Abstract
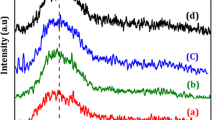
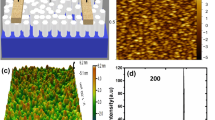
Repercussion of Swift Heavy Ion (SHI) irradiation on nickel-based nanorods of Metal-Organic Framework (NRs-Ni3HHTP2 MOF) for enhancement in the properties of ChemFET-based gas sensor has been investigated. Nanorods of Ni3HHTP2-MOF were synthesized by chemical method and exposed to C12+ ions irradiation with fluence 1 × 1011 ion/cm2 and 1 × 1012 ion/cm2. The structural, spectroscopic, morphological, and optical characterizations were carried out using x-ray diffraction (XRD), fourier transfer infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), atomic force microscopy (AFM) with scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and UV-visible spectroscopy, respectively, whereas the bandgap was calculated from the Tauc’s plot. The synthesized nanorods of Ni3HHTP2 MOF were drop-casted on gold-coated microelectrodes on silicon/silicon dioxide (Si/SiO2) substrate, where silicon layer serves as a gate and gold microelectrodes on silicon/silicon dioxide (Si/SiO2) substrate as a source and drain. The transmutations in material properties due to SHI irradiations were serviceable for enhancing field-effect transistor (transfer and output) properties and sensing properties. After Swift Heavy Ion (SHI) irradiation (1 × 1011 ion/cm2), it shows excellent response and recovery time i.e., 20 and 23 s, respectively, for 1 ppm SO2 concentration at room temp (RT) with a lower detection limit of 0.625 ppm.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.A. Bodkhe et al., Field effect transistor based on proton conductive metal organic framework (CuBTC). J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 52(33), 335105 (2019)
D. Wang, D. Jana, Y. Zhao, Metal–Organic Framework Derived Nanozymes in Biomedicine. Acc. Chem. Res. 53(7), 1389–1400 (2020)
G.A. Bodkhe et al., Selective and sensitive detection of lead Pb(II) ions: Au/SWNT nanocomposite-embedded MOF-199. J. Mater. Sci. 56(1), 474–487 (2020)
A. Rashti et al., Tuning MOF-derived Co3O4/NiCo2O4 nanostructures for high-performance energy storage. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 4(2), 1537–1547 (2021)
N. Ingle et al., Sulfur dioxide (SO2) detection using composite of Nickel benzene carboxylic (Ni3BTC2) and OH-functionalized single walled carbon nanotubes (OH-SWNTs). Front. Mater. 7, 93 (2020)
M. Dinari, F. Jamshidian, Preparation of MIL-101-NH2 MOF/triazine based covalent organic framework hybrid and its application in acid blue 9 removals. Polymer 215, 123383 (2021)
M. Mahadik et al., EDTA modified PANI/GO composite based detection of Hg(II) ions. Front. Mater. 7, 81 (2020)
H. Nazemi et al., Advanced micro-and nano-gas sensor technology: a review. Sensors 19(6), 1285 (2019)
A. Nowoświat, L. Dulak, Impact of cement dust pollution on the surface of sound-absorbing panels on their acoustic properties. Materials 13(6), 1422 (2020)
P.W. Sayyad et al., Chemiresistive SO2 sensor: graphene oxide (GO) anchored poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): poly (4styrenesulfonate)(PEDOT: PSS). Appl. Phys. A 126(11), 1–8 (2020)
Y. Wu et al., The high-resolution estimation of sulfur dioxide (SO2) concentration, health effect and monetary costs in Beijing. Chemosphere 241, 125031 (2020)
A. Yang et al., Single ultrathin WO3 nanowire as a superior gas sensor for SO2 and H2S: Selective adsorption and distinct IV response. Mater. Chem. Phys. 240, 122165 (2020)
Q. Zhou et al., High sensitive and low-concentration sulfur dioxide (SO2) gas sensor application of heterostructure NiO-ZnO nanodisks. Sens. Actuators B 298, 126870 (2019)
V. Kumar, D.R. Roy, Single-layer stanane as potential gas sensor for NO2, SO2, CO2 and NH3 under DFT investigation. Physica E 110, 100–106 (2019)
N. Ingle et al., A chemiresistive gas sensor for sensitive detection of SO 2 employing Ni-MOF modified–OH-SWNTs and–OH-MWNTs. Appl. Phys. A 127(2), 1–10 (2021)
M. Tchalala et al., Fluorinated MOF platform for selective removal and sensing of SO2 from flue gas and air. Nat. Commun. 10(1), 1–10 (2019)
A.S. El-Said et al., Tuning tailored single-walled carbon nanotubes by highly energetic heavy ions. Phys. Rev. Appl. 13(4), 044073 (2020)
H. Gupta et al., Defect-induced photoluminescence from gallium-doped zinc oxide thin films: influence of doping and energetic ion irradiation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21(27), 15019–15029 (2019)
P. Esquinazi et al., Induced magnetic ordering by proton irradiation in graphite. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91(22), 227201 (2003)
A. Krasheninnikov, K. Nordlund, Ion and electron irradiation-induced effects in nanostructured materials. J. Appl. Phys. 107(7), 3 (2010)
I.I.I. Wood et al., Perspectives on the relationship between materials chemistry and roll-to-roll electrode manufacturing for high-energy lithium-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 29, 254–265 (2020)
S. Raghuvanshi et al., Dual control on structure and magnetic properties of Mg ferrite: role of swift heavy ion irradiation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 471, 521–528 (2019)
A. Ratan et al., Enhanced electrical properties of few layers MoS2-PVA nanocomposite film via homogeneous dispersion and annealing effect induced by 80 MeV Carbon6 + swift heavy ion irradiation. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 108, 104877 (2020)
M. Karlušić et al., Nanopatterning surfaces by grazing incidence swift heavy ion irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 541, 148467 (2021)
R. Singh et al., Tuning of defects induced visible photoluminescence by swift heavy ion irradiation and thermal annealing in zinc oxide films. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 183, 109400 (2021)
J. Zeng et al., Graphene electrical properties modulated by swift heavy ion irradiation. Carbon 154, 244–253 (2019)
N. Manikanthababu et al., Swift heavy ion irradiation-induced modifications in the electrical and surface properties of β-Ga2O3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 117(14), 142105 (2020)
H.K. Patil et al., Reinforcement of polyaniline and poly-(o-toluidine) with SWNTs and tuning of their physicochemical properties by heavy ion beams. Appl. Phys. A 124(7), 491 (2018)
H.K. Patil, et al., Spectroscopic investigations upon 100 MeV oxygen ions irradiation on polyaniline and poly-o-toluidine. In: AIP Conference Proceedings. 2018. AIP Publishing LLC
O. Ochedowski et al., Radiation hardness of graphene and MoS2 field effect devices against swift heavy ion irradiation. J. Appl. Phys. 113(21), 214306 (2013)
T. Bolse, H. Paulus, W. Bolse, Swift heavy ion induced dewetting of metal oxide thin films on silicon. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 245(1), 264–268 (2006)
R. Dutta, A. Kumar, 100 MeV O7+ ion irradiation induced electrochemical enhancement in NiBTC metal-organic framework based composite polymer electrolytes incorporated with ionic liquid. Mater. Res. Exp. 6(8), 085305 (2019)
P.W. Sayyad et al., Tuning the properties of Fe-BTC metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) by swift heavy ion (SHI) irradiation. Radiat Effects Defects Solids (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/10420150.2020.1825958
N. Ingle et al., ChemFET Sensor: nanorods of nickel-substituted metal–organic framework for detection of SO2. Appl. Phys. A 126(9), 1–9 (2020)
T.D. Malouff et al., Carbon ion therapy: a modern review of an emerging technology. Front. Oncol. 10, 82 (2020)
K. Datta et al., Organic field-effect transistors: predictive control on performance parameters. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 46(49), 495110 (2013)
M. Ko et al., Employing conductive metal–organic frameworks for voltammetric detection of neurochemicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142(27), 11717–11733 (2020)
M.K. Smith et al., Direct self-assembly of conductive nanorods of metal–organic frameworks into chemiresistive devices on shrinkable polymer films. Chem. Mater. 28(15), 5264–5268 (2016)
M.K. Smith, K.A. Mirica, Self-organized frameworks on textiles (SOFT): conductive fabrics for simultaneous sensing, capture, and filtration of gases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139(46), 16759–16767 (2017)
J. Ram et al., Ion beam engineering in WO3-PEDOT: PSS hybrid nanocomposite thin films for gas sensing measurement at room temperature. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 119, 108000 (2020)
H. Xu et al., Ag/Ag2S nanoparticle-induced sensitization of recovered sulfur-doped SnO2 nanoparticles for SO2 detection. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 3(8), 8075–8087 (2020)
R.U. Mene, M.P. Mahabole, R.S. Khairnar, Surface modified hydroxyapatite thick films for CO2 gas sensing application: effect of swift heavy ion irradiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 80(6), 682–687 (2011)
H. Xu et al., Ag/Ag2S nanoparticle-induced sensitization of recovered sulfur-doped SnO2 nanoparticles for SO2 detection. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 8, 8075–8087 (2020)
Y. Liu et al., An integrated micro-chip with Ru/Al2O3/ZnO as sensing material for SO2 detection. Sens. Actuators B 262, 26–34 (2018)
L. Liu, S. Liu, Oxygen vacancies as an efficient strategy for promotion of low concentration SO2 gas sensing: the case of Au-modified SnO2. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6(10), 13427–13434 (2018)
S.K. Lim et al., Preparation of ZnO nanorods by microemulsion synthesis and their application as a CO gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B 160(1), 94–98 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Inter-University Accelerator Center (IUAC), New Delhi (UFR-62320 & UFR-62321) for material science beamline with SEM facilities and financial support and DST-SERB (Sanction No. EEQ/2017/000645), UGC-DAE CSR (RRCAT), Indore (Project No. CSR-IC-BL66/CSR-183/2016-17/847), UGC-SAP programme (F.530/16/DRS-1/2016 (SAP-II), dt. 16-04-2016), DST-FIST (Project No. No. SR/FST/PSI-210/2016(C) dtd. 16/12/2016), Rashtria Uchachatar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA), Government of Maharashtra for providing characterization facilities. The authors also thank Dr. Saif A. Khan, IUAC, New Delhi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ingle, N.N., Shirsat, S., Sayyad, P. et al. Influence of swift heavy ion irradiation on sensing properties of nickel-(NRs-Ni3HHTP2) metal-organic framework. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 18657–18668 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06353-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06353-z