Abstract
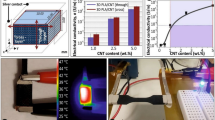
Three-dimensional nitrogen-doped graphene aerogels (3D N-GAs) were prepared by ultrasonic stripping, hydrothermal reduction and freeze drying. Those N-GAs exhibited high-specific surface area, high nitrogen doping amount, and 3D porous network structure. Soft electro-active ionic polymer actuators were developed for the first time using this 3D N-GA soft electrode. The developed soft actuator exhibited large peak-to-peak displacement of 11.8 mm (3 V and 0.1 Hz) and high air working durability for 93.8% after 6 h cycles. These successful demonstrations elucidated the wide potential of 3D N-GA soft actuators for the next-generation soft robotic devices.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Chen, Q.B. Pei, Electronic muscles and skins: a review of soft sensors and actuators. Chem. Rev. 117, 11239–11268 (2017)
S. Umrao, R. Tabassian, J.W. Kim, V.H. Nguyen, Q.T. Zhou et al., Mxene artificial muscles based on ionically cross-linked Ti3C2Tx electrode for kinetic soft robotics. Sci. Robot. 4, 17797 (2019)
L.R. Kong, W. Chen, Carbon nanotube and graphene-based bioinspired electrochemical actuators. Adv. Mater. 26, 1025–1043 (2014)
Y. Wang, C. Sun, E. Zhou, J. Su, Deformation mechanisms of electrostrictive graft elastomer. Smart Mater. Struct. 13, 1407 (2004)
Q.M. Zhang, V. Bharti, X. Zhao, Giant electrostriction relaxorferroelectric behavior electron-irradiated poly (vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene) copolymer. Science 280, 2101–2104 (1998)
L.J. Romasanta, M.A. Lopez-Manchado, R. Verdejo, Increasing the performance of dielectric elastomer actuators: a review from the materials perspective. Prog. Polym. Sci. 51, 188–211 (2015)
Y. Osada, H. Okuzaki, H. Hori, A polymer gel with electrically driven motility. Nature 355, 242–244 (1992)
T.F. Otero, J.G. Martinez, Physical and chemical awareness from sensing polymeric artificial muscles. Experiments and modeling. Prog. Polym. Sci. 44, 62–78 (2015)
C. Jo, D. Pugal, I.K. Oh, K.J. Kim, K. Asaka, Recent advances in ionic polymer-metal composite actuators and their modeling and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 38, 1037–1066 (2013)
J.C. Dias, D.M. Correia, C.M. Costa, C. Ribeiro, A. Maceiras, J.L. Vilas et al., Improved response of ionic liquid-based bending actuators by tailored interaction with the polar fluorinated polymer matrix. Electrochim. Acta 296, 598–607 (2019)
A. Punning, K.J. Kim, V. Palmre, F. Vidal, C. Plesse, N. Festin et al., Ionic electroactive polymer artificial muscles in space applications. Sci. Rep. 4, 6913 (2014)
N. Terasawa, K. Asaka, High-performance graphene oxide/vapor-grown carbon fiber composite polymer actuator. Sens. Actuators B 255, 2829–2837 (2018)
M. Kotal, J. Kim, K.J. Kim, I.K. Oh, Sulfur and nitrogen Co-doped graphene electrodes for high-performance ionic artificial muscles. Adv. Mater. 28, 1610–1615 (2016)
C. Lu, Y. Yang, J. Wang, R.P. Fu, X.X. Zhao, L. Zhao et al., High-performance graphdiyne-based electrochemical actuators. Nat. Commun. 9, 752 (2018)
Q.S. He, M. Yu, X. Yang, K.J. Kim, Z.D. Dai, An ionic electro-active actuator made with graphene film electrode, chitosan and ionic liquid. Smart Mater. Struct. 24, 065026 (2015)
D.J. Guo, Y.B. Han, J.J. Huang, E.C. Meng, L. Ma, H. Zhang et al., Hydrophilic poly(vinylidene fluoride) film with enhanced inner channels for both water- and ionic liquid-driven ion-exchange polymer metal composite actuators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 2386–2397 (2019)
H.S. Wang, J. Cho, D.S. Song, J.H. Jang, J.Y. Jho, J.H. Park, High-performance electroactive polymer actuators based on ultra-thick ionic polymer-metal composites with nanodispersed metal electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 21998–22005 (2017)
K. Bian, H. Liu, G. Tai, K.J. Zhu, K. Xiong, Enhanced actuation response of Nafion-based ionic polymer metal composites by doping BaTiO3 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 12377–12384 (2016)
L.F. Chang, H.L. Chen, Z.C. Zhu, B. Li, Manufacturing process and electrode properties of palladium-electroded IPMC. Smart Mater. Struct. 21, 065018 (2012)
G. Wu, X.J. Wu, Y.J. Xu, H.Y. Cheng, J.K. Meng, Q. Yu et al., High-performance hierarchical black-phosphorous-based soft electrochemical actuators in bioinspired applications. Adv. Mater. 31, 1806492 (2019)
F.Z. Lu, K. Xiang, Y.N. Wang, T. Chen, Electrochemical actuators based on nitrogen-doped carbons derived from zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Mater. Design 187, 108405 (2020)
M. Shahinpoor, K.J. Kim, Ionic polymer-metal composites: I. Fundamentals. Smart Mater. Struct. 10, 819–833 (2001)
J. Kim, J.H. Jeon, H.J. Kim, H. Lim, I.K. Oh, Durable and water-floatable ionic polymer actuator with hydrophobic and asymmetrically laser-scribed reduced graphene oxide paper electrodes. ACS Nano 8, 2986–2997 (2014)
L.H. Lu, J.H. Liu, Y. Hu, Y.W. Zhang, H. Randriamahazaka, W. Chen, Highly stable air working bimorph actuator based on a graphene nanosheet/carbon nanotube hybrid electrode. Adv. Mater. 24, 4317–4321 (2012)
M. Kotal, J. Kim, R. Tabassian, S. Roy, V.H. Nguyen, N. Koratkar et al., Highly bendable ionic soft actuator based on nitrogen-enriched 3D hetero-nanostructure electrode. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1802464 (2018)
R. Tabassian, J. Kim, V.H. Nguyen, M. Kotal, I.K. Oh, Functionally antagonistic hybrid electrode with hollow tubular graphene mesh and nitrogen-doped crumpled graphene for high-performance ionic soft actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1705714 (2018)
Y.F. Ma, Y.S. Chen, Three-dimensional graphene networks: synthesis, properties and applications. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2, 40–53 (2015)
M.A. Worsley, P.J. Pauzauskie, T.Y. Olson et al., Synthesis of graphene aerogel with high electrical conductivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 14067–14069 (2010)
G. Wu, Y. Hu, Y. Liu, J.J. Zhao, X.L. Chen, V. Whoehling et al., Graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet electrode-based high-performance ionic actuator. Nat. Commun. 6, 7258 (2015)
X.J. Yan, X.Y. Wang, Y.Z. Dai, Y.Y. He, Z.B. Cai, Y. Wang et al., In situ self-assembly of SiO2-coating Co3O4/graphene aerogel and its enhanced electrochemical performance for supercapacitors. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 17218–17226 (2019)
X.Y. Zhu, C. Yang, P.W. Wu, Z.Q. Ma, Y.Y. Shang, G.Z. Bai et al., Precise control of versatile microstructure and properties of graphene aerogel via freezing manipulation. Nanoscale 12, 4882–4894 (2020)
M.A. Riaz, P. Hadi, I.H. Abidi, A. Tyagi, X.W. Ou, Z.T. Luo, Recyclable 3D graphene aerogel with bimodal pore structure for ultrafast and selective oil sorption from water. RSC Adv. 7, 29722–29731 (2017)
X. Han, M. Kong, M.J. Li, X.K. Li, W.Q. Yang, C.X. Li, Nacre-based carbon nanomeshes for a soft ionic actuator with large and rapid deformation. J. Mater. Chem. C 8, 1634–1641 (2020)
L.H. Lu, J.H. Liu, Y. Hu, Y.W. Zhang, W. Chen, Graphene-stabilized silver nanoparticle electrochemical electrode for actuator design. Adv. Mater. 25, 1270–1274 (2013)
N. Terasawa, K. Asaka, Superior performance of PEDOT:poly(4-styrenesulfonate)/vapor-grown carbon fibre/ionic liquid actuators exhibiting synergistic effects. Sens. Actuators B 248, 273–279 (2017)
D.M. Correia, J.C. Barbosa, C.M. Costa, P.M. Reis, J.M.S.S. Esperanca, V.D.Z. Bermudez et al., Ionic liquid cation size-dependent electromechanical response of ionic liquid/poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based soft actuators. J. Phys. Chem. C 123, 12744–12752 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51603102), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2018M630554).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, K., Chen, T. & Wang, Y. The highly stable air-working electro-active ionic polymer actuator based on nitrogen-doped graphene aerogel flexible electrode. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 21395–21405 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06643-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06643-6