Abstract
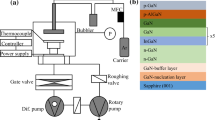
By using metal organic chemical vapor deposition technique, InGaN/GaN solar cell (SC) structure is deposited over sapphire (Al2O3) wafer as GaN buffer and GaN epitaxial layers. Structural properties of InGaN/GaN/Al2O3 SC structure is investigated by using high resolution X-ray diffraction technique dependent on In content. By using reciprocal space mapping, reciprocal space data are converted to w–θ data with a software. These w–θ data and full width at half maximum data are used for calculating lattice parameters. When compared with w–θ measurements in literature it is seen that especially a- lattice parameter is found very near to universal value from RSM. It is calculated as 3.2650 nm for sample A (S.A) GaN layer and 3.2570 nm for sample B (S.B) GaN layer on (105) asymmetric plane. Strain and stress calculations are made by using these lattice parameters. Strain and stress are calculated as 0.02363 and 8.6051 GPa for S.A GaN layer respectively. Other results are given in tables in the results and discussion section of this article. Edge, screw and mixed type dislocations are calculated as mosaic defects. All these calculations are made for two samples on (002) symmetric and (105) asymmetric planes. As a result it is seen that measurements by using RSM give more sensitive results. a- lattice parameter calculated with this technique is the best indicator of this result.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Strite, H. Morkoc, Gan, Ain, and Inn: a review. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 10(4), 1237–1266 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1116/1.585897
J.W. Orton, C.T. Foxon, Group III nitride semiconductors for short wavelength light-emitting devices. Rep. Prog. Phys. 61(1), 1 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1088/0034-4885/61/1/001
B.G. Streetman, Elements of Solid State Electronics, in Prentice Hall Solid State Physics Series (Texas University, Austin, 1998), p. 0133356035
Y.D. Qi et al., Comparison of blue and green InGaN/GaN multiple-quantum-well light-emitting diodes grown by metalorganic vapor phase epitaxy. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2005). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1866634
K.S. Ramaiah et al., A comparative study of blue, green and yellow light emitting diode structures grown by metal organic chemical vapor deposition. Solid-State Electron. 50(2), 119–124 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sse.2005.10.028
T.K. Kim et al., Influence of growth parameters on the properties of InGaN/GaN multiple quantum well grown by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition. Curr. Appl. Phys. 7(5), 469–473 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4841575
Y. Nanishi, Y. Saito, T. Yamaguchi, RF-molecular beam epitaxy growth and properties of InN and related alloys. Japn. J. Appl. Phys. 1 42(5a), 2549–2559 (2003)
J. Singh, Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of semiconductor Structures (Cambridge University Press, New York, 2003)
G. Bauer, W. Richter, Optical Characterization of Epitaxial Semiconductor Layers (Springer, Berlin, 1996). ISBN 978-3-642-79678-4
D.K. Bower, B.K. Tanner, High Resolution X-ray Diffractometry and Topography (Taylor & Francis Group, London, 2002). ISBN 9780850667585
M.K. Ozturk et al., Structural analysis of an InGaN/GaN based light emitting diode by X-ray diffraction. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 21(2), 185–191 (2010)
M.K. Ozturk et al., Strain-stress analysis of AlGaN/GaN heterostructures with and without an AlN buffer and interlayer. Strain 47, 19–27 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-1305.2009.00730.x
C. Kisielowski, Strain in GaN thin films and heterostructures. Semiconductors Semimetals 57, 275–317 (1999)
Y. Bas, In x Ga 1–x N (x = 0.075; 0.090; 0.100) Mavi LED’lerin Mikroyapısal Kusurlarının Ters Örgü Uzay Haritası İle İncelenmesi (Gazi University, Ankara, 2015)
M.A. Moram, M.E. Vickers, X-ray diffraction of III-nitrides. Rep. Prog. Phys. 72(3), 036502 (2009)
M. Schuster et al., Determination of the chemical composition of distorted InGaN GaN heterostructures from X-ray diffraction data. J. Phys. D 32(10a), A56–A60 (1999)
B.G. Streetmann, Solid State Electronics Devices (Prentice-Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, 1995)
S. Nakamura, Gan growth using gan buffer layer. Japn. J. Appl. Phys. 2 30(10a), L1705–L1707 (1991)
S.M. Sze, Semiconductor Devices, Physics and Technology (Wiley, New York, 2002)
R. Chierchia et al., Microstructure of heteroepitaxial GaN revealed by X-ray diffraction. J. Appl. Phys. 93(11), 8918–8925 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilgili, A.K., Akpinar, Ö., Kurtulus, G. et al. Structural properties of InGaN/GaN/Al2O3 structure from reciprocal space mapping. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 12373–12380 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9351-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9351-2