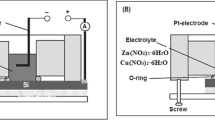
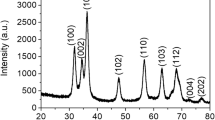
Abstract
The rising demand for optoelectronic devices to be operable in adverse environments necessitates the sensing of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Here, a highly sensitive, fast responding Cu doped zinc oxide nanoparticles (Nps) based UV photodetector (PD) is reported. For the first time, Cu doped ZnO Nps are grown via forced hydrolysis of acetate salt of metals in a polyol medium. Various characterization methods including X-Ray diffraction, high resolution transmission electron microscopy and Fourier infrared spectroscopy are used to testify the presence of Cu element in ZnO Nps, although the diffuse reflectance and PL characterization are used to study the optical properties. The performance of the PD has been established by photocurrent measurements under different power density. Our device exhibited good photoresponse under UV illumination (375 nm) at 1 V bias voltage. Furthermore, the response of the PD is much better than other detectors based on oxide semiconductors nanostructures, and, especially, it shows a higher responsivity as compared with other photodetectors. In addition, achieved a highest responsivity of 40.12 A/W, quick response (rise/decay time of 0.8 s/3 s) and high sensitivity (2 × 104) for the Cu doped ZnO Nps annealed at 300 °C. It is established that the devices under higher power incident light show much lower 1/f noise. These results are meaningful to the noise control and performance improvement in the development of Schottky diode based PD-devices.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Shabannia, High-sensitivity UV photodetector based on oblique and vertical Co-doped ZnO nanorods. Mater. Lett. 214, 254–256 (2018)
S.S. Shendage, V.L. Patil, S.A. Vanalakar, S.P. Patil, N.S. Harale, J.L. Bhosale, P.S. Patil, Sensitive and selective NO2 gas sensor based on WO3 nanoplates. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 240, 426–433 (2017)
S. Dhar, T. Majumder, P. Chakraborty, S.P. Mondal, DMSO modified PEDOT: PSS polymer/ZnO nanorods Schottky junction ultraviolet photodetector: Photoresponse, external quantum efficiency, detectivity, and responsivity augmentation using N doped graphene quantum dots. Org. Electro. 53, 101–110 (2017)
V.L. Patil, S.A. Vanalakar, P.S. Patil, J.H. Kim, Fabrication of nanostructured ZnO thin films based NO2 gas sensor via SILAR technique. Sens Actuators B Chem 239, 1185–1193 (2017)
Z. Bai, Y. Zhang, Self-powered UV–visible photodetectors based on ZnO/Cu2O nanowire/electrolyte heterojunctions. J. Alloy. Compd. 675, 325–330 (2016)
M.L. Yola, T. Eren, N. Atar, S. Wang, Adsorptive and photocatalytic removal of reactive dyes by silver nanoparticle-colemanite ore waste. Chem. Eng. J. 242, 333–340 (2014)
V.K. Gupta, N. Atar, M.L. Yola, Z. Üstündağ, L. Uzun, A novel magnetic Fe@ Au core–shell nanoparticles anchored graphene oxide recyclable nanocatalyst for the reduction of nitrophenol compounds. Water Res. 48, 210–217 (2014)
V.K. Gupta, S. Agarwal, A. Olgun, Hİ. Demir, M.L. Yola, N. Atar, Adsorptive properties of molasses modified boron enrichment waste based nanoclay for removal of basic dyes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 34, 244–249 (2016)
S.P. Patil, V.L. Patil, S.S. Shendage, N.S. Harale, S.A. Vanalakar, J.H. Kim, P.S. Patil, Spray pyrolyzed indium oxide thick films as NO2 gas sensor. Ceram. Int. 42(14), 16160–16168 (2016)
S.A. Vanalakar, V.L. Patil, N.S. Harale, S.A. Vhanalakar, M.G. Gang, J.Y. Kim, J.H. Kim, Controlled growth of ZnO nanorod arrays via wet chemical route for NO2 gas sensor applications. Sens Actuators B Chem. 221, 1195–1201 (2015)
S.J. Young, Y.H. Liu, Low-frequency noise properties of MgZnO nanorod ultraviolet photodetectors with and without UV illumination. Sens. Actuators, A 269, 363–368 (2018)
B.A. Gozeh, A. Karabulut, A. Yildiz, F. Yakuphanoglu, Solar light responsive ZnO nanoparticles adjusted using Cd and La Co-dopant photodetector. J. Alloy. Compd. 732, 16–24 (2018)
Y.T. Kwon, S.O. Kang, J.A. Cheon, Y. Song, J.J. Lee, Y.H. Choa, Fabrication of a Graphene/ZnO based pn junction device and its ultraviolet photoresponse properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 415, 2–7 (2017)
P.S. Shewale, N.K. Lee, S.H. Lee, K.Y. Kang, Y.S. Yu, Ti doped ZnO thin film basedUV photodetector: fabrication and characterization. J. Alloy. Compd. 624, 251–257 (2015)
H.S. Al-Salman, M.J. Abdullah, Fabrication and characterization of undoped andcobalt-dopedZnO Based UV photodetector prepared by RF-sputtering. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 29, 1139–1145 (2013)
R. Rajalakshmi, S. Angappane, Synthesis, characterization and photoresponsestudy of undoped and transition metal (Co, Ni, Mn) doped ZnO thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 178, 1068–1075 (2013)
Z. Banu Bahsi, A. Yavuz Oral, Effects of Mn and Cu doping on the microstructures andoptical properties of sol–gel derived ZnO thin films. Opt. Mater. 29, 672 (2007)
A. Mezni, A. Mlayah, V. Serin, L.S. Smiri, Synthesis of hybrid Au–ZnO nanoparticles using a one pot polyol process. Mater. Chem. Phys. 147, 496–503 (2014)
I.B. Elkamel, N. Hamdaoui, A. Mezni, R. Ajjel, L. Beji, High responsivity and 1/f noise of an ultraviolet photodetector based on Ni doped ZnO nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 8, 32333–32343 (2018)
T. Ghosh, D. Basak, Highly enhanced ultraviolet photoresponse property in Cudoped and Cu–Li co-doped ZnO films. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 42, 1453045 (2009)
F.M. Li, C.T. Zhu, S.Y. Ma, A.M. Sun, H.S. Song, X.B. Li, X. Wang, Investigation of the blue–green emission and UV photosensitivity of Cu-doped ZnO films. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16, 1079–1085 (2013)
M. Mittal, M. Sharma, O.P. Pandey, UV–Visible light induced photocatalytic studies of Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation method. Sol. Energy 110, 386–397 (2014)
J.R. Torres-Hernández, E. Ramírez-Morales, L. Rojas-Blanco, J. Pantoja-Enriquez, G. Oskam, F. Paraguay-Delgado, G. Pérez-Hernández, Structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of ZnO nanoparticles modified with Cu. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 37, 87–92 (2015)
P.D. Cullity, Elements of X-ray Diffraction (Addison-Wesley, Boston, 1978)
R. Javed, M. Usman, B. Yücesan, M. Zia, E. Gürel, Effect of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles on physiology and steviol glycosides production in micropropagated shoots of Stevia rebaudianaBertoni. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 110, 94–99 (2017)
S. Fabbiyola, V. Sailaja, L.J. Kennedy, M. Bououdina, J.J. Vijaya, Optical and magnetic properties of Ni-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 694, 522–531 (2017)
M. Anbuvannan, M. Ramesh, G. Viruthagiri, N. Shanmugam, N. Kannadasan, Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by biological method. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 143, 304–308 (2015)
A.C. Janaki, E. Sailatha, S. Gunasekaran, Synthesis, characteristics and antimicrobial activity of ZnO nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 144, 17–22 (2015)
V. Shanmugam, K.S. Jeyaperumal, Investigations of visible light driven Sn and Cu doped ZnO hybrid nanoparticles for photocatalytic performance and antibacterial activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 449, 617–630 (2018)
K.P. Raj, K. Sadayandi, Effect of temperature on structural, optical and photoluminescence studies on ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by the standard co-precipitation method. Phys. B 487, 1–7 (2016)
D. Verma, A.K. Kole, P. Kumbhakar, Red shift of the band-edge photoluminescence emission and effects of annealing and capping agent on structural and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 625, 122–130 (2015)
S.A. Vanalakar, S.S. Mali, M.P. Suryawanshi, N.L. Tarwal, P.R. Jadhav, G.L. Agawane, J.Y. Kim, Photoluminescence quenching of a CdS nanoparticles/ZnO nanorods core–shell heterogeneous film and its improved photovoltaic performance. Opt. Mater. 37, 766–772 (2014)
A.N. Mallika, A.R. Reddy, K.S. Babu, C. Sujatha, K.V. Reddy, Structural and photoluminescence properties of Mg substituted ZnO nanoparticles. Opt. Mater. 36, 879–884 (2014)
M. Ashokkumar, S. Muthukumaran, Effect of Ni doping on electrical, photoluminescence and magnetic behavior of Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 162, 97–103 (2015)
S.K. Shahi, N. Kaur, J.S. Shahi, V. Singh, Investigation of morphologies, photoluminescence and photocatalytic properties of ZnO nanostructures fabricated using different basic ionic liquids. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 6, 3718 (2016)
C. Abinaya, M. Marikkannan, M. Manikandan, J. Mayandi, P. Suresh, V. Shanmugaiah, J.M. Pearce, Structural and optical characterization and efficacy of hydrothermal synthesized Cu and Ag doped zinc oxide nanoplate bactericides. Mater. Chem. Phys. 184, 172–182 (2016)
J. Xia, X. Huang, L.Z. Liu, M. Wang, L. Wang, B. Huang, D.D. Zhu, J.J. Li, C.Z. Gu, X.M. Meng, Nanoscale 6, 8949 (2014)
O. Lopez-Sanchez, D. Lembke, M. Kayci, A. Radenovic, A. Kis, Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 497 (2013)
S.R. Tamalampudi, Y.Y. Lu, U.R. Kumar, R. Sankar, C.D. Liao, B.K. Moorthy, C.H. Cheng, F.C. Chou, Y.T. Chen, Nano Lett. 14, 2800 (2014)
S.L. Zhao, H.A. Wang, Y. Zhou, L. Liao, Y. Jiang, X. Yang, G.C. Chen, M. Lin, Y. Wang, H.L. Peng, Z.F. Liu, Nano Res. 8, 288 (2015)
C. Wang, S.J. Chang, Y.K. Su, Y. Chiou, C. Chang, T. Lin, H. Liu, J.J. Tang, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 20, 485 (2005)
S.I. Inamdar, V.V. Ganbavle, K.Y. Rajpure, ZnO based visible–blind UV photodetector by spray pyrolysis. Superlattices Microstruct. 76, 253–263 (2014)
M.S. Mahdi, K. Ibrahim, N.M. Ahmed, A. Hmood, F.I. Mustafa, S.A. Azzez, M. Bououdina, High performance and low-cost UV–Visible–NIR photodetector based on tin sulphide nanostructures. J. Alloy. Compd. 735, 2256–2262 (2018)
Y. Wei, Z. Ren, A. Zhang, P. Mao, H. Li, X. Zhong, J. Wang, Hybrid organic/PbS quantum dot bilayer photodetector with low dark current and high detectivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28(11), 1706690 (2018)
Z. Ke, Z. Yang, M. Wang, M. Cao, Z. Sun, J. Shao, Low temperature annealed ZnO film UV photodetector with fast photoresponse. Sens. Actuators, A 253, 173–180 (2017)
F.H. Alsultany, Z. Hassan, N.M. Ahmed, N.G. Elafadill, H.R. Abd, Effects of ZnO seed layer thickness on catalyst-free growth of ZnO nanostructures for enhanced UV photoresponse. Opt. Laser Technol. 98, 344–353 (2018)
A.S. Al-Asadi, L.A. Henley, S. Ghosh, A. Quetz, I. Dubenko, N. Pradhan, M. Terrones, Fabrication and characterization of ultraviolet photosensors from ZnO nanowires prepared using chemical bath deposition method. J. Appl. Phys. 119(8), 084306 (2016)
R. Sugumar, S. Angappane, Influence of substrate heating and annealing on the properties and photoresponse of manganese doped zinc oxide thin films. Superlattices Microstruct. 110, 57–67 (2017)
K.H. Kim, K.C. Park, D.Y. Ma, J. Appl. Phys. 81, 7764 (1997)
S. Park, S. Kim, G.J. Sun, D.B. Byeon, S.K. Hyun, W.I. Lee, C. Lee, ZnO-core/ZnSe-shell nanowire UV photodetector. J. Alloy. Compd. 658, 459–464 (2016)
K. Singh, I. Rawal, R. Punia, R. Dhar, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy investigations of band offsets in Ga0. 02Zn0. 98O/ZnO heterojunction for UV photodetectors. J. Appl. Phys. 122(15), 155301 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben Elkamel, I., Hamdaoui, N., Mezni, A. et al. Synthesis and characterization of Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles for stable and fast response UV photodetector at low noise current. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 9444–9454 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01276-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01276-2