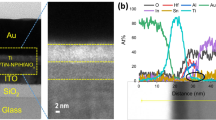
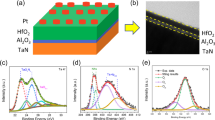
Abstract
Future artificial intelligence circuits will require expandable electronic synapses with extremely high bit density and computing speed. In this regard, the nanostructure of two-dimensional materials achieves the goal and provides device scalability in both horizontal and vertical dimensions. In this work, we report the nonvolatile bipolar resistive switching characteristics of Ni–Al layer double hydroxide (LDH)-adsorbed thiadiazole memristors. The Ni–Al LDH-adsorbed thiadiazole memristors implement a progressive reduction process and can be used to simulate the “learning” and “forgetting” functions of biological synapses. At the same positive and negative voltage pulse width, multiple resistance stages can be observed for continuous pulse number. In addition, the application of pulse train operation scheme is an effective method to control the simulated synaptic devices during the reset process, which helps understand the nature of the evolution of conductive nanofilaments.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Pei, Z. Zhou, A.P. Chen, J. Chen, X. Yan, A carbon-based memristor design for associative learning activities and neuromorphic computing. Nanoscale 12, 13531 (2020)
R.S. Zucker, W.G. Regehr, Short-term synaptic plasticity. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 64, 355–405 (2002)
A. Thomas, A.N. Resmi, A. Ganguly, K.B. Jinesh, Programmable electronic synapse and nonvolatile resistive switches using MoS2 quantum dots. Sci. Rep. 10, 12450 (2020)
Y. Yuan, X. Cao, Y. Sun, J. Su, C. Liu, L. Cheng, Y. Li, L. Yuan, H. Zhang, J. Li, Intrinsic mechanism in nonvolatile polycrystalline zirconium oxide sandwiched structure. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 2301–2306 (2018)
H.-L. Park, Y. Lee, N. Kim, D.-G. Seo, G.-T. Go, T.-W. Lee, Flexible neuromorphic electronics for computing, soft robotics, and neuroprosthetics. Adv. Mater. 15, 1903558 (2019)
J. Zhu, Y. Yang, R. Jia, Z. Liang, W. Zhu, Z.U. Rehman, L. Bao, X. Zhang, Y. Cai, L. Song, R. Huang, Ion gated synaptic transistors based on 2D van der Waals crystals with tunable diffusive dynamics. Adv. Mater. 30, 1800195 (2018)
X. Yan, Q. Zhao, A.P. Chen, J. Zhao, Z. Zhou, J. Wang, H. Wang, L. Zhang, X. Li, Z. Xiao, K. Wang, C. Qin, G. Wang, Y. Pei, H. Li, D. Ren, J. Chen, Q. Liu, Vacancy induced synaptic behavior in 2D WS2 nanosheet-based memristor for low power neuromorphic computing. Small 15, 1901423 (2019)
S. Wang, C. Chen, Z. Yu, Y. He, X. Chen, Q. Wan, Y. Shi, D. Wei Zhang, H. Zhou, X. Wang, P. Zhou, AMoS2/PTCDA hybrid heterojunction synapse with efficient photoelectric dual modulation and versatility. Adv. Mater. 31, 1806227 (2019)
J.D. Meindl, Limits on silicon nanoelectronics for terascale integration. Science 293, 2044–2049 (2001)
S.H. Jo, W. Lu, CMOS Compatible nanoscale nonvolatile resistance switching memory. Nano Lett. 8, 392–397 (2008)
R. Guo, W. Lin, X. Yan, T. Venkatesan, J. Chen, Ferroic tunnel junctions and their application in neuromorphic networks. Appl. Phys. Rev. 7, 011304 (2020)
S.H. Jo, K.-H. Kim, W. Lu, Programmable resistance switching in nanoscale two-terminal devices. Nano Lett. 9, 496–500 (2009)
C. Tan, Z. Liu, W. Huang, H. Zhang, Non-volatile resistive memory devices based on solution-processed ultrathin twodimensional nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 2615–2628 (2015)
Y. Sun, D. Wen, X. Bai, J. Lu, C. Ai, Ternary resistance switching memory behavior based on graphene oxide embedded in a polystyrene polymer layer. Sci. Rep. 7, 3938 (2017)
G. Zhou, Z. Ren, L. Wang, B. Sun, S. Duan, Q. Song, Artificial and wearable albumen protein memristor arrays with integrated memory logic gate functionality. Mater. Horiz. 6, 1877–1882 (2019)
L. Sun, Y. Zhang, G. Han, G. Hwang, J. Jiang, B. Joo, K. Watanabe, T. Taniguchi, Y.-M. Kim, W.J. Yu, B.-S. Kong, R. Zhao, H. Yang, Self-selective van der Waals heterostructures for large scale memory array. Nat. Commun. 10, 3161 (2019)
B. Sun, Y. Chen, M. Xiao, G. Zhou, S. Ranjan, W. Hou, X. Zhu, Y. Zhao, S.A.T. Redfern, Y.N. Zhou, A unified capacitive-coupled memristive model for the nonpinched current-voltage hysteresis loop. Nano Lett. 19, 6461–6465 (2019)
V.K. Sangwan, M.C. Hersam, Neuromorphic nanoelectronic materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 15, 517–528 (2020)
G. Zhou, Z. Ren, L. Wang, J. Wu, B. Sun, A. Zhou, G. Zhang, S. Zheng, S. Duan, Q. Song, Resistive switching memory integrated with amorphous carbon-based nanogenerators for self- powered device. Nano Energy 63, 103793 (2019)
B. Sun, X. Zhang, G. Zhou, P. Li, Y. Zhang, H. Wang, Y. Xia, Y. Zhao, An organic nonvolatile resistive switching memory device fabricated with natural pectin from fruit peel. Org. Electron. 42, 181–186 (2017)
Y. Sun, D. Wen, Y. Xie, F. Sun, X. Mo, J. Zhu, H. Sun, Logic gate functions built with nonvolatile resistive switching and thermoresponsive memory based on biologic proteins. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 10, 7745–7752 (2019)
Y. Sun, D. Wen, Nonvolatile WORM and rewritable multifunctional resistive switching memory devices from poly(4-vinyl phenol) and 2-amino-5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole composite. J. Alloy. Compound. 806, 215–226 (2019)
Y. Sun, D. Wen, Conductance quantization in nonvolatile resistive switching memory based on the polymer composite of Zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 122, 10582–10591 (2018)
Y. Sun, D. Wen, Physically transient random number generators based on flexible carbon nanotube composite threshold switching. J. Alloy. Compound. 844, 156144 (2020)
B. Sarkar, B. Lee, V. Misra, Understanding the gradual reset in Pt/Al2O3/Ni RRAM for synaptic applications. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 30, 105014 (2015)
J. Li, C. Ge, J. Du, C. Wang, G. Yang, K. Jin, Reproducible ultrathin ferroelectric domain switching for high-performance neuromorphic computing. Adv. Mater. 32, 1905764 (2019)
E. Pérez, Ó.G. Ossorio, S. Dueñas, H. Castán, H. García, C. Wenger, Programming pulse width assessment for reliable and low-energy endurance performance in Al:HfO2-based RRAM arrays. Electronics 9, 864 (2020)
Y.M. Sun, D.Z. Wen, F.Y. Sun, Influence of blending ratio on resistive switching effect in donor–acceptor type composite of PCBM and PVK-based memory devices. Org. Electron. 65, 141–149 (2019)
J. Lee, W. Schell, X. Zhu, E. Kioupakis, W.D. Lu, Charge transition of oxygen vacancies during resistive switching in oxide-based RRAM. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11, 11579–11586 (2019)
L. Zhao, H.Y. Chen, S.C. Wu, Z. Jiang, S. Yu, T.H. Hou, H.S.P. Wong, Y. Nishi, Multi-level control of conductive nano-filament evolution in HfO2 ReRAM by pulse-train operations. Nanoscale 6, 5698–5702 (2014)
M. Zahedinejad, A.A. Awad, S. Muralidhar, R. Khymyn, H. Fulara, H. Mazraati, M. Dvornik, J. Åkerman, Two-dimensional mutually synchronized spin hall nano-oscillator arrays for neuromorphic computing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 15, 47–52 (2020)
T.H. Park, Y.J. Kwon, H.J. Kim, H.C. Wo, G.S. Kim, C.H. An, Y. Kim, D.E. Kwon, C.S. Hwang, Balancing the source and sink of oxygen vacancies for the resistive switching memory. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 27, 21445–21450 (2018)
S. Yu, Y. Wu, R. Jeyasingh, D. Kuzum, H.-S. Wong, An electronic synapse device based on metal oxide resistive switching memory for neuromorphic computation. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 58, 2729–2737 (2011)
A. Vincent, J. Larroque, W. Zhao, N.B. Romdhane, D. Querlioz, Spin-transfer torque magnetic memory as a stochastic memristive synapse for neuromorphic systems. IEEE Trans. Biomedical Circuits Syst. 9, 166–174 (2015)
V. Chanthbouala, R.O. Garcia, K. Cherifi, S. Bouzehouane, X. Fusil, S. Moya, H. Xavier, C. Yamada, N.D. Deranlot, Mathur a ferroelectric memristor. Nature Mater. 11, 860–864 (2012)
S.H. Jo, T. Chang, I. Ebong, B.B. Bhadviya, P. Mazumder, W. Lu, Nanoscale memristor device as synapse in neuromorphic systems. Nano Lett. 10, 1297–1301 (2010)
L. Jackson, B. Rajendran, G.S. Corrado, M. Breitwisch, D.S. Modha, Nano-scale electronic synapses using phase change devices. ACM J. Emerg. Technol. Comput. 9(1), 20 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 62065001, 61761048), and partially supported by Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects (Grant No. 202001BA070001-060).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, E., Liu, G., Xing, C. et al. Nonvolatile resistive switching characteristics based on Ni–Al LDHs and its electronic synapse application. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 9938–9945 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05651-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05651-w