Abstract
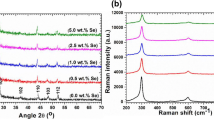
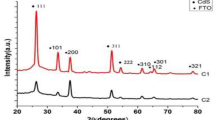
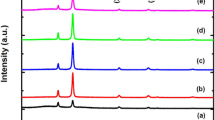
In current article authors aim is to present an insight on structural, opto-nonlinear-limiting properties of Cadmium sulfide (CdS) thin films affected by various concentrations of tellurium (Te) doping. Hence, the thin films of pure and Te:CdS were fabricated by spray pyrolysis technique by keeping the substrate at 300 °C. X-ray diffraction and FT-Raman spectroscopy analyses confirmed the hexagonal phase of CdS. The values of Lave, ρave and εave are found in range of 18–20 nm, 2.6–3 nm−2 and 1.7–1.9, respectively. Furthermore, the energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy/scanning electron microscopy mapping (SEM) confirmed the presence and homogeneous doping of Te in CdS. SEM study shows that the fabricated films are free from any pin holes and possess very fine nanostructures. The optical transparency of grown films was noticed ~ 70%, which is quite impressive for colored materials. The absorption index, refractive index values are found in range of 0.04 to 0.25, 1.25 to 3.2 in 200 to 2500 nm wavelength region. The direct energy gap of CdS was noticed to be reduced from 2.44 to 2.35 eV (ΔEg = 0.09) with Te doping content. Photoluminescence emission spectra contains an intense green emission band at ~ 528 ± 4 nm. The dielectric constant and optical conductivity were noticed in range of 1.5 to 10 and 0.02 to 0.6 (× 105), respectively. The values of third order susceptibility and nonlinear refractive index was found of the order of 10−10 esu. The output power of the 532 nm laser passed from films is found to be reducing with increasing the Te content in CdS films. Hence, the deposited films of Te:CdS will be more applicable as optical limiter in sensor device protection from intense lights.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Göde, S. Ünlü, Synthesis and characterization of CdS window layers for PbS thin film solar cells. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 90, 92–100 (2019)
F. Khodam, A.R. Amani-Ghadim, S. Aber, Preparation of CdS quantum dot sensitized solar cell based on ZnTi-layered double hydroxide photoanode to enhance photovoltaic properties. Sol. Energy 181, 325–332 (2019)
K. Ravichandran, P. Philominathan, Investigations on microstructural and optical properties of CdS films fabricated by a low-cost, simplified spray technique using perfume atomizer for solar cell applications. Sol. Energy 82, 1062–1066 (2008)
C.R. Kagan, P. Andry (eds.), Thin-film transistors (CRC Press (Marcel and Dekker Inc.), New York, 2003). ISBN 0-203-91177-6
J. Jie, W. Zhang, Y. Jiang, X. Meng, Y. Li, S. Lee, Photoconductive characteristics of single-crystal CdS nanoribbons. Nano Lett. 6, 1887–1892 (2006)
J. Hernández-Borja, Y. Vorobiev, R. Ramírez-Bon, Thin film solar cells of CdS/PbS chemically deposited by an ammonia-free process. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 95, 1882–1888 (2011)
W. Wondmagegn, I. Mejia, A. Salas-Villasenor, H. Stiegler, M. Quevedo-Lopez, R. Pieper, B. Gnade, CdS thin film transistor for inverter and operational amplifier circuit applications. Microelectron. Eng. 157, 64–70 (2016)
Y.L. Song, Y. Li, F.Q. Zhou, P.F. Ji, X.J. Sun, M.L. Wan, M.L. Tian, White electroluminescence from a prototypical light-emitting diode based on CdS/Si heterojunctions. Mater. Lett. 196, 8–11 (2017)
B.-G. An, Y.W. Chang, H.-R. Kim, G. Lee, M.-J. Kang, J.-K. Park, J.-C. Pyun, Highly sensitive photosensor based on in situ synthesized CdS nanowires. Sens. Actuators B 221, 884–890 (2015)
Y. Zhao, M. Yuan, Y. Chen, Y. Huang, J. Lian, S. Cao, H. Li, L. Wu, Size controllable preparation of sphere-based monolayer CdS thin films for white-light photodetectors. Ceram. Int. 44, 2407–2412 (2018)
Y. Cui, C.M. Lieber, Functional nanoscale electronic devices assembled using silicon nanowire building blocks. Science 291, 851–853 (2001)
D.-H. Kim, N. Lu, R. Ghaffari, J.A. Rogers, Inorganic semiconductor nanomaterials for flexible and stretchable bio-integrated electronics. NPG Asia Mater. 4, e15 (2012)
X. Hu, G. Li, J.C. Yu, Design, fabrication, and modification of nanostructured semiconductor materials for environmental and energy applications. Langmuir 26, 3031–3039 (2009)
C.M. Lieber, Nanoscale science and technology: building a big future from small things. MRS Bull. 28, 486–491 (2003)
E. Comini, C. Baratto, G. Faglia, M. Ferroni, A. Vomiero, G. Sberveglieri, Quasi-one dimensional metal oxide semiconductors: preparation, characterization and application as chemical sensors. Prog. Mater Sci. 54, 1–67 (2009)
Y.-P. Sun, R. Guduru, F. Lin, T. Whiteside, Preparation of nanoscale semiconductors through the rapid expansion of supercritical solution (RESS) into liquid solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 39, 4663–4669 (2000)
P. Ball, L. Garwin, Science at the atomic scale. Nature 355, 761–766 (1992)
S.B. Mirov, V. Fedorov, D. Martyshkin, I. Moskalev, M. Mirov, V. Gapontsev, Progress in mid-IR Cr 2 + and Fe 2 + doped II-VI materials and lasers. Opt. Mater. Express 1, 898–910 (2011)
H. Haug, Optical nonlinearities and instabilities in semiconductors (Academic Press Inc., San Diego, 2012)
C.-H. Lai, M.-Y. Lu, L.-J. Chen, Metal sulfide nanostructures: synthesis, properties and applications in energy conversion and storage. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 19–30 (2012)
J. Jie, W. Zhang, I. Bello, C.-S. Lee, S.-T. Lee, One-dimensional II–VI nanostructures: synthesis, properties and optoelectronic applications. Nano today 5, 313–336 (2010)
J.P. Enrı́quez, X. Mathew, Influence of the thickness on structural, optical and electrical properties of chemical bath deposited CdS thin films. Sol. Energy Mater. Solar Cells 76, 313–322 (2003)
A. Cortes, H. Gómez, R.E. Marotti, G. Riveros, E.A. Dalchiele, Grain size dependence of the bandgap in chemical bath deposited CdS thin films. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 82, 21–34 (2004)
A.E. Rakhshani, A.S. Al-Azab, Characterization of CdS films prepared by chemical-bath deposition. J. Phys. 12, 8745 (2000)
D.-S. Chuu, C.-M. Dai, Quantum size effects in CdS thin films. Phys. Rev. B 45, 11805 (1992)
E. Çetinörgü, C. Gümüş, R. Esen, Effects of deposition time and temperature on the optical properties of air-annealed chemical bath deposited CdS films. Thin Solid Films 515, 1688–1693 (2006)
C. Guillén, M. Martınez, J. Herrero, Accurate control of thin film CdS growth process by adjusting the chemical bath deposition parameters. Thin Solid Films 335, 37–42 (1998)
Z.R. Khan, M. Shkir, V. Ganesh, S. AlFaify, I.S. Yahia, H.Y. Zahran, Linear and nonlinear optics of CBD grown nanocrystalline F doped CdS thin films for optoelectronic applications: an effect of thickness. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 5386–5395 (2018)
D. Boosagulla, S. Mandati, R. Allikayala, B.V. Sarada, Room temperature pulse electrodeposition of CdS thin films for application in solar cells and photoelectrochemical cells. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 7, P440–P446 (2018)
B. Altiokka, A.K. Yildirim, Electrodeposition of CdS thin films at various pH values. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 72, 687–691 (2018)
S. Yılmaz, İ. Polat, M. Tomakin, T. Küçükömeroğlu, S. Töreli, E. Bacaksız, Sm-doped CdS thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis: a structural, optical, and electrical examination. Appl. Phys. A 124, 502 (2018)
G. Balaji, R. Balasundaraprabhu, S. Prasanna, N. Prabavathy, M. Venkatraman, V. Asokan, N. Muthukumarasamy, M. Kannan, K. Sivakumaran, Investigations on Hot-wall deposited cadmium sulphide buffer layer for thin film solar cell. Mater. Lett. 222, 82–87 (2018)
S. Yılmaz, İ. Polat, M. Tomakin, S. Töreli, T. Küçükömeroğlu, E. Bacaksız, Optical and electrical optimization of dysprosium-doped CdS thin films. J. Mater. Sci. 29, 14774–14782 (2018)
S. Yılmaz, The investigation of spray pyrolysis grown CdS thin films doped with flourine atoms. Appl. Surf. Sci. 357, 873–879 (2015)
S. Aksu, E. Bacaksiz, M. Parlak, S. Yılmaz, I. Polat, M. Altunbaş, M. Türksoy, R. Topkaya, K. Özdoğan, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Mn diffusion-doped CdS thin films prepared by vacuum evaporation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 130, 340–345 (2011)
S. Butt, N.A. Shah, A. Nazir, Z. Ali, A. Maqsood, Influence of film thickness and In-doping on physical properties of CdS thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 587, 582–587 (2014)
A. Rmili, F. Ouachtari, A. Bouaoud, A. Louardi, T. Chtouki, B. Elidrissi, H. Erguig, Structural, optical and electrical properties of Ni-doped CdS thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. J. Alloys Compd. 557, 53–59 (2013)
A. Podestà, N. Armani, G. Salviati, N. Romeo, A. Bosio, M. Prato, Influence of the fluorine doping on the optical properties of CdS thin films for photovoltaic applications. Thin Solid Films 511–512, 448–452 (2006)
N. Saxena, P. Kumar, V. Gupta, Target swapping in PLD: an efficient approach for CdS/SiO 2 and CdS: Ag (1%)/SiO 2 nanocomposite thin films with enhanced luminescent properties. J. Lumin. 186, 62–67 (2017)
S.R. Rosario, I. Kulandaisamy, A.M.S. Arulanantham, K. Deva Arun Kumar, S. Valanarasu, M. Shkir, A. Kathalingam, S. AlFaify, Fabrication and characterization of lead sulfide (PbS) thin film based heterostructure (FTO/CdS/PbS/Ag) solar cell by nebulizer spray method. Mater. Res. Express 6, 056416 (2019)
S. SanthoshKumarJacob, I. Kulandaisamy, S. Valanarasu, A.M.S. Arulanantham, M. Shkir, A. Kathalingam, N. Soundaram, Improving the conductivity of cuprous oxide thin film by doping calcium via feasible nebulizer spray technique for solar cell (FTO/ZnO/Ca-Cu2O). Mater. Res. Express 6, 046405 (2019)
A. Arulanantham, S. Valanarasu, A. Kathalingam, M. Shkir, H.-S. Kim, An investigation on SnS layers for solar cells fabrication with CdS, SnS 2 and ZnO window layers prepared by nebulizer spray method. Appl. Phys. A 124, 776 (2018)
R.D. Prabu, S. Valanarasu, V. Ganesh, M. Shkir, S. AlFaify, A. Kathalingam, S. Srikumar, R. Chandramohan, An effect of temperature on structural, optical, photoluminescence and electrical properties of copper oxide thin films deposited by nebulizer spray pyrolysis technique. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 74, 129–135 (2018)
Y.Y. Ma, R.H. Bube, Properties of CdS films prepared by spray pyrolysis. J. Electrochem. Soc. 124, 1430–1435 (1977)
J. Hiie, T. Dedova, V. Valdna, K. Muska, Comparative study of nano-structured CdS thin films prepared by CBD and spray pyrolysis: annealing effect. Thin Solid Films 511, 443–447 (2006)
K.M. Saleh, Study influence of substrate temperature on optical properties of CdS thin films prepared by chemical spray pyrolysis. Ibn AL-Haitham J. Pure Appl. Sci. 32, 7–16 (2019)
R. Panda, V. Rathore, M. Rathore, V. Shelke, D. Jain, P. Gupta, V. Ganesan, Structural and photo-conducting properties of Cd1-xAlxS thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 2100 (AIP Publishing, New York), p. 020186
R. Murugesan, S. Sivakumar, K. Karthik, P. Anandan, M. Haris, Structural, optical and magnetic behaviors of Fe/Mn-doped and co-doped CdS thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis method. Appl. Phys. A 125, 281 (2019)
Z.R. Khan, M. Shkir, A.S. Alshammari, V. Ganesh, S. AlFaify, M. Gandouzi, Structural, linear and third order nonlinear optical properties of sol-gel grown Ag-CdS nanocrystalline thin films. J. Electron. Mater. 48(2), 1122–1132 (2019)
R. Panda, V. Rathore, M. Rathore, V. Shelke, N. Badera, L.S. Chandra, D. Jain, M. Gangrade, T. Shripati, V. Ganesan, Carrier recombination in Cu doped CdS thin films: photocurrent and optical studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 5086–5093 (2012)
A.A. Aboud, A. Mukherjee, N. Revaprasadu, A.N. Mohamed, The effect of Cu-doping on CdS thin films deposited by the spray pyrolysis technique. J. Mater. Res. Technol, 8, 2021–2030 (2019)
K. Karthik, S. Pushpa, M. Madhukara Naik, M. Vinuth, Influence of Sn and Mn on structural, optical and magnetic properties of spray pyrolysed CdS thin films. Mater. Res. Innov. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/14328917.2019.1597436
S. Yılmaz, İ. Polat, M. Tomakin, E. Bacaksız, A research on growth and characterization of CdS: Eu thin films. Appl. Phys. A 125, 67 (2019)
S. Yılmaz, İ. Polat, M. Tomakin, E. Bacaksız, Determination of optimum Er-doping level to get high transparent and low resistive Cd 1–x Er x S thin films. J. Mater. Sci. 30, 5662–5669 (2019)
N. Badera, B. Godbole, S. Srivastava, P. Vishwakarma, L.S. Chandra, D. Jain, M. Gangrade, T. Shripathi, V. Sathe, Ganesan, Quenching of photoconductivity in Fe doped CdS thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 7042–7048 (2008)
Z. Wei, Y. Wang, L. Ma, X.S. Wu, Structural and optical properties of Te doped CdS films. Physica B 525, 98–103 (2017)
R. Banerjee, S. Ray, A.K. Barua, Properties of tellurium doped vacuum evaporated CdS thin films. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 21, L43–L45 (1982)
B. Lokhande, P. Patil, M. Uplane, Studies on structural, optical and electrical properties of boron doped zinc oxide films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique. Physica B 302, 59–63 (2001)
S. Sebastian, I. Kulandaisamy, A. Arulanantham, S. Valanarasu, A. Kathalingam, M. Shkir, S. AlFaify, Enhancement in photovoltaic properties of Nd: SnS films prepared by low-cost NSP method. Rare Metals (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01295-2
A. Khan, M. Shkir, M.A. Manthrammel, V. Ganesh, I.S. Yahia, M. Ahmed, A.M. El-Toni, A. Aldalbahi, H. Ghaithan, S. AlFaify, Effect of Gd doping on structural, optical properties, photoluminescence and electrical characteristics of CdS nanoparticles for optoelectronics. Ceram. Int. 45, 10133–10141 (2019)
K. Murakoshi, H. Hosokawa, M. Saitoh, Y. Wada, T. Sakata, H. Mori, M. Satoh, S. Yanagida, Preparation of size-controlled hexagonal CdS nanocrystallites and the characteristics of their surface structures. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 94, 579–586 (1998)
M. Shkir, A. Khan, A.M. El-Toni, A. Aldalbahi, I.S. Yahia, S. AlFaify, Structural, morphological, opto-nonlinear-limiting studies on Dy:PbI2/FTO thin films derived facilely by spin coating technique for optoelectronic technology. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 130, 189–196 (2019)
M. Shkir, M.T. Khan, S. AlFaify, Novel Nd-doping effect on structural, morphological, optical, and electrical properties of facilely fabricated PbI2 thin films applicable to optoelectronic devices. Appl. Nanosci. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-00983-w
M.T. Khan, M. Shkir, A. Almohammedi, S. AlFaify, Fabrication and characterization of La doped PbI2 nanostructured thin films for opto-electronic applications. Solid State Sci. 90, 95–101 (2019)
M. Shkir, M. TaukeerKhan, V. Ganesh, I.S. Yahia, B. Ul Haq, A. Almohammedi, P.S. Patil, S.R. Maidur, S. AlFaify, Influence of Dy doping on key linear, nonlinear and optical limiting characteristics of SnO2 films for optoelectronic and laser applications. Opt. Laser Technol. 108, 609–618 (2018)
M. Arif, M. Shkir, S. AlFaify, A. Sanger, P.M. Vilarinho, A. Singh, Linear and nonlinear optical investigations of N:ZnO/ITO thin films system for opto-electronic functions. Opt. Laser Technol. 112, 539–547 (2019)
R. Kostić, N. Romčević, Raman spectroscopy of CdS nanoparticles. Phys. Status Solidi C 1(11), 2646–2649 (2004)
R. Rossetti, S. Nakahara, L.E. Brus, Quantum size effects in the redox potentials, resonance Raman spectra, and electronic spectra of CdS crystallites in aqueous solution. J. Chem. Phys. 79, 1086–1088 (1983)
C.T. Tsai, D.S. Chuu, G.L. Chen, S.L. Yang, Studies of grain size effects in rf sputtered CdS thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 79, 9105–9109 (1996)
K. Sooklal, L.H. Hanus, H.J. Ploehn, C.J. Murphy, A blue-emitting CdS/dendrimer nanocomposite. Adv. Mater. 10, 1083–1087 (1998)
M. Munirah, Spectroscopic studies of solegel grown CdS nanocrystalline thin films for optoelec-tronic devices. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16, 1894–1898 (2013)
M. Shkir, S. AlFaify, Effect of Gd3 + doping on structural, morphological, optical, dielectric, and nonlinear optical properties of high-quality PbI2 thin films for optoelectronic applications. J. Mater. Res. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.121
S. AlFaify, M. Shkir, A facile one pot synthesis of novel pure and Cd doped PbI2 nanostructures for electro-optic and radiation detection applications. Opt. Mater. 88, 417–423 (2019)
S. Alfaify, M. Shkir, A one pot room temperature synthesis of pure and Zn doped PbI2 nanostructures and their structural, morphological, optical, dielectric and radiation studies. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 14, 255–260 (2019)
O. Zelaya-Angel, L. Hernandez, O. de Melo, J.J. Alvarado-Gil, R. Lozada-Morales, C. Falcony, H. Vargas, R. Ramirez-Bon, Band-gap shift in CdS: phase transition from cubic to hexagonal on thermal annealing. Vacuum 46, 1083–1085 (1995)
A. Fernández-Pérez, M. Sandoval-Paz, Synthesis and characterization of chemically deposited CdS thin films without toxic precursors. J. Phys. 720, 012029 (2016)
C. Lokhande, S. Pawar, Optical and transport properties of chemical bath deposited CdS: Al films. Solid State Commun. 44, 1137–1139 (1982)
A.E. Abken, D.P. Halliday, K. Durose, Photoluminescence study of polycrystalline photovoltaic CdS thin film layers grown by close-spaced sublimation and chemical bath deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 064515 (2009)
K. Usha, R. Sivakumar, C. Sanjeeviraja, Optical constants and dispersion energy parameters of NiO thin films prepared by radio frequency magnetron sputtering technique. J. Appl. Phys. 114, 123501 (2013)
D. Panda, T.-Y. Tseng, Growth, dielectric properties, and memory device applications of ZrO2 thin films. Thin Solid Films 531, 1–20 (2013)
M.V. Fischetti, W.G. Vandenberghe, Dielectric properties of semiconductors, in Advanced Physics of Electron Transport in Semiconductors and Nanostructures, ed. by M.V. Fischetti, W.G. Vandenberghe (Springer, Cham, 2016), pp. 223–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-01101-1
M.-S. Kim, K.-G. Yim, J.-S. Son, J.-Y. Leem, Effects of Al concentration on structural and optical properties of Al-doped ZnO thin films. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 33, 1235–1241 (2012)
T. Mitsuyu, K. Ohkawa, T. Karasawa, Nonlinear optical thin-film, US Patent 5,079,594 (7 Jan 1992)
M. Yoshida, Y. Manabe, T. Mitsuyu, I. Tanahashi, Nonlinear, optical thin-films and manufacturing method thereof, U.S. Patent No. 5,113,473 (12 May 1992)
S. Mathew, B. Samuel, A. Mujeeb, M. Kailasnath, V.P.N. Nampoori, C.P. Girijavallabhan, Effect of Au coating on optical properties of CdS nanoparticles and their optical limiting studies. Opt. Mater. 72, 673–679 (2017)
A.A. Ziabari, F. Ghodsi, Growth, characterization and studying of sol–gel derived CdS nanoscrystalline thin films incorporated in polyethyleneglycol: effects of post-heat treatment. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 105, 249–262 (2012)
M. Frumar, J. Jedelský, B. Frumarova, T. Wagner, M. Hrdlička, Optically and thermally induced changes of structure, linear and non-linear optical properties of chalcogenides thin films. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 326, 399–404 (2003)
R. Adair, L. Chase, S.A. Payne, Nonlinear refractive index of optical crystals. Phys. Rev. B 39, 3337 (1989)
H. Ticha, L. Tichy, Semiempirical relation between non-linear susceptibility (refractive index), linear refractive index and optical gap and its application to amorphous chalcogenides. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 4(2), 381–386 (2002)
J. Fournier, E. Snitzer, The nonlinear refractive index of glass. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 10, 473–475 (1974)
C.C. Wang, Empirical relation between the linear and the third-order nonlinear optical susceptibilities. Phys. Rev. B 2, 2045 (1970)
J. Wynne, Nonlinear optical spectroscopy of χ(3) in LiNb O 3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 29, 650 (1972)
H. Nasu, J.D. Mackenzie, Nonlinear optical properties of glasses and glass or gel-based composites. Opt. Eng. 26, 262102 (1987)
P. Sharma, S. Katyal, Linear and nonlinear refractive index of As–Se–Ge and Bi doped As–Se–Ge thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 107, 113527 (2010)
M. Shkir, V. Ganesh, S. AlFaify, I. Yahia, H. Zahran, Tailoring the linear and nonlinear optical properties of NiO thin films through Cr 3 + doping. J. Mater. Sci. 29, 6446–6457 (2018)
E. Shaaban, M. El-Hagary, H.S. Hassan, Y.A. Ismail, M. Emam-Ismail, A. Ali, Structural, linear and nonlinear optical properties of co-doped ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. A 122, 20 (2016)
L.W. Tutt, A. Kost, Optical limiting performance of C60 and C70 solutions. Nature 356, 225 (1992)
G.L. Wood, W.W. Clark, M.J. Miller, G.J. Salamo, E.J. Sharp, Evaluation of passive optical limiters and switches. Proc. SPIE 1105, Materials for Optical Switches, Isolators, and Limiters, International Society for Optics and Photonics, Proc. SPIE 1105, Materials for Optical Switches, Isolators, and Limiters, 30 August 1989, pp. 154–181
L.G. Holmen, M.W. Haakestad, Optical limiting properties and z-scan measurements of carbon disulfide at 2.05 μm wavelength. JOSA B 33, 1655–1660 (2016)
P. Poornesh, P.K. Hegde, G. Umesh, M. Manjunatha, K. Manjunatha, A. Adhikari, Nonlinear optical and optical power limiting studies on a new thiophene-based conjugated polymer in solution and solid PMMA matrix. Opt. Laser Technol. 42, 230–236 (2010)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through Research Groups Program under Grant No. R.G.P. 2/42/40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shkir, M., Shaikh, S.S. & AlFaify, S. An investigation on optical-nonlinear and optical limiting properties of CdS: an effect of Te doping concentrations for optoelectronic applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 17469–17480 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02097-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02097-z