Abstract
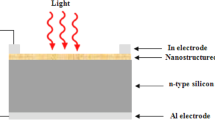
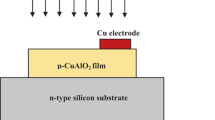
In the current work, CuO thin films (~ 110 nm) are grown by employing chemical bath deposition (CBD) method on Si substrate for fabricating the p-CuO/n-Si heterojunction photodetectors. The as-grown films are annealed at 250, 550 and 850 °C for 10 min in Ar ambient for tuning optoelectronic properties of the as-grown CuO thin films. Comparative study on systematic annealing of the film within 250–550 °C indicates a morphological change of the as-grown CuO film to nano-fiber type with its chemical composition remaining unchanged. A variation of refractive index and dielectric constant in the range of 2.65–2.93 and 7.2–9.7, and a change of absorption coefficient and bandgap from 1.33 × 105 to 6.06 × 105 cm− 1 and 1.5 to 2.16 eV have been observed. The current–voltage characteristics both in dark and illuminated conditions suggest that the annealing of CuO film at 550 °C provides the best performance in terms of photo-to-dark current ratio and photoresponsivity. A respective enhancement of 5.07 and 10% for the photo-to-dark ratio and photoresponsivity has been observed for the 550 °C annealed sample.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Awgouropoules, T. Joaminides, C. Papadopoulou, J. Batista, S. Hocever, H.K. Matralis, A comparative study of Pt/γ-Al2O3, Au/α-Fe2O3 and CuO–CeO2 catalyst for the selective oxidation of carbon monoxide in excess hydrogen. Catal. Today 75, 157–167 (2002)
K. Nagase, Y. Zhang, Y. Kodama, J. Kakuta, Dynamic study of the oxidation state of copper in the course of carbon monoxide oxidation over powdered CuO and Cu2O. J. Catal. 187, 123–130 (1999)
J. Sultana, S. Paul, A. Karmakar, R. Yi, G.K. Dalapati, S. Chattopadhyay, Chemical bath deposited (CBD) CuO thin films on n-silicon substrate for electronic and optical applications: impact of growth time. Appl. Surf. Sci. 418, 380–387 (2016)
S. Chandrasekaran, A novel single step synthesis, high efficiency and cost effective photovoltaic applications of oxidized copper nano particles. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 109, 220–226 (2013)
S. Wang, C.H. Hsiao, S.J. Chang, Z.Y. Jiao, S.J. Young, S.C. Hung, B.R. Huang, ZnO branched nanowires and the p-CuO/n-ZnO heterojunction nanostructured photodetector. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 12(2), 263–269 (2013)
T. Mahalingam, J.S.P. Chitra, J.P. Chu, H. Moon, H.J. Kwon, Y.D. Kim, Photoelectrochemical solar cell studies on electroplated cuprous oxide thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 17, 519–523 (2006)
Z. Jin, X. Zhang, Y. Li, S. Li, G. Lu, 5.1% apparent quantum efficiency for stable hydrogen generation over eosin-sensitized CuO/TiO2 photocatalyst under visible light irradiation. Catal. Commun. 8, 1267–1273 (2007)
L. Fu, J. Gao, T. Zhang, Q. Cao, L.C. Yang, Y.P. Wu, R. Holze, Effect of Cu2O coating on graphite as anode material of lithium ion battery in PC-based electrolyte. J. Power Sources 171, 904–907 (2007)
Y. Nakamura, H. Zhuang, A. Kishimoto, O. Okada, H. Yanagida, Enhanced CO and CO2 gas sensitivity of the CuO/ZnO heterocontact made by quenched CuO ceramics. J. Electrochem. Soc. 145, 632–637 (1998)
J. Chen, N.Y. Huang, S.Z. Deng, J.C. She, N.S. Xu, W.X. Zhang, X.G. Wen, S.H. Yang, Effects of light illumination on field emission from CuO nanobelt arrays. Appl. Phy. Lett. 86, 157–159 (2005)
P.C. Dai, H.A. Mook, G. Aeppli, S.M. Hayden, F. Dogan, Resonance as a measure of pairing cor-relations in the high-Tc superconductor YBa2Cu3O6.6. Nature 406, 965–968 (2000)
S. Paul, J. Sultana, A. Karmakar, A. Bhattacharyya, S. Chattopadhyay, Investigation of the comparative photovoltaic performance of n-ZnO nanowire/P-Si and n-ZnO nanowire/p-CuO heterojunctions grown by chemical bath deposition method OPTIK 164, 745–748 (2018)
T. Karlsson, A. Roos, Observation of diffuse interference in reflectance from oxide-coated metals. Sol. Energy Mater. 10, 105 (1984)
D. Wu, Q. Zhang, M. Tao, LSDA+ U study of cupric oxide: electronic structure and native point defects. Phys. Rev. B 73(23), 206–235 (2006)
J.S. Sagu, T.A.N. Peiris, K.G.U. Wijayantha, Rapid and simple potentiostatic deposition of copper (II) oxide thin films. Electrochem. Commun. 42, 68–71 (2014)
J. Sultana, A. Das, A. Das, N.R. Saha, A. Karmakar, S. Chattopadhyay, Characterization of nano-powder grown ultra-thin film p-CuO/n-Si hetero-junctions by employing vapour-liquid-solid method for photovoltaic applications. Thin Solid Films 612, 331–336 (2016)
E.A. Christie, Spectrally selective blacks for energy collection. International Solar Energy Society Conference (1970), pp. 1–7
A.O. Musa, T. Akomolafe, M.J. Carter, Production of cuprous oxide, a solar cell material, by thermal oxidation and a study of its physical and electrical properties. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 51, 305–316 (1998)
M.A. Brookshier, C.C. Chusuei, D.W. Goodman, Control of CuO particle size on SiO2 by spin coating. Langmuir 15, 2043–2046 (1999)
J.F. Xu, W. Ji, Z.X. Shen, S.H. Tang, X.R. Ye, D.Z. Jia, X.Q. Xin, Preparation of CuO and characterization nanocrystals. J. Solid State Chem. 147, 516–519 (1999)
Y.K. Su, C.M. Shen, H.T. Yang, L. Li, H.J. Gao, Controlled synthesis of highly ordered CuO nano-wire arrays by template based sol–gel route. Trans. Nonferr. Metals Soc. China 17, 783–786 (2007)
X.L. Tang, L. Ren, L.N. Sun, W.G. Tian, M.H. Cao, C.W. Hu, A solvothermal route to Cu2O nano-cubes and Cu nanoparticles. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 22, 547–551 (2006)
C.O. Yuan, H.F. Jiang, C. Lin, S.J. Liao, Shape and size-controlled electrochemical synthesis of cupric oxide nanocrystals. J. Cryst. Growth 303, 400–406 (2007)
J.T. Chen, F. Zhang, J. Wang, G.A. Zhang, B.B. Mian, X.Y. Fan, D. Yan, P.X. Yan, CuO nanowires synthesized by thermal oxidation route. J. Alloy. Compd. 454, 268–273 (2008)
P.K. Nair, M.T.S. Nair, V.M. Garcia, O.L. Arenas, Y. Pena, A. Castillo, I.T. Ayala, O. Gomezdaza, A. Sanchez, J. Campos, H. Hu, R. Suarez, M.E. Rincon, Semiconductor thin films by chemical bath deposition for solar energy related applications. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 52, 313–344 (1998)
P.K. Nair, P. Parmananda, M.T.S. Nair, Mathematical model simulating the growth of compound semiconductor thin films via chemical bath deposition. J. Cryst. Growth 206, 68–74 (1999)
L.F. Koao, B.F. Dejene, H.C. Swart, T.E. Motaung, Dependent of reaction time on Cu-doped ZnO nanostructures prepared by chemical bath method. Int. J. Lumin. Appl. 5, 54–61 (2015)
J.Q. Qi, H.Y. Tian, L.T. Li, H.L.W. Chan, Fabrication of CuO nanoparticle interlinked microsphere cages by solution method. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2, 107–111 (2007)
Z. jian, W. Hejing, The physical meaning of 5 basic parameters for an X-ray diffraction peak and their application. Chin. J. Geochem. 22, 38–44 (2003)
S.L. Mammah, F.E. Opara, V.B.O. Pepple, J.E.E. Ntibi, S.C. Ezugwu, F.I. Ezema, Annealing effect on the optical and solid state properties of cupric oxide thin films deposited using the Aqueous Chemical Growth (ACG) method. Nat. Sci. 5, 389–399 (2013)
K.H. Yoon, W.J. Choi, D.H. Kang, Photoelectrochemical properties of copper oxide thin films coated on an n-Si substrate. Thin Solid Films 372, 250–256 (2000)
J.P. Tobin, W. Hirschwald, J. Cunningham, XPS and XAES studies of transient enhancement of Cu1 at CuO surfaces during vacuum outgassing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 16, 441–452 (1983)
Z. Zhang, P. Wang, Highly stable copper oxide composite as an effective photocathode for water splitting via a facile electrochemical synthesis strategy. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 2456–2464 (2012)
Y.L. Liu, L. Liao, J.C. Li, C.X. Pan, From copper nanocrystalline to CuO nanoneedle array: synthesis, growth mechanism, and properties. J. Phys. Chem. 111, 5050–5056 (2007)
T. Ito, H. Yamaguchi, K. Okabe, T. Masumi, Single-crystal growth and characterization of Cu2O and CuO. J. Mater. Sci. 33, 3555–3566 (1998)
J. Tang, L. Brzozowski, D.A.R. Barkhouse, X.H. Wang, R. Debnath, R. Wolowiec, E. Palmiano, L. Levina, A.G.P. Abraham, D. Jamakosmanovic, E.H. Sargent, Quantum dot photovoltaics in the extreme quantum confinement regime: the surface-chemical origins of exceptional air-and light-stablity. ACS Nano 4, 869–878 (2010)
R. Sahay, J. Sundaramurthy, P. Suresh Kumar, V. Thavasi, S.G. Mhaisalkar, and S.Ramakrishna, “Synthesis and characterization of CuO nanofibers and investigation for its suitability as blocking layer in ZnO NPs based dye sensitized solar cell and as photocatalyst in organic dye degradation. J. Solid State Chem. 186, 261–267 (2012)
P. Chand, A. Gaur, A. Kumar, U.K. Gaur, Effect of NaOH molar concentration on morphology, optical and ferroelectric properties of hydrothermally grown CuO nanoplates. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process 38, 72–80 (2015)
Z. Liang, Y. Wang, M. Su, W. Mai, J. Xu, W. Xie, P. Liu, Improving the quality of the Si/Cu2O interface by methyl-group passivation and its application in photovoltaic devices, Adv. Mater. Interfaces (2017) https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201600833
G. Akgul, F.A. Akgul, E. Mulazimoglu, H.E. Unalan, R. Turan, Fabrication and characterization of copper oxide-silicon nanowire heterojunction photodiodes. J. Phys. D 47, 1–7 (2014)
Acknowledgements
Miss. Jenifar Sultana and Somdatta Paul would like to acknowledge the DST inspire program and University Grants Commission (UGC), India, for providing financial support to pursue their research. The authors would also like to acknowledge the DST Purse program and Center of Excellence (COE), TEQIP for providing infrastructure and financial support to conduct this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sultana, J., Paul, S., Karmakar, A. et al. Optimizing the thermal annealing temperature: technological route for tuning the photo-detecting property of p-CuO thin films grown by chemical bath deposition method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 12878–12887 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9407-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9407-3