Abstract
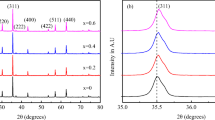
Mg1−xZnxFe2O4 nanocrystalline ferrites (1.0 ≥ x ≥ 0.0) were prepared using a sucrose autocombustion-assisted route. X-ray diffraction (XRD) showed secondary phase formation at Zn contents higher than x = 0.2. The obvious increase in the lattice parameters from 8.3937 to 8.4454 Å upon increasing the Zn content might be attributed to the ionic radius of Zn2+ ions being larger than that of Mg2+ ions. The crystallite sizes calculated using Scherrer’s formula confirmed the nanocrystalline nature of the prepared samples. The Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectra exhibited characteristic ferrite bands attributed to tetrahedral and octahedral sites, and there was an obvious splitting in the tetrahedral absorption band attributed to the Jahn–Teller distortion effect. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images showed agglomerated spherical particles with sizes that are in full agreement with results obtained by XRD. A reliable cation distribution was suggested based on the obtained structural parameters to address the preferential occupation of the entirety of the cations with increasing Zn content. The magnetic parameters estimated by vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) measurements were utilized to confirm the suggested cation distribution and address the effect of Zn substitution on the entire system. All the investigated samples, except for ZnFe2O4, exhibited soft ferromagnetic characteristics. The obtained coercivities were higher than those reported in the literature and suggested the presence of an elevated demagnetization field and reflected the impact of the present synthesis method. The AC conductivity indicated semiconducting properties, and there was a ferromagnetic-to-paramagnetic magnetic transition in all samples with increasing temperature. The dielectric measurements also confirmed this transition by exhibiting relaxations in the same temperature range.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Matz, D. Gotsch, R. Karmazin, R. Männer, B. Siessegger, Low temperature cofirable MnZn ferrite for power electronic applications. J. Electroceram. 22, 209–215 (2009)
M.R. Syue, F.J. Wei, C.S. Chou, C.M. Fu, Magnetic and electrical properties of Mn–Zn ferrites synthesized by combustion method without subsequent heat treatments. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 07A324 (2011)
X. Gao, L. Liu, B. Birajdar, M. Ziese, W. Lee, M. Alexe, D. Hesse, High-density periodically ordered magnetic cobalt ferrite nanodot arrays by template-assisted pulsed laser deposition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 3450–3455 (2009)
S. Mohapatra, S.R. Rout, S. Maiti, T.K. Maiti, A.B. Panda, Monodisperse mesoporous cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: synthesis and application in targeted delivery of antitumor drugs. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 9185–9193 (2011)
C. Barcena, A.K. Sra, G.S. Chaubey, C. Khemtong, J.P. Liu, J. Gao, Zinc ferrite nanoparticles as MRI contrast agents. Chem. Commun. 19, 2224–2226 (2008)
A.B. Gadkari, T.J. Shinde, P.N. Vasambekar, Ferrite gas sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 11, 849–861 (2011)
J. Smith, H.P.J. Wijn, Ferrites (Wiley, New York, 1959)
A. Goldman, Modern Ferrite Technology, 2nd edn. (Springer, New York, 2006)
K. Nadeemn, S. Rahman, M. Mumtaz, Effect of annealing on properties of Mg doped Zn-ferrite nanoparticles. Progress Natl. Sci. 25, 111–116 (2015)
A. Manikandan, J. Judith Vijaya, M. Sundararajan, C. Meganathan, L. John Kennedy, M. Bououdina, Optical and magnetic properties of Mg-doped ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by rapid microwave combustion method. Superlattices Microstruct. 64, 118–131 (2013)
H. Kavas, A. Baykal, M.S. Toprak, Y. Kseoglua, M. Sertkol, B. Aktas, Cation distribution and magnetic properties of Zn doped NiFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by PEG-assisted hydrothermal route. J. Alloys Compd. 479, 49–55 (2009)
C. Yao, Q. Zeng, G.F. Goya, T. Torres, J. Liu, H. Wu, M. Ge, Y. Zeng, Y. Wang, J.Z. Jiang, ZnFe2O4 Nanocrystals: synthesis and magnetic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 12274–12278 (2007)
Y.Y. Meng, Z.W. Liu, H.C. Dai, H.Y. Yu, D.C. Zeng, S. Shukla, R.V. Ramanujan, Structure and magnetic properties of Mn(Zn)Fe2−xRExO4 ferrite nano-powders synthesized by co-precipitation and refluxing method. Powder Technol. 229, 270–275 (2012)
J. Hu, G. Shi, Z. Ni, L. Zheng, A. Chen, Effects of V2O5 addition on NiZn ferrite synthesized using two-step sintering process. Phyisca B 407, 2205–2210 (2012)
D.C. Bharti, K. Mukherjee, S.B. Majumder, Wet chemical synthesis and gas sensing properties of magnesium zinc ferrite nano-particles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 120, 509–517 (2010)
G.P. Nagabhushana, B. Rudraswamy, G.T. Chandrappa, Thermal effect on magnetic properties of Mg-Zn ferrite nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 116, 227–230 (2014)
C. Choodamani, S. Hajarpour, A.H. Raouf, K. Gheisari, Structural evolution and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline magnesium–zinc soft ferrites synthesized by glycine–nitrate combustion process. J. Magn Magn. Mater. 363, 21–25 (2014)
K. Mukherjee, S.B. Majumder, Synthesis process induced improvement on the gas sensing characteristics of nano-crystalline magnesium zinc ferrite particles. Sens. Actuators B 162, 229–236 (2012)
C. Choodamani, G.P. Nagabhushana, S. Ashoka, B. Daruka Prasad, B. Rudraswamy, G.T. Chandrappa, Structural and magnetic studies of Mg(1–x)ZnxFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by a solution combustion method. J. Alloys Compd. 578, 103–109 (2013)
S. Hajarpour, K. Gheisari, A.H. Raouf, Characterization of nanocrystalline Mg0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4 soft ferrites synthesized by glycine-nitrate combustion process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 329, 165–169 (2013)
P. Masina, T. Moyo, H.M.I. Abdallah, Synthesis, structural and magnetic properties of ZnxMg1-xFe2O4 nanoferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 381, 41–49 (2015)
S. Rahman, K. Nadeem, M. Anis-ur-Rehman, M. Mumtaz, S. Naeem, I. Letofsky-Papst, Structural and magnetic properties of ZnMg-ferrite nanoparticles prepared using the co-precipitation method. Ceram. Int. 39, 5235–5239 (2013)
R.G. Kulkarni, H.H. Joshi, The magnetic properties of the Mg-Znferrite system by Mossbauer spectroscopy. Sol. State Commun. 53, 1005–1008 (1985)
K.A. Mohammed, A.D. Al-Rawas, A.M. Gismelseed, A. Sellai, H.M. Widatallah, A. Yousif, M.E. Elzain, M. Shongwe, Infrared and structural studies of Mg1–xZnxFe2O4 ferrites. Phys. B 407, 795–804 (2012)
M.M. Haque, M. Huq, M.A. Hakim, Effect of Zn2+ substitution on the magnetic properties of Mg1-xZnxFe2O4 ferrites. Phys. B 404, 3915–3921 (2009)
D. Kotsikau, M. Ivanovskaya, V. Pankov, Y. Fedotova, Structure and magnetic properties of manganese zinc-ferrites prepared by spray pyrolysis method. Sol. State Sci. 39, 69–73 (2015)
K. Mukherjee, S.B. Majumder, Promising methane-sensing characteristics of hydrothermal synthesized magnesium zinc ferrite hollow spheres. Scrip. Mater. 67, 617–620 (2012)
H. Dutta, M. Sinha, Y.C. Lee, S.K. Pradhan, Microstructure characterization and phase transformation kinetics of ball-mill prepared nanocrystalline Mg–Zn-ferrite by Rietveld’s analysis and electron microscopy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 105, 31–37 (2007)
M.A. Gabal, A.A. Al-Al-Juaid, S.M. Al-Rashed, M.A. Hussein, Synthesis, characterization and electromagnetic properties of Zn-substituted CoFe2O4 via sucrose assisted combustion route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 670–679 (2017)
S. Ghatak, M. Sinha, A.K. Meikap, S.K. Pradhan, Electrical transport behavior of nonstoichiometric magnesium–zinc ferrite. Mater. Res. Bull. 45, 954–960 (2010)
A. Xia, S. Liu, C. Jin, L. Chen, Y. Lv, Hydrothermal Mg1-xZnxFe2O4 spinel ferrites: phase formation and mechanism of saturation magnetization. Mater. Lett. 105, 199–201 (2013)
S. Raghuvanshi, F. Mazaleyrat, S.N. Kane, Mg1-xZnxFe2O4 nanoparticles: interplay between cation distribution and magnetic properties. AIP Adv. 8, 047804 (2018)
H. Saqib, S. Rahman, R. Susilo, B. Chen, N. Dai, Structural, vibrational, electrical, and magnetic properties of mixed spinel ferrites Mg1-xZnxFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation. AIP Adv. 9, 055306 (2019)
P.Y. Reyes-Rodriguez, D.A. Cortes-Hernandez, J.C. Escobedo-Bocardo, J.M. Almanza-Robles, H.J. Sanchez-Fuentes, A. Jasso-Teran, L.E. De Leon-Prado, J. Mendez-Nonell, G.F. Hurtado-Lopez, Structural and magnetic properties of Mg-Zn ferrites (Mg1−xZnxFe2O4) prepared by sol-gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 427, 268–271 (2017)
M.A. Gabal, R.M. El-Shishtawy, Y.M. Al Angari, Structural and magnetic properties of nano-crystalline Ni–Zn ferrites synthesized using egg-white precursor. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 2258–2264 (2012)
R.D. Shannon, Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 32, 751–767 (1976)
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-ray Diffraction, 2nd edn. (Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, 1978)
M.A. Gabal, Y.M. Al Angari, H.M. Zaki, Structural, magnetic and electrical characterization of Mg–Ni nano-crystalline ferrites prepared through egg-white precursor. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 363, 6–12 (2014)
R.S. Yadav, I. Kuritka, J. Vilcakova, P. Urbanek, M. Machovsky, M. Masar, M. Holek, Structural, magnetic, optical, dielectric, electrical and modulus spectroscopic characteristics of ZnFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles synthesized via honey-mediated sol-gel combustion method. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 110, 87–99 (2017)
S.M. Patange, S.E. Shirsath, G.S. Jangam, K.S. Lohar, S.S. Jadhav, K.M. Jadhav, Rietveld structure refinement, cation distribution and magnetic properties of Al3+ substituted NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 053909 (2011)
R.D. Waldron, Infrared spectra of ferrites. Phys. Rev. 99, 1727–1735 (1955)
S.J. Kenye, J. Manjanna, G. Venkateswaran, R. Kameswaran, Corros. Sci. 48, 2780–2798 (2006)
A. Pradeep, P. Priyadharsini, G. Chandrasekaran, Sol–gel route of synthesis of nanoparticles of MgFe2O4 and XRD, FTIR and VSM study. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 2774–2779 (2008)
J.L. Martin de Vidales, A. Lopez-Delgado, E. Vila, F.A. Lopez, The effect of the starting solution on the physico-chemical properties of zinc ferrite synthesized at low temperature. J. Alloys Compds. 287, 276–283 (1999)
P.A. Shaikh, R.C. Kambale, A.V. Rao, Y.D. Kolekar, Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of Co–Ni–Mn ferrites synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Alloys Compd. 492, 590–596 (2010)
L. Neel, Aimanation a saturation des ferrites mixtes de nickel et de zinc. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 230, 375–377 (1950)
K. Nadeem, H. Krenn, T. Traussnig, R. Wurschum, D.V. Szabo, I. Letofsky-Papst, Spin-glass freezing of maghemite nanoparticles prepared by microwave plasma synthesis. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 113911 (2012)
Y. Yafet, C. Kittle, Antiferromagnetic arrangements in ferrites. Phys. Rev. 87, 290–294 (1952)
R. Topkaya, A. Baykal, A. Demir, Yafet–Kittel-type magnetic order in Zn-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with uniaxial anisotropy. J. Nanopart. Res. 15, 1359 (2013)
C.C. Chauhan, A.R. Kagdi, R.B. Jotania, A. Upadhyay, C.S. Sandhu, S.E. Shirsath, S.S. Meen, Structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of Co-Zr substituted M-type calcium hexagonal ferrite nanoparticles in the presence of α-Fe2O3 phase. Ceram. Int. 44, 17812–17823 (2018)
A.R. Kagdi, N.P. Solanki, F.E. Carvalho, S.S. Meena, P. Bhatt, R.C. Pullar, R.B. Jotania, Influence of Mg substitution on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of X-type bariumezinc hexaferrites Ba2Zn2-xMgxFe28O46. J. Alloys Compd. 741, 377–391 (2018)
A.K. Nikumbh, R.A. Pawar, D.V. Nighot, G.S. Gugale, M.D. Sangale, M.B. Khanvilkar, A.V. Nagawade, Structural, electrical, magnetic and dielectric properties of rare-earth substituted cobalt ferrites nanoparticles synthesized by the co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 355, 201–209 (2014)
H.M. Zaki, S.H. Al-Heniti, T.A. Elmosalami, Structural, magnetic and dielectric studies of copper substituted nano-crystalline spinel magnesium zinc ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 633, 104–114 (2015)
S.J. Haralkar, R.H. Kadam, S.S. More, S.E. Shirsath, M.L. Mane, S. Patil, D.R. Mane, Substitutional effect of Cr3+ ions on the properties of Mg–Zn ferrite nanoparticles. Phys. B 407, 4338–4346 (2012)
N. Sivakumar, A. Narayanasamy, J.-M. Greneche, R. Murugaraj, Y.S. Lee, Electrical and magnetic behaviour of nanostructured MgFe2O4 spinel ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 504, 395–402 (2010)
D. Narsimulu, B.N. Rao, M. Venkateswarlu, E.S. Srinadhu, N. Satyanarayan, Electrical and electrochemical studies of nanocrystalline mesoporous MgFe2O4 as anode material for lithium battery applications. Ceram. Int. 42, 16789–16797 (2016)
D.K. Mahato, Ac conductivity analysis of nanocrystallite MgFe2O4 ferrite. Mater. Today: Proceedings 5, 9191–9195 (2018)
A.A. Yaremchenko, A.V. Kovalevsky, E.N. Naumovich, V.V. Kharton, J.R. Fradea, High-temperature electrical properties of magnesiowustite Mg1−xFexO and spinel Fe3−x−yMgxCryO4 ceramics. Sol. State Ionics 192, 252–258 (2011)
S.M. Antao, I. Hassan, J.B. Parise, Cation ordering in magnesioferrite, MgFe2O4 to 982°C using in situ synchrotron X-ray powder diffraction. Am. Mineral. 90, 219–228 (2005)
H.S.C. O’Neill, H. Annersten, D. Virgo, The temperature dependence of the cation distribution in magnesioferrite (MgFe2O4) from powder XRD structural refinements and Mossbauer spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 77, 725–740 (1992)
N.K. Thanh, T.H. Loan, N.P. Duong, L.N. Anh, D.T. Nguyet, N.H. Nam, S. Soontaranon, W. Klysubun, T.D. Hien, Cation distribution assisted tuning of magnetization in nanosized magnesium ferrite. Phys. Status Solidi A 215, 1700397 (2018)
M.A. Gabal, M.A. Ahmed, Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of copper-cadmium ferrites prepared from metal oxalates. J. Mater. Sci. 40, 387–398 (2005)
M.A. El Hiti, Dielectric behavior and ac electrical conductivity of Zn-substituted Ni-Mg ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 164, I87–196 (1996)
S. Sen, R.N.P. Choudhary, P. Pramanik, Structural and electrical properties of Ca2+-modified PZT electroceramics. Phys. B 387, 56–62 (2007)
S. Khadhraoui, A. Triki, S. Hcini, S. Zemni, M. Oumezzine, Structural and impedance spectroscopy properties of Pr0.6Sr0.4Mn1−xTixO3±δ perovskites. J. Alloys Compd. 574, 290–298 (2013)
J.E. Bauerle, Study of solid electrolyte polarization by a complex admittance method. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 30, 2657–2670 (1969)
E. Oumezzine, S. Hcini, F.I.H. Rhouma, M. Oumezzine, Frequency and temperature dependence of conductance, impedance and electrical modulus studies of Ni0.6Cu0.4Fe2O4 spinel ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 726, 187–194 (2017)
A. Selmi, S. Hcini, H. Rahmouni, A. Omri, M.L. Bouazizi, A. Dhahri, Synthesis, structural and complex impedance spectroscopy studies of Ni0.4Co0.4Mg0.2Fe2O4 spinel ferrite. Phase Transit. 90, 942–954 (2017)
J. Lario-Garcia, R. Pallas-Areny, Constant-phase element identification in conductivity sensors using a single square wave. Sens. Actuators A 132, 122–128 (2006)
B. Hirschorn, M.E. Orazem, B. Tribollet, V. Vivier, I. Frateur, M. Musiani, Determination of effective capacitance and film thickness from constant-phase-element parameters. Electrochim. Acta 55, 6218–6227 (2010)
P. Cordoba-Torres, T.J. Mesquita, O. Devos, B. Tribollet, V. Roche, R.P. Nogueira, On the intrinsic coupling between constant-phase element parameters α and Q in electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta 72, 172–178 (2012)
Z. Stoynov, D. Vladikova, Differential Impedance Analysis (Marin Drinov Academic Publishing House, Sofia, 2005)
P. Zoltowski, On the electrical capacitance of interfaces exhibiting constant phase element behaviour. J. Electroanal. Chem. 443, 149–154 (1998)
S. Kallel, A. Nasri, N. Kallel, H. Rahmouni, O. Pena, K. Khirouni, M. Oumezzine, Complex impedance spectroscopy studies of (La0.70−xNdx) Sr0.30Mn0.70Cr0.30O3 (x≤ 030) perovskite compounds. Phys. B 406, 2172–2176 (2011)
M.A. El Hiti, Dielectric behavior in Mg-Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 192, 305–313 (1999)
K.M. Batoo, G. Kumar, Y. Yang, Y. Al-Douri, M. Singh, R.B. Jotania, A. Imran, Structural, morphological and electrical properties of Cd2+ doped MgFe2-xO4 ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compds. 726, 179–186 (2017)
J.C. Maxwell, Electricity and Magnetism (Oxford University Press, New York, 1954), p. 328
K.W. Wagner, The distribution of relaxation times in typical dielectrics. Ann. Phys. 40, 817–819 (1973)
C.G. Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audio frequencies. Phys. Rev. 83, 121–124 (1951)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gabal, M.A., Al-Juaid, A.A. Structural and electromagnetic studies of Mg1-xZnxFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized via a sucrose autocombustion route. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 10055–10071 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03551-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03551-z