Abstract
Phase-change random access memory (PCRAM) has the advantages of nonvolatile, good scalability, high speed, low power, long life and compatibility with standard complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) process. The key material in PCRAM is phase-change material, which can greatly affect the performance of PCRAM device. Ge2Sb2Te5 (GST) is the most mature phase-change material and has been studied most widely at present. In this paper, GST films with thickness of 500 nm, 100 nm, 50 nm and 20 nm were studied by scanning electron microscope (SEM)–electron backscattering diffraction (EBSD) technique. According to the experiments, it is found that the crystal grain size has a tendency to grow larger and the GST film has a more obvious < 0001 > texture as its thickness decreases. During this process, surface energy plays an increasingly important role with the decrease in GST film thickness. Finally, (0001) plane with the highest work function and lowest surface energy leads to visible Z < 0001 > texture corresponding to film thickness. These results of regularity are helpful as the semiconductor industry today has the need for PCRAM devices with higher density and smaller size.

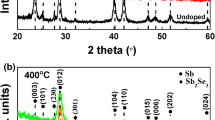
Source: Created by Origin (2019)

Source: Created by HKL Channel 5 of Oxford Instruments

Source: Created by Origin (2019)

Source: Created by HKL Channel 5 of Oxford Instruments
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.F. Scott, Ferroelectric Memories (Springer, Berlin, 2013)
N. Nishimura, T. Hirai, A. Koganei, T. Ikeda, K. Okano, Y. Sekiguchi, Y. Osada, Magnetic tunnel junction device with perpendicular magnetization films for high-density magnetic random access memory. J. Appl. Phys. 91(8), 5246–5249 (2002)
G.Y. Sun, X.Y. Dong, Y. Xie, J. Li, Y.R. Chen, A novel architecture of the 3D stacked MRAM L2 cache for CMPs. IEEE 15th international symposium of high performance computer architecture (HPCA), 239–249, 2009
J.W. Seo, J.W. Park, K.S. Lim, J.H. Yang, S.J. Kang, Transparent resistive random access memory and its characteristics for nonvolatile resistive switching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 223505 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3041643
H.S.P. Wong, H.Y. Lee, S.M. Yu, Y.H. Chen, Y. Wu, P.S. Chen et al., Metal-oxide RRAM P. IEEE 100(6), 1951–1970 (2012)
Z.T. Song, Phase change memory and application fundamentals. (Science Press, 2013) (in Chinese)
S. Raoux, Phase change materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 39, 25–48 (2009)
D. Yu, S. Brittman, J.S. Lee, A.L. Falk, H. Park, Minimum voltage for threshold switching in nanoscale phase-change memory. Nano Lett. 8(10), 3429–3433 (2008)
S. Raoux, G.W. Burr, M.J. Breitwisch, C.T. Rettner, Y.C. Chen, R.M. Shelby et al., Phase-change random access memory: a scalable technology. IBM J. Res. Dev. 52(4/5), 465–479 (2008)
X.Q. Wei, L.P. Shi, T.C. Chong, R. Zhao, H.K. Lee, Thickness dependent nano-crystallization in Ge2Sb2Te5 films and its effect on devices. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 46, 2211–2214 (2007)
C.D. Wright, M. Armand, M.M. Aziz, Terabit-per-square-inch data storage using phase-change media and scanning electrical nanoprobes. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 5, 50–61 (2006)
S. Raoux, J.L. Jordan-Sweet, A.J. Kellock, Crystallization properties of ultrathin phase change films. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 7 (2008)
J.M. Li, J.J. Wang, Y. Jia, Influence of the quantum size effects on properties of the ultrathin Pb (1 1 1) film. J. Zhengzhou Univ. 42(1), 103–111 (2010)
Y. Guo, Y.F. Zhang, X.Y. Bao, T.Z. Han, Z. Tang, L.X. Zhang et al., Superconductivity modulated by quantum size effects. Science 306(5703), 1915–1917 (2004)
D. Xie, W.H. Qi, M.P. Wang, Size and shape dependent melting-thermodynamic properties of metallic nanoparticles. Acta Metall. Sin. 10, 1041–1044 (2004)
G.C. Fan, Z. Ma, Z.Y. Huan, X.C. Tan, X.C. Yao, Surface thermodynamic properties of micro/nano peanut-shaped CaMoO4. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 10, 1007–1010 (2014)
M. Wuttig, N. Yamada, Phase-change materials for rewriteable data storage. Nat. Mater. 6, 824–832 (2007)
Y.C. Wang, Y.F. Chen, D.L. Cai, Y. Cheng, X.G. Chen, Y.Q. Wang et al., Understanding the early cycling evolution behaviors for phase change memory application. J. Appl. Phys. 116(20), 7020–7028 (2014)
Y.C. Wang, X.G. Chen, Y. Cheng, X.L. Zhou, S.L. Lv, Y.F. Chen et al., RESET distribution improvement of phase change memory: the impact of pre-programming. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 35(5), 536–538 (2014)
Y.H. Zheng, Y. Cheng, R. Huang, R.J. Qi, F. Rao, K.Y. Ding et al., Surface energy driven cubic-to-hexagonal grain growth of Ge2Sb2Te5 thin film. Sci. Rep. 7, 5915 (2017)
Y.H. Zheng, Y. Wang, T.J. Xin, Y. Cheng, R. Huang, P. Liu et al., Direct atomic identification of cation migration induced gradual cubic-to-hexagonal phase transition in Ge2Sb2Te5. Commun. Chem. 2, 13 (2019)
EBSD software AZtecHKL introduction (OXFORD official website 2019) https://nano.oxinst.com/products/ebsd. Accessed 3 May 2019
HKL Channel 5 software introduction (OXFORD official website 2019) 2019.5.3 http://www.oxford-instruments.cn/products/microanaiysis/ebsd/ebsd-post-processing-software. Accessed 3 May 2019
S. Suwas, R.K. Ray, Crystallographic Texture of Materials (Springer, London, 2014), pp. 11–21
J. Wang, J.J. Bian, G.F. Wang, Calculation of surface energy density of rough surface by atomic simulation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 484, 184–188 (2019)
D.P. Ji, S.Q. Wang, Study of surface energy and work function of hex metals by first-principles calculation. Acta Metall. Sin. 51(5), 597–602 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFA0303403, 2017YFA0206101, 2017YFB0405601).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Q., He, T., Yu, K. et al. The effect of thickness on texture of Ge2Sb2Te5 phase-change films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 5848–5853 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02645-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02645-7