Abstract
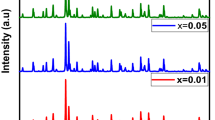
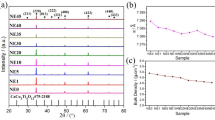
This study reported the effect of Eu substitutions on the conductivity and dielectric properties of Y3−xEuxAl5O12 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 0.1), YAG:xEu3+. All products were fabricated by solid state route. The formation of YAG was approved through X-ray diffraction powder diffraction and high-resolution transmission electron microscope. It was found that the lattice parameters are increasing with increase the substitution content due to the difference in ionic radii between Y3+ and Eu3+. Electrical and dielectric properties of YAG (Y3Al5O12) and YAG:xEu3+ ceramics were investigated extensively for a variety of concentrations (0.00 ≤ x ≤ 0.1) of the substitutional Eu3+ ion from the 4f lanthanide group. The temperature dependence of dielectric loss, dielectric constant, loss tangent and ac/dc conductivity were examined up to 5.0 MHz to understand the electrical and dielectric properties for both doped and undoped YAG ceramics. The experimental results revealed that Eu3+ ion substitutions (especially x = 0.05) in YAG ceramics meaningfully influence the lossy mechanisms, conductivity and dielectric constant which is probably due to the contribution to the conduction mechanism of the 4f–Eu and 3d–Al ions. So, this can be incorporated at the exceptional sites of both Oh (octahedral) and Td (tetrahedral) symmetries in YAG: xEu3+ ceramics.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Zhou, C.A. Randall, L.X. Pang, H. Wang, X.G. Wu, J. Guo, G.Q. Zhang, L. Shui, X. Yao, Microwave dielectric properties of Li2(M2+)2Mo3O12 and Li3(M3+)2Mo3O12 (M = Zn, Ca, Al, and In) lyonsite-related-type ceramics with ultra-low sintering temperatures. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 802–805 (2011)
Q.L. Zhang, H. Yang, H.P. Sun, A new microwave ceramic with low- permittivity for LTCC applications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 28, 605–609 (2008)
I.M. Reaney, D. Iddles, I.M. Reaney, D. Iddles, Microwave dielectric ceramics for resonators and filters in mobile phone networks. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 89, 2063–2072 (2006)
B. Ullah, W. Lei, Z.-Y. Zou, X.-H. Wang, W.Z. Lu, Synthesis strategy, phase-chemical structure and microwave dielectric properties of paraelectric Sr(1–3x/2)CexTiO3 ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 695, 648–655 (2017)
Z.Y. Shen, Q.G. Hu, Y.M. Li, Z.M. Wang, W.Q. Luo, Y. Hong, Z.X. Xie, R.H. Liao, X. Tan, Structure and dielectric properties of Re0.02Sr0.97TiO3 (Re = La, Sm, Gd, Er) ceramics for high-voltage capacitor applications. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 551–2555 (2013)
J. Krupka, K. Derzakowski, M. Tobar, J. Hartnett, R.G. Geyer, Complex permittivity of some ultra-low loss dielectric crystals at cryogenic temperatures. Meas. Sci. Technol. 10, 387–392 (1999)
Q. Liu, J. Liu, J. Li, et al., Solid-state reactive sintering of YAG transparent ceramics for optical applications. J. Alloys Compd. 616, 81–88 (2014)
J.M. Yang, S.M. Jeng, S. Chang, Fracture behavior of directionally solidified Y3Al5O12/Al2O3 eutectic fiber. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 79, 1218 (1996)
A. Kareiva, J. Harlan, C.B. MacQueen D, R.L. Cook, A.R. Barron, Carboxylate-substituted alumoxanes as processable precursors to transition metal—aluminum and lanthanide—aluminum mixed-metal oxides: atomic scale mixing via a new transmetalation reaction. Chem. Mater. 8, 2331 (1996)
R. Asakura, T. Isobe, K. Kurokawa, T. Takagi, H. Aizawa, M. Ohkubo, Effects of citric acid additive on photoluminescence properties of YAG: Ce3+ nanoparticles synthesized by glycothermal reaction. J. Lumin. 127, 416–422 (2007)
X. Li, H. Liu, J. Wang, H. Cui, F. Han, YAG:Ce nano-sized phosphor particles prepared by a solvothermal method. Mater. Res. Bull. 39, 1923–1930 (2004)
Y. Hakuta, T. Haganuma, K. Sue, T. Adschiri, K. Arai, Continuous production of phosphor YAG:Tb nanoparticles by hydrothermal synthesis in supercritical water. Mater. Res. Bull. 38, 1257–1265 (2003)
G. Seeta, R. Raju, H.C. Jung, J.Y. Park, J.W. Chung, B.K. Moon, J.H. Jeong, S.M. Son, J.H. Kim, Sintering temperature effect and luminescent properties of Dy3+: YAG nanophosphor. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 12(6), 1273–1278 (2010)
H.M.H. Fadlalla, C.C. Tang, E.M. Elssfah, F. Shi, Synthesis and characterization of single crystalline YAG: Eu nano-sized powder by sol–gel method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 109, 436–439 (2008)
M.L. Saladino, E. Caponetti, Co-precipitation synthesis of Nd: YAG nanopowders II: the effect of Nd dopant addition on luminescence properties. Opt. Mater. 32, 89–93 (2009)
W. Jin, W. Yin, S. Yun, M. Tang, T. Xu, B. Kang, H. Huang, Microwave dielectric properties of pure YAG transparent ceramics. Mater. Lett. 173, 47–49 (2016)
S. Maletic, D. Popovic, D. Cerovic, J. Dojcilovic, Study of structural and spectral characteristics of crystal Y3Al5O12, Al2O3 and SrTiO3 doped by 3d- or 4f- ions. Contemp. Mater. 2, 190 (2016)
I.A. Auwal, B. Unal, H. Güngüneş, S.E. Shirsath, A. Baykal, Dielectric properties, cationic distribution calculation and hyperfine interactions of La3+ and Bi3+ doped strontium hexaferrites. Ceram. Int. 42, 9100 (2016)
E. Talebian, M. Talebia, A general review on the derivation of Clausius–Mossotti relation. Optik 124, 2324 (2013)
M.A. Almessiere, B. Unal, A. Baykal, Dielectric and microstructural properties of YAG:Dy3+ ceramics. J. Rare Earths (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2018.04.011 (In press)
M.A. Almessiere, N.M. Ahmed, I. Massoudia, A.L. Al-Otaibia, A.A. Al-shehria, M. Al Shafouri, Study of the structural and luminescent properties of Ce3+ and Eu3+ co-doped YAG synthesized by solid state reaction. Optik 158, 152–163 (2018)
X. Niu, J. Xun, Y. Zhang, The spectroscopic properties of Dy3+ and Eu3+ co-doped Y3Al5O12 (YAG) phosphors for White LED. Progr. Nat. Sci. 25, 209–214 (2015)
M. Skruodiene, M. Misevicius, M. Sakalauskaite, A. Katelnikovas, R. Skaudzius, Doping effect of Tb3+ ions on luminescence properties of Y3Al5O12: Cr3+ phosphor. J. Lumin. 179, 355–360 (2016)
Y. Zhou, J. Lin, M. Yu, S. Wang, Comparative study on the luminescent properties of Y3Al5O12:RE3+ (RE: Eu, Dy) phosphors synthesized by three methods. J. Alloys Compd. 375, 93 (2004)
S.A. Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi, Low temperature synthesis and luminescence properties of YAG:Eu nanopowders prepared by modified sol-gel method. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 21, 2443 (2011)
Q. Liu, Y. Yuan, J. Li, J. Liu, C. Hu, M. Chen, L. Lina, H. Kou, Y. Shi, W. Liu, H. Chen, Y. Pan, J. Guo, Preparation and properties of transparent Eu:YAG fluorescent ceramics with different doping concentrations. Ceram. Int. 40, 8539–8545 (2014)
S. Verma, J. Chand, M. Singh, Mössbauer, magnetic, dielectric and dc conductivity of Al3+ ions substituted Mg-Mn-Ni nano ferrite synthesized by citrate precursor method”. Adv. Mater. Lett. 4, 310 (2013)
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to the Institute for Research & Medical Consultations (IRMC) of Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faysal University for the financial assistance to pursue this research (Grant No: 2018-IRMC-S-1). The technical assistance provided by Core Labs of King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) are highly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almessiere, M.A., Unal, B., Baykal, A. et al. The impact of Eu3+ ion substitution on dielectric properties of Y3−xEuxAl5O12 (0.00 ≤ x ≤ 0.10) ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 2489–2500 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0523-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0523-x