Abstract
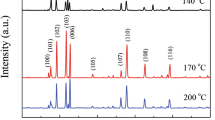
Ethanol is one of the volatile organic compounds as well as organic pollutants that is essentially to be monitored using high response sensors. Semiconducting metal oxide nanostructures can be the potential sensor material for high-performance ethanol sensing application. Herein, we present the fabrication and characterization of highly sensitive and selective ethanol gas sensor based on flower-shaped CuO composed of thin nanoplates synthesized by facile hydrothermal process. The prepared flower-shaped CuO was examined by various techniques viz FESEM, XRD, EDS, elemental mapping, HRTEM, SAED, UV-visible spectroscopy, FTIR spectroscopy, and Raman spectroscopy, which confirmed the high-density growth, monoclinic crystal structure, and optical band gap of ~2.5 eV. The fabricated resistive sensor device based on flower-shaped CuO, at optimum experimental conditions, i.e., 250 °C, 100 ppm ethanol concentration, exhibited a high sensing response of 241%, while, at 10 ppm of ethanol concentration, the response was observed to be 5%. The transient responses as well as the stability of the sensor were analyzed and reported here. The selectivity of CuO sensor device was studied for NO2, CO2, CO, and CH4 gases and remarkably it was seen that the developed gas sensor devices demonstrated outstanding selectivity toward ethanol gas. Finally, the gas response mechanism of the fabricated resistive ethanol gas sensor was explained on the basis of the ionosorption model.











Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
03 July 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06428-x
References
R. Kumar, O. Al-Dossary, G. Kumar, A. Umar, Zinc oxide nanostructures for NO2 gas sensor applications: a review. Nano Micro Lett. 7, 97–120 (2015)
R. Feng, Y. Xia, Synthesis of hierarchical hetero-junction composite and gas detection performance in asphalt road. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 15, 516–522 (2020)
A. Umar, M. Alduraibi, O. Al-Dossary, NOx gas sensing properties of Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Sci. Adv. Mater. 12, 908–914 (2020)
L. Qi, Y. Pan, A novel sensor apply in detection of indoor Air. Sci. Adv. Mater. 12, 282–288 (2020)
Q. Wei, L. Liu, C. Wu, A novel net like structure sensor and gas detection performance in tunnel construction. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 15, 54–58 (2020)
A. Umar, M. Alduraibi, O. Al-Dossary, Development of ethanol gas sensor using α-Fe2O3 nanocubes synthesized by hydrothermal process. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 15, 59–64 (2020)
J. Forsyth, S. Hull, The effect of hydrostatic pressure on the ambient temperature structure of CuO. J. Phys 3(28), 5257 (1991)
C.H. Kuo, C.H. Chen, M.H. Huang, Seed-mediated synthesis of monodispersed Cu2O nanocubes with five different size ranges from 40 to 420 nm. Adv. Funct. Mater. 17(18), 3773–3780 (2007)
X. Zhang, G. Zhang, S. Wang, S. Li, S. Jiao, Porous CuO microsphere architectures as high-performance cathode materials for aluminum-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 6(7), 3084–3090 (2018)
A. Musa, T. Akomolafe, M. Carter, Production of cuprous oxide, a solar cell material, by thermal oxidation and a study of its physical and electrical properties. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 51(3–4), 305–316 (1998)
A. Rydosz, The use of copper oxide thin films in gas-sensing applications. Coatings 8(12), 425 (2018)
N. Baghdadi, A. Saeed, A.R. Ansari, A.H. Hammad, A. Afify, N. Salah, Controlled nanostructuring via aluminum doping in CuO nanosheets for enhanced thermoelectric performance. J. Alloys Compds. 869, 159370 (2021)
H. Wang, J.Z. Xu, J.J. Zhu, H.Y. Chen, Preparation of CuO nanoparticles by microwave irradiation. J. Cryst. Growth 244(1), 88–94 (2002)
C. Xu, Y. Liu, G. Xu, G. Wang, Preparation and characterization of CuO nanorods by thermal decomposition of CuC2O4 precursor. Mater. Res. Bull. 37(14), 2365–2372 (2002)
W. Zhu, W. Zhu, W. Huangfu, J. Chi, L. Xu, A Novel CuO flower like nanomaterials and its fault detection performance in power cable. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 15, 1146–1150 (2020)
B.J. Hansen, N. Kouklin, G. Lu, I.K. Lin, J. Chen, X. Zhang, Transport, analyte detection, and opto-electronic response of p-type CuO nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. C 114(6), 2440–2447 (2010)
F. Zhang, A. Zhu, Y. Luo, Y. Tian, J. Yang, Y. Qin, CuO nanoplates for sensitive and selective determination of H2S with high recovery ability. J. Phys. Chem. C 114(45), 19214–19219 (2010)
X. Gou, G. Wang, J. Yang, J. Park, D. Wexler, Chemical synthesis, characterisation and gas sensing performance of copper oxide nanoribbons. J. Mater. Chem. 18(9), 965–969 (2008)
Y. Zhang, X. He, J. Li, H. Zhang, X. Gao, Gas-sensing properties of hollow and hierarchical copper oxide microspheres. Sens. Actuators B 128(1), 293–298 (2007)
P. Patil, U.T. Nakate, Y.T. Nakate, R.C. Ambare, Acetaldehyde sensing properties using ultrafine CuO nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 101, 76–81 (2019)
C. Yang, F. Xiao, J. Wang, X. Su, 3D flower- and 2D sheet-like CuO nanostructures: microwave-assisted synthesis and application in gas sensors. Sens. Actuat. B 207, 177 (2015)
J. Huang, Y. Dai, C. Gu, Y. Sun, J. Liu, Preparation of porous flower-like CuO/ZnO nanostructures and analysis of their gas-sensing property. J. Alloys Compds. 575, 115 (2013)
M. Zhou, X. Chen, L. Zhang, W. Zeng, High performance novel gas sensor device for site environmental protection using Ti0.5Sn0.5O2 nanomaterials. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 15, 1423–1428 (2020)
H.R. Kim, A. Haensch, I.D. Kim, N. Barsan, U. Weimar, J.H. Lee, The role of NiO doping in reducing the impact of humidity on the performance of SnO2-based gas sensors: synthesis strategies, and phenomenological and spectroscopic studies. Adv. Funct. Mater. 21(23), 4456–4463 (2011)
H.-R. Kim, K.I. Choi, K.M. Kim, I.D. Kim, G. Cao, J.H. Lee, Ultra-fast responding and recovering C2H5OH sensors using SnO2 hollow spheres prepared and activated by Ni templates. Chem. Commun. 46(28), 5061–5063 (2010)
M. Hübner, C.E. Simion, A.T. Stănoiu, S. Pokhrel, N. Bârsan, U. Weimar, Influence of humidity on CO sensing with p-type CuO thick film gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B 153(2), 347–353 (2011)
A. Umar, H.Y. Ammar, R. Kumar, A.A. Ibrahim, M.S. AlAssiri, Square disks-based crossed architectures of SnO2 for ethanol gas sensing applications- an experimental and theoretical investigation. Sens. Actuators B 304, 127 (2020)
G. Korotcenkov, Metal oxides for solid-state gas sensors: what determines our choice? Mater. Sci. Eng. B 139(1), 1–23 (2007)
A.M. Azad, S.A. Akbar, S.G. Mhaisalkar, L.D. Birkefeld, K.S. Goto, Solid state gas sensors: a review. J. Electrochem. Soc. 139, 3690 (1997)
M.J. Madou, S.R. Morrison, Chemical Sensing with Solid State Devices (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2012).
I. Jimenez, J. Arbiol, G. Dezanneau, A. Cornet, J.R. Morante, Crystalline structure, defects and gas sensor response to NO2 and H2S of tungsten trioxide nanopowders. Sens. Actuators B 93(1–3), 475–485 (2003)
U.T. Nakate, R. Ahmad, P. Patil, Y.T. Yu, Y.-B. Hahn, Ultra thin NiO nanoplates for high performance hydrogen gas sensor device. Appl. Surf. Sci. 506, 144971 (2020)
S.P. Choudhury, N. Kumari, A. Bhattacharjee, Enhanced surface activity of SnO2 thin film verified by LM algorithm. Superlattices Microstruct. 92, 24–36 (2016)
S.H. Kim, A. Umar, S.-W. Hwang, Rose-like CuO nanostructures for highly sensitive glucose chemical sensor application. Ceram. Int. 41(8), 9468–9475 (2015)
A. Umar, J.H. Lee, R. Kumar, O. Al-Dossary, A.A. Ibrahim, S. Baskoutas, Development of highly sensitive and selective ethanol sensor based on lance-shaped CuO nanostructures. Mater. Des. 105, 16–24 (2016)
L. Shi, C. Fan, X. Fu, S. Yu, G. Qian, Z. Wang, Carbonate-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of porous hierarchical Co3O4/CuO composites as high capacity anodes for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 197, 23–31 (2016)
M. Rokhmat, E. Wibowo, Sutisna, Khairurrijal, M. Abdullah, Performance improvement of TiO2/CuO solar cell by growing copper particle using fix current electroplating method. Procedia Eng. 170, 72–77 (2017)
K.Y. Hwa, P. Karuppaiah, N.S.K. Gowthaman, V. Balakumar, S. Shankar, H.N. Lim, Ultrasonic synthesis of CuO nanoflakes: a robust electrochemical scaffold for the sensitive detection of phenolic hazard in water and pharmaceutical samples. Ultrasonics Sonochem. 58, 1046 (2019)
P.K. Raul, S. Senapati, A.K. Sahoo, I.M. Umlong, R.R. Devi, A.J. Thakur, V. Veer, CuO nanorods: a potential and efficient adsorbent in water purification. RSC Adv. 4(76), 40580–40587 (2014)
K.R. Reddy, Green synthesis, morphological and optical studies of CuO nanoparticles. J. Mol Struct 1150, 553–557 (2017)
C. Yang, X. Su, F. Xiao, J. Jian, J. Wang, Gas sensing properties of CuO nanorods synthesized by a microwave-assisted hydrothermal method. Sens. Actuators B 158(1), 299–303 (2011)
C. Han, X. Chen, D. Liu, P. Zhou, S. Zhao, H. Bi, D. Meng, D. Wei, Y. Shen, Fabrication of shrub-like CuO porous films by a top-down method for high-performance ethanol gas sensor. Vacuum 157, 332–339 (2018)
H. Gong, J.Q. Hu, J.H. Wang, C.H. Ong, F.R. Zhu, Nano-crystalline Cu-doped ZnO thin film gas sensor for CO. Sens. Actuators B 115(1), 247–251 (2006)
K. Arshak, I. Gaidan, Development of a novel gas sensor based on oxide thick films. Mater. Sci. Eng B 118(1–3), 44–49 (2005)
C. Prajapati, S. Pandey, P. Sahay, Sensing of LPG with nanostructured zinc oxide thin films grown by spray pyrolysis technique. Physica B 406(13), 2684–2688 (2011)
A. Gurlo, Interplay between O2 and SnO2: oxygen ionosorption and spectroscopic evidence for adsorbed oxygen. ChemPhysChem 7(10), 2041–2052 (2006)
T. Jinkawa, G. Sakai, J. Tamaki, N. Miura, N. Yamazoe, Relationship between ethanol gas sensitivity and surface catalytic property of tin oxide sensors modified with acidic or basic oxides. J. Mol. Catal. A 155(1–2), 193–200 (2000)
H.-J. Kim, J.-H. Lee, Highly sensitive and selective gas sensors using p-type oxide semiconductors: overview. Sens. Actuators B 192, 607–627 (2014)
Y.-H. Choi, D.H. Kim, S.H. Hong, K.S. Hong, H2 and C2H5OH sensing characteristics of mesoporous p-type CuO films prepared via a novel precursor-based ink solution route. Sens. Actuators B 178, 395–403 (2013)
A.S. Zoolfakar, M.Z. Ahmad, R.A. Rani, J.Z. Ou, S. Balendhran, S. Zhuiykov, K. Latham, W. Wlodarski, K.K. Zadeh, Nanostructured copper oxides as ethanol vapour sensors. Sens. Actuators B 185, 620–627 (2013)
A. Ghosh, A. Maity, R. Banerjee, S.B. Majumder, Volatile organic compound sensing using copper oxide thin films: addressing the cross sensitivity issue. J. Alloys Compd. 692, 108–118 (2017)
A. Umar, J.H. Lee, R. Kumar, O. Al-Dossary, Synthesis and characterization of CuO nanodisks for high-sensitive and selective ethanol gas sensor applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 17(2), 1455–1459 (2017)
P. Raksa, A. Gardchareon, T. Chairuangsri, P. Mangkorntong, N. Mangkorntong, S. Choopun, Ethanol sensing properties of CuO nanowires prepared by an oxidation reaction. Ceram. Int. 35(2), 649–652 (2009)
Y. Sang, G. Song, Z. Gao, X. Zhang, T. Wang, Y. Li, L. Zhang, Y. Fu, L. Guo, Sea urchin-like CuO particles prepared using Cu3(PO4)2 flowers as precursor for high-performance ethanol sensing. Nanotechnology 31(16), 165504 (2020)
L. Liao, Z. Zhang, B. Yan, Z. Zheng, Q.L. Bao, T. Wu, C.M. Li, Z.X. Shen, J.X. Zhang, H. Gong, Multifunctional CuO nanowire devices: p-type field effect transistors and CO gas sensors. Nanotechnology 20(8), 085203 (2009)
H.T. Hsueh, S.J. Chang, F.Y. Hung, W.Y. Weng, C.L. Hsu, T.J. Hsueh, S.S. Lin, B.T. Dai, Ethanol gas sensor of crabwise CuO nanowires prepared on glass substrate. J. Electrochem. Soc. 158(4), J106 (2011)
C. Wang, X.Q. Fu, X.Y. Xue, Y.G. Wang, T.H. Wang, Surface accumulation conduction controlled sensing characteristic of p-type CuO nanorods induced by oxygen adsorption. Nanotechnology 18(14), 145506 (2007)
D. Barreca, E. Comini, A. Gasparotto, C. Maccato, C. Sada, G. Sberveglieri, E. Tondello, Chemical vapor deposition of copper oxide films and entangled quasi-1D nanoarchitectures as innovative gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B 141(1), 270–275 (2009)
A. Umar, A.A. Ibrahim, U.T. Nakate, H. Albargi, M.A. Alsaiari, F. Ahmed, F.A. Alharthi, A.A. Alghamdi, N. Al-Zaqri, CuO nanoplates as potential scaffolds for gas sensing applications. Sens. Actuators B 250, 24–31 (2017)
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to acknowledge the support of the Deputy for Research and Innovation-Ministry of Education, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia for the research through a Grant (NU/IFC/INT/01/004) under the institutional funding committee at Najran University, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AU, AAI, HA, UTN, and SPC: experiments conduction, data analyzation, original drafting, and writing—review and editing; AU, TA, HA, MAA, and SB: visualization, revision, and validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umar, A., Ibrahim, A.A., Algadi, H. et al. Selective ethanol gas sensing performance of flower-shaped CuO composed of thin nanoplates. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 18565–18579 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06249-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06249-y