Abstract
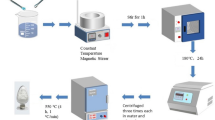
Recently, the metal organic frameworks (MOFs) structure is concerned by its unique porous structure and regular morphology. In this paper, ZnO has been prepared by calcining MOF-5 precursors which obtained via a solvothermal method. For a better comparison, the reaction time needs to be appropriately changed to control the sizes of samples. The obtained samples were analyzed for composition and morphology by a series of characterization methods, and the results showed that particle size of MOF-5 precursors increased with reaction time. The ZnO particles formed after calcination are composed of crystal grains of 20–30 nm and thus have a porous structure. Gas-sensitive performance tests show that the sensor based on MOF-5-derived ZnO has good gas sensitivity. Among them, the responsiveness of MOF-5-derived ZnO prepared by solvothermal reaction for 4 h was the highest at 300 °C, and the response value to 100 ppm triethylamine (TEA) was 120.6. In addition, MOF-5-derived ZnO has better selectivity and repeatability than ZnO which is prepared using other methods.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.E. Bildirici, M.G. Seyit, Environmental pollution, hydropower energy consumption and economic growth: evidence from G7 countries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 75, 68–85 (2016)
I. You, H. Jeon, K. Lee, Polydopamine coating in organic solvent for material-independent immobilization of water-insoluble molecules and avoidance of substrate hydrolysis. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 46, 379–385 (2017)
T. Yang, K. Gu, M. Zhu, ZnO-SnO2 heterojunction nanobelts: synthesis and ultraviolet light irradiation to improve the TEA sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B 279, 410–417 (2019)
X.Z. Li, Y. Wang, W.D. Tian, Graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets decorated flower-like NiO composites for high-performance triethylamine detection. ACS Omega. 4, 9645–9653 (2019)
W. Jiang, D.D. Wei, S.F. Zhang, The facile synthesis of MoO3 microsheet and its excellent gas-sensing performance toward triethylamine: high selectivity, excellent stability and superior repeatability. New J. Chem. 42, 15111–15120 (2018)
Z.P. Li, Q.Q. Zhao, W.L. Fan, Porous SnO2 nanospheres as sensitive gas sensors for volatile organic compounds detection. Nanoscale. 3, 1646–1652 (2011)
M.W.G. Hoffmann, L. Mayrhofer, O. Casals, A highly selective and self-powered gas sensor via organic surface functionalization of p-Si/n-ZnO diodes. Adv. Mater. 26, 8017–8022 (2014)
F. Aliyu, T. Sheltami, Development of an energy-harvesting toxic and combustible gas sensor for oil and gas industries. Sens. Actuators B 231, 265–275 (2016)
H.J. Kim, J.H. Lee, Highly sensitive and selective gas sensors using p-type oxide semiconductors: overview. Sens. Actuators B 192, 607–627 (2014)
V.D.B. Michael, N.T. Rose, S.F.J. De Wekker, Potential of a low-cost gas sensor for atmospheric methane monitoring. Sens. Actuators B 238, 501–509 (2017)
D.Z. Zhang, Z.M. Yang, Z.L. Wu, G.K. Dong, Metal-organic frameworks-derived hollow zinc oxide/cobalt oxide nanoheterostructure for highly sensitive acetone sensing. Sens. Actuators B 283, 42–51 (2019)
D.Z. Zhang, Z.L. Wu, X.Q. Zong, Flexible and highly sensitive H2S gas sensor based on in situ polymerized SnO2/rGO/PANI ternary nanocomposite with application in halitosis diagnosis. Sens. Actuators B 289, 32–41 (2019)
S.T. Navale, D.K. Bandgar, S.R. Nalage, Synthesis of Fe2O3 nanoparticles for nitrogen dioxide gas sensing applications. Ceram. Int. 39, 6453–6460 (2013)
T. Wang, Y. Liu, Q. Fang, Low temperature synthesis wide optical band gap Al and (Al, Na) co-doped ZnO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 2341–2345 (2011)
J.J. Hassan, M.A. Mahdi, C.W. Chin, A high-sensitivity room-temperature hydrogen gas sensor based on oblique and vertical ZnO nanorod arrays. Sens. Actuators B 176, 360–367 (2013)
L.A. Patil, L.S. Sonawane, D.G. Patil, Room temperature ammonia gas sensing using MnO2-modified ZnO thick film resistors. J. Mod. Phys. 02, 1214–1220 (2011)
L.M. Song, H. Yue, H.Y. Li, Hierarchical porous ZnO microflowers with ultra-high ethanol gas-sensing at low concentration. Chem. Phys. Lett. 699, 1–7 (2018)
X. Xie, X.Z. Wang, J. Tian, Growth of porous ZnO single crystal hierarchical architectures with ultrahigh sensing performances to ethanol and acetone gases. Ceram. Int. 43, 1121–1128 (2017)
J. Xie, H. Wang, M. Duan, Synthesis and photocatalysis properties of ZnO structures with different morphologies via hydrothermal method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 6358–6363 (2011)
F. Liu, X. Chu, Y. Dong, Acetone gas sensors based on graphene-ZnFe2O4 composite prepared by solvothermal method. Sens. Actuators B 188, 469–474 (2013)
D. Bradshaw, S. Elhankari, L. Lupicaspagnolo, Supramolecular templating of hierarchically porous metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 45, 5431–5443 (2015)
F.D. Qu, H.F. Jiang, M.H. Yang, MOF-derived Co3O4/NiCo2O4 double-shelled nanocages with excellent gas sensing properties. Mater. Lett. 190, 75–78 (2017)
M.J. Wang, T.Y. Hou, Z.R. Shen, MOF-derived Fe2O3: phase control and effects of phase composition on gas sensing performance. Sens. Actuators B 292, 171–179 (2019)
G.Y. Xu, B. Ding, L.F. Shen, Sulfur embedded in metal organic framework-derived hierarchically porous carbon nanoplates for high performance lithium–sulfur battery. J. Mater. Chem. A. 1, 4490–4496 (2013)
W.H. Li, X.F. Wua, N. Han, MOF-derived hierarchical hollow ZnO nanocages with enhanced low-concentration VOCs gas-sensing performance. Sens. Actuators B 225, 158–166 (2016)
Z. Zhao, X. Ma, A. Kasik, Gas separation properties of metal organic framework (MOF-5) membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52, 1102–1108 (2013)
D. Han, P. Song, S. Zhang, Enhanced methanol gas-sensing performance of Ce-doped In2O3 porous nanospheres prepared by hydrothermal method. Sens. Actuators B 216, 488–496 (2015)
Z.R. Ma, P. Song, Z.X. Yang, Q. Wang, Trimethylamine detection of 3D rGO/mesoporous In2O3 nanocomposites at room temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 465, 625–634 (2019)
L. Liu, Y.T. Zhao, P. Song, Z.X. Yang, Q. Wang, ppb level triethylamine detection of yolk-shell SnO2/Au/Fe2O3 nanoboxes at low-temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 476, 391–401 (2019)
Y. Kimitsuka, E. Hosono, S. Ueno, Fabrication of porous cubic architecture of ZnO using Zn-terephthalate MOFs with characteristic microstructures. Inorg. Chem. 52, 14028–14033 (2013)
J.K. Zhu, D.M. Song, T. Pu, Two-dimensional porous ZnCo2O4 thin sheets assembled by 3D nanoflake array with enhanced performance for aqueous asymmetric supercapacitor. Chem. Eng. J. 336, 679–689 (2018)
L. Zhang, J. Zhao, H. Lu, Highly sensitive and selective dimethylamine sensors based on hierarchical ZnO architectures composed of nanorods and nanosheet-assembled microspheres. Sens. Actuators B 171, 1101–1109 (2012)
W. Li, H. Xu, T. Zhai, High-sensitivity, high-selectivity, and fast-recovery-speed triethylamine sensor based on ZnO micropyramids prepared by molten salt growth method. J. Alloy. Compd. 295, 2930–2936 (2017)
S. Zhang, M. Yang, K. Liang, An acetone gas sensor based on nanosized Pt-loaded Fe2O3 nanocubes. Sens. Actuators B 290, 59–67 (2019)
P. Song, Q. Wang, Z.X. Yang, Preparation, characterization and acetone sensing properties of Ce-doped SnO2 hollow spheres. Sens. Actuators B 173, 839–846 (2012)
H.Y. Yang, X.L. Cheng, X.F. Zhang, A novel sensor for fast detection of triethylamine based on rutile TiO2 nanorod arrays. Sens. Actuators B 205, 322–328 (2014)
D.X. Ju, H.Y. Xu, Z.W. Qiu, Near room temperature, fast-response, and highly sensitive triethylamine sensor assembled with au-loaded ZnO/SnO2 core-shell nanorods on flat alumina substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 7, 19163–19171 (2015)
X.Q. Qiao, Z.W. Zhang, D.F. Hou, Tunable MoS2/SnO2 P − N heterojunctions for an efficient trimethylamine gas sensor and 4-nitrophenol reduction catalyst. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6, 12375–12384 (2018)
B. Liu, L.H. Zhang, H. Zhao, Synthesis and sensing properties of spherical flowerlike architectures assembled with SnO2 submicron rods. Sens. Actuators B 173, 643–651 (2012)
Y.Z. Lv, C.R. Li, L. Guo, Triethylamine gas sensor based on ZnO nanorods prepared by a simple solution route. Sens. Actuators B 141, 85–88 (2009)
M.Z. Wu, X.F. Zhang, S. Gao, Construction of monodisperse vanadium pentoxide hollow spheres via a facile route and triethylamine sensing property. CrystEngComm 15, 10123–10131 (2013)
F.H. Zhang, H.Q. Yang, X.L. Xie, Controlled synthesis and gas-sensing properties of hollow sea urchin-like –Fe2O3 nanostructures and –Fe2O3 nanocubes. Sens. Actuators B 141, 381–389 (2009)
W.H. Jiang, D.D. Wei, S.F. Zhang, The facile synthesis of MoO3 microsheets and their excellent gas-sensing performance toward triethylamine: high selectivity, excellent stability and superior repeatability. New J. Chem. 42, 15111 (2018)
Acknowledgement
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61102006) and Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (Nos. ZR2018LE006 and ZR2015EM019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Wei, Q., Song, P. et al. Porous ZnO cubes derived from metal–organic frameworks with excellent sensing performance triethylamine. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 838–847 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02594-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02594-1