Department, Govt. of West Bengal for JRF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AD, AKD, BS, and SS synthesized the phosphors and performed the XRD and FTIR characterization. AD, AKD, SP, and AA performed the photoluminescence study. SP and AA analyzed the XPS and HRTEM results. All authors contributed to write the manuscript. SD and UKG supervised the project.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Human and animal consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De, A., Dey, A.K., Samanta, B. et al. Upconversion luminescence and time decay study of Yb–Er-doped BaWO4 nanophosphor. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 9641–9649 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07607-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07607-6