Abstract
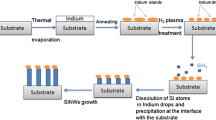
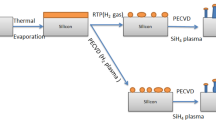
In this work, we report on vapor–liquid–solid growth of silicon nanowires (SiNWs) catalyzed by indium, a low-eutectic post-transition metal. The indium catalyst is synthesized ex situ by annealing indium-coated substrates using two different annealing processes: rapid thermal annealing (RTA) and conventional process. The effect of annealing parameters on indium catalyst properties is studied. We show that after conventional annealing at 600 °C during 45 min, the indium layer is cracked into elongated and inhomogeneous islands of different sizes. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis depicts in addition to pure indium planes the presence of new peaks attributed to indium oxide planes formed during annealing. While by using RTA process, oxide-free indium particles were successfully grown in one step by during short time (5 min) at 400 and 450 °C. Quasi-spherical and homogeneously distributed indium particles were obtained at 450 °C. A comparative study between SiNWs catalyzed by indium catalyst prepared following the two different processes was carried out. The indium oxide presence negatively affected the catalytic property of indium, resulting in a lower density of the grown SiNWs. An improvement of the SiNWs density was achieved with RTA-annealed catalyst, as more indium particles were present to act as active catalyst to the growth. The catalyst annealing conditions also affected the size of the SiNWs, with shorter wires with RTA process. However, the shape of the SiNWs was similar in both studied cases, where the wires were bent and kinked. The morphology investigation of the SiNWs also shows that the SiNWs have a core–shell structures consisting of amorphous and crystalline silicon.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Morin, D. Kohen, V. Tileli, P. Faucherand, M. Levis, A. Brioude, B. Salem, T. Baron, S. Perraud, Patterned growth of high aspect ratio silicon wire arrays at moderate temperature. J. Cryst. Growth 321, 151–156 (2011)
T.I. Kamins, R.S. Williams, D.P. Basile, T. Hesjedal, J.S. Harris, Ti-catalyzed Si nanowires by chemical vapor deposition: microscopy and growth mechanisms. J. Appl. Phys. 89, 1008 (2001)
Y. Ke, X. Weng, J.M. Redwing, C.M. Eichfeld, T.R. Swisher, S.E. Mohney, Y.M. Habib, Fabrication and electrical properties of Si nanowires synthesized by Al catalyzed vapor-liquid-solid growth. Nano Lett. 9, 4494 (2009)
J. Arbiol, A.F. Morral, S. Estrade, F. Peiro, B. Kalache, P.R. Cabarrocas, J.R. Morante, Influence of the (111) twinning on the formation of diamond cubic/diamond hexagonal heterostructures in Cu-catalyzed Si nanowires. J. Appl. Phys. 104, 064312 (2008)
S. Conesa-Boj, I. Zardo, S. Estrade, L. Wei, P.J. Alet, P.R. Cabarrocas, J.R. Morante, F. Peiro, A.F. Morral, Defect formation in Ga-catalyzed silicon nanowires. J. Arbiol. Cryst. Growth Des. 10, 1534 (2010)
T. Baron, M. Gordon, F. Dhalluin, C. Ternon, P. Ferret, P. Gentile, Si nanowire growth and characterization using a microelectronics-compatible catalyst:PtSi. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 233111 (2006)
R.S. Wagner, W.C. Ellis, Vapor-liquid-solid mechanism of single crystal growth. Appl. Phys. Lett. 4, 89 (1964)
W.M. Bullis, Properties of gold in silicon. Solid-State Electron. 9, 143 (1966)
M. Abdolirad, R. Khalilzadeh, M. Alijanianzadeh, Growth of silicon nanowires from bio-templated gold nanoparticles. Superlatt. Microstruct. 120, 370 (2018)
N. Ahmed, P.B. Bhargav, A. Rayerfrancis, B. Chandra, P. Ramasamy, Study the effect of plasma power density and gold catalyst thickness on Silicon Nanowires growth by Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapour Deposition. Mater. Lett. 219, 127 (2018)
M. Legallais, T.T.T. Nguyen, M. Mouis, B. Salem, E. Robin, P. Chenevier, C. Ternon, An innovative large scale integration of silicon nanowire-based field effect transistors. Solid-State Electron. 143, 97 (2018)
B. Le Borgne, L. Pichon, A.C. Salaun, B. Le Bihan, A. Jolivet-Gougeon, S. Martin, R. Roger, O. De Sagazan, Bacteria electrical detection using 3D silicon nanowires based resistor. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 273, 1794 (2018)
P. Dytrych, V. Drinek, J. Bumba, F. Kastanek, O. Solcova, Silicon nanowires based photoanode for hydrogen evolution. Int. J. Hydrog Energy 43, 18136 (2018)
R.R. Kumar, K.N. Rao, A.R. Phani, Growth of silicon nanowires by electron beam evaporation using indium catalyst. Mater. Lett. 66, 110 (2012)
M.Y. Tabassi, R.B. Zaghouani, M. Khelil, K. Khirouni, W. Dimassi, Study of indium catalyst thickness effect on PECVD-grown silicon nanowires properties. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 9717 (2017)
Y. Zhang, H. Ago, J. Liu, M. Yumura, K. Uchida, S. Ohshima, S. Iijima, J. Zhu, X. Zhang, The synthesis of In, In2O3 nanowires and In2O3 nanoparticles with shape-controlled. J. Cryst. Growth 264, 363 (2004)
I. Rodriguez-Sanchez, M.C. Blanco, M.A. Lopez-Quintela, Electrochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 9683 (2000)
N.H. Chou, X.L. Ke, P. Schiffer, R.E. Schaak, Room-temperature chemical synthesis of shape-controlled indium nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 8140 (2008)
R.A. Ganeev, A.I. Ryasnyanskiy, U. Chakravarty, P.A. Naik, H. Srivastava, M.K. Tiwari, P.D. Gupta, Structural, optical and nonlinear optical properties of indium nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation. Appl. Phys. B 86, 337 (2007)
X. Xie, X. Zeng, P. Yang, C. Wang, Q. Wang, In-situ formation of indium catalysts to synthesize crystalline silicon nanowires on flexible stainless steel substrates by PECVD. J. Cryst. Growth 347, 7 (2012)
L. Yu, B. O’Donnel, P.J. Alet, P.R. iCabarrocas, All-in situ fabrication and characterization of silicon nanowires on TCO/glass substrates for photovoltaic application. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 94, 1855 (2010)
S.K. Chong, B. Goh, C. Dee, S. Rahman, Effect of substrate to filament distance on formation and photoluminescence properties of indium catalyzed silicon nanowires using hot-wire chemical vapor deposition. Thin Solid Films 529, 153 (2013)
A. Convertino, M. Cuscun, G. Nicotra, C. Spinella, L. Felisari, G. Fortunato, F. Martelli, Low-temperature growth of In-assisted silicon. Cryst. Growth 335, 10 (2011)
F. Iacopi, Y. Eichhammer, C. Massy, P.M. Vereecken, N. Moelans, O. Richard, D. Smeets, B. Blanpain, S. De Gendt, M. Heyns, Indium-assisted growth of Si nanowires: perespectives on controlled growth for CMOS applications, in MRS Proceedings, 1080. https://doi.org/10.1557//proc-1080-o05-01
I. Zardo, L. Yu, S. Conesa Boj, S. Estrade, P.J. Alet, J. Rossler, M. Frimmer, P.R. Cabarrocas, F. Peiro, J. Arbiol, J.R. Morante, A.F. Moral, Gallium assisted plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition of silicon nanowires. Nanotechnology 20, 155602 (2009)
L. Yu, P.J. Alet, G. Picardi, I. Maurin, P.R.I. Cabarrocas, Synthesis, morphology and compositional evolution of silicon nanowires directly grown on SnO2 substrates. Nanotechnology 19, 485605 (2008)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benabderrahmane Zaghouani, R., Yaacoubi Tabassi, M., Khirouni, K. et al. Vapor–liquid–solid silicon nanowires growth catalyzed by indium: study of indium oxide effect. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 9758–9766 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01311-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01311-2