Abstract
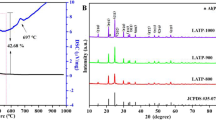
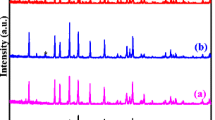
Lithium superionic conductor (LISICON) Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 (LATP) is known as a high lithium-ion conductive solid electrolyte. The top-down approach was utilized in this work to synthesize LATP in which Ag with concentrations of 1, 2, 4, 6, 8 wt% was incorporated in the host material and the performance of the fabricated solid electrolyte was examined and compared with that of the pristine material. Substitution of Li+ by Ag+ in LATP structure resulted in bulk conductivity of 1.1 × 10–3 S cm−1 and grain boundary conductivity of 1.0 × 10–3 S cm−1 at 25 °C for the optimum Ag concentration of 4 wt%. The calcination process was performed in several temperature steps to prevent the release of volatile substances. To obtain a pure LATP structure, phase analyses were performed using X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns to improve the synthesis conditions. High density, low unwanted and amorphous phases and increased ionic conductivity were achieved by applying sintering process and optimizing the amounts of additives. Effective surface area of about 16 g m−2 was measured using Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) analysis. Negligible decomposition of the products was observed by employing thermal analyses (TGA/DSC). The bulk conductivity of the fabricated solid electrolyte is among the highest reported bulk conductivity for LATP and the grain boundary conductivity revealed by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) test is higher than other reported values for LATP. So, the fabricated solid electrolyte is recommended for using in electrically charged solid-state lithium batteries.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Aono, E. Sugimoto, Y. Sadaoka, N. Imanaka, G. Adachi, The electrical properties of ceramic electrolytes for LiMxTi2-x(PO4)3+yLi2O, M = Ge, Sn, Hf, and Zr systems. J. Electrochem. Soc. 140, 1827–1833 (1993)
J.G. Kim, B. Son, S. Mukherjee, N. Schuppert, A. Bates, O. Kwon et al., A review of lithium and non-lithium based solid state batteries. J. Power Sources 282, 299–322 (2015)
A. Kraytsberg, Ein-Eli Y Review on Li–air batteries—opportunities, limitations and perspective. J. Power Sources 196, 886–893 (2011)
A.J. Moulson, Herbert JM Electroceramics: Materials, Properties, Applications (Wiley, New York, 2003)
H. Tuller, Handbook of Electronic and Photonic Materials (Springer, New York, 2017)
E. Barsoukov, Macdonald JR Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and Applications (Wiley, New York, 2018)
A.R. West, Solid State Chemistry and Its Applications (Wiley, New York, 2014)
E.D. Zanotto, A bright future for glass-ceramics. Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 89, 19–27 (2010)
P. Knauth, Inorganic solid Li ion conductors: an overview. Solid State Ionics 180, 911–916 (2009)
M. Chen, W. Hua, J. Xiao, D. Cortie, W. Chen, E. Wang, Z. Hu, Q. Gu, X. Wang, S. Indris, S.L. Chou, Dou SX NASICON-type air-stable and all-climate cathode for sodium-ion batteries with low cost and high-power density. Nat. Commun. 10, 1480 (2019)
Y. Sun, Lithium ion conducting membranes for lithium-air batteries. Nano Energy 2(5), 801–816 (2013)
P. Maldonado-Manso, E.R. Losilla, M. Martínez-Lara, M.A. Aranda, S. Bruque, F.E. Mouahid et al., High lithium ionic conductivity in the Li1+ x Al x Ge y Ti2-x-y(PO4)3 NASICON series. Chem. Mater. 15, 1879–1885 (2003)
A. Svitan’Ko, S. Novikova, D. Safronov, A. Yaroslavtsev, Cation mobility in Li1+x Ti2–x Crx (PO4)3 NASICON-type phosphates. Inorg. Mater. 47, 1391–1395 (2011)
E. Jeong, K.Y. Yoon, H.A. Jung, T. Nakayma, M.J. Ji, H. Hwang, Fabrication and electrochemical properties of Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 solid electrolytes by sol-gel method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 473, 622–626 (2019)
J. Liu, T. Liu, Y. Pu, M. Guan, Z. Tang, F. Ding, Z. Xu, Y. Li, Facile synthesis of NASICON-type Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 solid electrolyte and its application for enhanced cyclic performance in lithium ion batteries through the introduction of an artificial Li3PO4 SEI layer. RSC Adv. 7, 46545–46552 (2017)
W.C. West, J.F. Whitacre, J.R. Lim, Chemical stability enhancement of lithium conducting solid electrolyte plates using sputtered LiPON thin films. J. Power Sources 126, 134–138 (2004)
J.P. Han, B. Zhang, L.Y. Wang, H.L. Zhu, Y.X. Qi, L.W. Yin, H. Li, N. Lun, Y.J. Bai, Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 Behaving as a fast ionic conductor and bridge to boost the electrochemical performance of Li4Ti5O12. Chem. Eng. 6(6), 7273–7282 (2018)
J.G. Kim, D. Shi, M.S. Park, G. Jeong, Y.U. Heo, M. Seo, Y.J. Kim, J.H. Kim, S.X. Dou, Controlled Ag-driven superior rate-capability of Li4Ti5O12 anodes for lithium rechargeable batteries. Nano Res. 6(5), 365–372 (2013)
K. Arbi, S. Mandal, J.M. Rojo, J. Sanz, Dependence of ionic conductivity on composition of fast ionic conductors Li1+xTi2−xAlx(PO4)3, 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.7. A parallel NMR and electric impedance study. Chem. Mater. 14, 1091–1097 (2002)
A. Mertens, S. Yu, N. Schön, D.C. Gunduz, H. Tempel, R. Schierholz, F. Hausen, H. Kungl, J. Granwehr, R.A. Eichel, Superionic bulk conductivity in Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 solid electrolyte. Solid State Ionics 309, 180–186 (2017)
K.P. Abhilash, P. Christopher Selvin, B. Nalini, P. Nithyadharseni, on pure and Ag doped lithium lanthanum titanate (LLTO) nanocrystalline ceramic electrolytes for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Ceram. Int. 39, 947–952 (2013)
E. Zhao, F. Ma, Y. Jin, K. Kanamura, Pechini synthesis of high ionic conductivity Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 solid electrolytes: the effect of dispersant. J. Alloys Compds. 680, 646–653 (2016)
J.S. Lee, C.M. Chang, Y.I. Lee, J.H.S.H. Lee Hong, Spark plasma sintering (SPS) of NASICON ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 87, 305–307 (2004)
K. Ullah, A. Ullah, A. Aldalbahi, J. Chung, W.C. Oh, Enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity and hydrogen evolution through novel heterostructure AgI–FG–TiO2 nanocomposites. J. Mol. Catal. A 410, 242–252 (2015)
Y. Liu, J. Liu, Q. Sun, D. Wang, K.R. Adair, J. Liang, C. Zhang, L. Zhang, S. Lu, H. Huang, X. Song, X. Sun, Insight into the microstructure and ionic conductivity of cold sintered NASICON solid electrolyte for solid-state batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11(31), 27890–27896 (2019)
S. Duluard, A. Paillassa, L. Puech, P. Vinatier, V. Turq, P. Rozier, P. Lenormand, P.L. Taberna, P. Simon, F. Ansart, Lithium conducting solid electrolyte Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 obtained via solution chemistry. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 33(6), 1145–1153 (2013)
G. Tan, F. Wu, L. Li, Y. Liu, Chen R Magnetron sputtering preparation of nitrogen-incorporated lithium–aluminum–titanium phosphate based thin film electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 3817–3826 (2012)
S.V. Rathan, G.X. Govindaraj, Thermal and electrical relaxation studies in Li(4+x) TixNb1− xP3O12 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 1.0) phosphate glasses. Solid State Sci. 12, 730–735 (2012)
N. Mustaffa, S. Adnan, M. Sulaiman, Mohamed N Low-temperature sintering effects on NASICON-structured LiSn2P3 O 12 solid electrolytes prepared via citric acid-assisted sol-gel method. Ionics 21, 955–965 (2015)
G. Govindaraj, C.R. Mariappan, Synthesis, characterization and ion dynamic studies of NASICON type glasses. Solid State Ionics 147(1–2), 49–59 (2002)
A. Rodrigues, J. Narváez-Semanate, A. Cabral, A. Rodrigues, Determination of crystallization kinetics parameters of a Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5 (PO4)3 (LAGP) glass by differential scanning calorimetry. Mater. Res. 16, 811–816 (2013)
J.L. Narváez-Semanate, A.C.M. Rodrigues, Microstructure and ionic conductivity of Li1+xAlxTi2−x(PO4)3 NASICON glass-ceramics. Solid State Ionics 181, 1197–1204 (2010)
V.M. Fokin, A.A. Cabral, R.M. Reis, M.L. Nascimento, Zanotto ED Critical assessment of DTA–DSC methods for the study of nucleation kinetics in glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 356, 358–367 (2010)
K. Ullah, I.J. Kim, S. Yang, W.C. Oh, Preparation of highly expanded graphene with large surface area and its additional conductive effect for EDLC performance. J. Mater. Sci. 26, 6945–6953 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to research council of the University of Kashan for providing financial support to undertake this work (Grant No. 785216).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soweizy, M., Zahedifar, M. & Karimi, M. Fabrication and characterization of Ag-doped Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 solid electrolyte with high ionic conductivity. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 9614–9621 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03504-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03504-6