Abstract
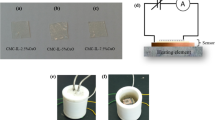
The steadily increasing concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) gas in the atmosphere is a significant environmental problem in modern society. Henceforth, there is triggering interest in the new technological solutions for CO2 monitoring. This work reports the fabrication of a novel, low cost, chemiresistive carbon dioxide sensor based on the PVA/[EMIM][SCN] based ionogel membrane. Here, the lightweight transparent ionogel membrane with enhanced ionic conductivity is acted as the electrically conductive region of the sensor. The response rate of the CO2 sensor was monitored in terms of direct as well as alternating current resistance using a high-precision multimeter and an impedance spectroscopy, respectively. The CO2 desorption kinetics were also studied to check the reliability of the sensor using the conductometric approach. The selectivity of the sensor for CO2 gas was well evidently quantified by comparing the response rate of the sensor with both CO2 and N2 gases. The optical microscopic images were periodically taken before and after CO2 exposure in conjunction with the conductivity data revealed the physisorption mechanism of the sensor. The upshots presented herein will promote the development of an organic CO2 gas sensor, which will be worthwhile for numerous industrial and practical applications and for air quality control in the future.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. M. Organization, Wmo Greenhouse Gas Bulletin (2017).
M. A. Raza, A. Habib, Z. Kanwal, S. S. Hussain, M. J. Iqbal, M. Saleem, S. Riaz, and S. Naseem, 2018, (2018).
T. Li, Y. Wu, J. Huang, S. Zhang, Sensors Actuators B. Chem. 243, 566 (2017)
X. Wang, H. Qin, L. Sun, J. Hu, Sensors Actuators B. Chem. 188, 965 (2013)
(n.d.).
M. Honda, Y. Takei, K. Ishizu, H. Imamoto, T. Itoh, R. Maeda, K. Matsumoto, I. Shimoyama, IEEE 98, 4 (2012)
D. Wei, A. Ivaska, Anal. Chim. Acta 607, 126 (2008)
M. Watanabe, M.L. Thomas, S. Zhang, K. Ueno, T. Yasuda, K. Dokko, Chem. Rev. 117, 7190 (2017)
H. Ohno, Electrochemical Aspects of Ionic Liquids (n.d.).
Y. Liu, R. Zhao, M. Ghaffari, J. Lin, S. Liu, H. Cebeci, R. Guzmán, D. Villoria, R. Montazami, D. Wang, B.L. Wardle, J.R. Heflin, Q.M. Zhang, Sensors Actuators A. Phys. 181, 70 (2012)
Z. Dai, R.D. Noble, D.L. Gin, X. Zhang, L. Deng, J. Memb. Sci. 497, 1 (2016)
K. Behera, S. Pandey, A. Kadyan, S. Pandey, 30487 (2015).
P.S.E.V.E. Visser, A. 35487 Department of chemistry and center for green manufacturing, The University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, M. by A. E. Visser, JRDRAKLDDN James H. Davis, in Ion. Liq. (2002), pp. 69–87.
O. Oter, K. Ertekin, D. Topkaya, S. Alp, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 386, 1225 (2006)
O. Oter, K. Ertekin, D. Topkaya, S. Alp, Sensors Actuators B Chem. 117, 295 (2006)
O. Oter, K. Ertekin, S. Derinkuyu, Talanta 76, 557 (2008)
R.N. Dansby-Sparks, J. Jin, S.J. Mechery, U. Sampathkumaran, T.W. Owen, B.D. Yu, K. Goswami, K. Hong, J. Grant, Z.L. Xue, Anal. Chem. 82, 593 (2010)
S. Aydogdu, K. Ertekin, A. Suslu, M. Ozdemir, E. Celik, U. Cocen, J. Fluoresc. 21, 607 (2011)
Y. Liu, Y. Tang, N.N. Barashkov, I.S. Irgibaeva, J.W.Y. Lam, R. Hu, D. Birimzhanova, Y. Yu, B.Z. Tang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 13951 (2010)
S.M. Borisov, M.C. Waldhier, I. Klimant, O.S. Wolfbeis, Chem. Mater. 19, 6187 (2007)
K. Ishizu, Y. Takei, M. Honda, K. Noda, A. Inaba, T. Itoh, R. Maeda, K. Matsumoto, I. Shimoyama, Transducers 978, 1633 (2013)
B.A. Rosen, J.L. Haan, P. Mukherjee, B. Braunschweig, W. Zhu, A. Salehi-Khojin, D.D. Dlott, R.I. Masel, J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 15307 (2012)
C. Xiao, X. Zeng, J. Electrochem. Soc. 160, H749 (2013)
S.K.P. Hussan, M.S. Thayyil, V.K. Rajan, A. Antony, J. Phys. Chem. B 123, 6618 (2019)
K.P. Safna Hussan, T. Mohamed Shahin, S.K. Deshpande, T.V. Jinitha, J. Kolte, Solid State Ion. 310, 166 (2017)
K.P. Safna Hussan, T. Mohamed Shahin, T.V. Jinitha, K. Jayant, J. Mol. Liq. 274, 402 (2019)
K.P. Safna Hussan, M.S. Thayyil, T.V. Jinitha, J. Kolte, J. Mol. Liq. 274, 402 (2019)
S. Naduparambath, M. P. Sreejith, T. V Jinitha, V. Shaniba, K. B. Aparna, E. Purushothaman, (2017).
C. Chiang, K. Tsai, Y. Lee, H. Lin, Y. Yang, C. Shih, C. Lin, H. Jeng, Y. Weng, Y. Cheng, K. Ho, C. Dai, Microelectron. Eng. 111, 409 (2013)
P.M. Junais, Mater. Res. Express 6, 045914 (2019)
R. Cheruku, D. S. Bhaskaram, and G. Govindaraj, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 0, 0 (n.d.).
R.R. Nigmatullin, Y.E. Ryabov, Phys. Solid State 39, 87 (1997)
T.V. Jinitha, S.H.K.P.N. Subair, V. Shaniba, A.K. Balan, E. Purushothaman, RSC Adv. 8, 34388 (2018)
G. Giannoukos, M. Min, Int. J. Circuits, Syst. Signal Process. 8, 600 (2014).
L. Kumar, I. Rawal, A. Kaur, S. Annapoorni, Sensors Actuators B Chem. 240, 408 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussan, K.P.S., Moidu, H.H., Thayyil, M.S. et al. Physisorption mechanism in a novel ionogel membrane based CO2 gas sensor. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 25164–25174 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06973-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06973-5