Abstract
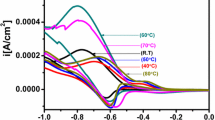
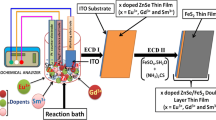
Mn2+ doped FeS2 thin films were deposited on ITO coated conducting glass substrate at 50 °C in an aqueous medium by simple electrochemical deposition technique. The structural and phase purity of the Mn2+ doped FeS2 thin films were investigated using XRD technique. The XRD analysis revelaed that the fabricated thin films were cubic structure along with the (200) plane preferential orientation. The diffraction peak slightly shifted towards lower 2θ values which confirmed that doping of Mn ions into FeS2 host matrixes. The calculated band gap energy of Mn2+ doped FeS2 thin films showed a red shift of absorption edge compared to undoped FeS2 thin film. EIS indicated that Mn2+ doped FeS2 thin films showed lower charge transfer resistance with better conductivity nature compared to undoped sample. Moreover, the photo electrochemical measurements carried out for the optimized Mn2+ doped FeS2 thin film which revealed the faster migration of photo-induced charge-carriers. Electro catalytic activity of Mn-doped FeS2 thin films were studied for the redox reaction of iodide/triiodide (I−/I3−) by using cyclic voltammetry measurement.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Khalid, M.A. Malik, D.J. Lewis, P. Kevin, E. Ahmed, Y. Khan, P. O’Brien, Transition metal doped pyrite (FeS2) thin films: structural properties and evaluation of optical band gap energies. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 12068–12076 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TC03275J
P. Prabukanthan, S. Thamaraiselvi, G. Harichandran, Single step electrochemical deposition of p-type undoped and Co2+ doped FeS2 thin films and performance in heterojunction solid solar cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 164, D581–D589 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0991709jes
M. Gong, A. Kirkeminde, S. Ren, Symmetry-defying iron pyrite (FeS2) nanocrystals through oriented attachment. Sci. Rep. 3, 1–6 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02092
S. Bae, D. Kim, W. Lee, Degradation of diclofenac by pyrite catalyzed Fenton oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 134–135, 93–102 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.12.031
I. Zutic, J. Fabian, S. Das Sarma, Spintronics: fundamentals and applications. Rev. Mod. Phys. 76, 323–410 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.76.323
J. Xia, J.Q. Jiao, B.L. Dai, W.D. Qiu, S.X. He, W.T. Qiu, P.K. Shen, L.P. Chen, Fecile synthesis of FeS2 nanocrystals and their magnetic and electrochemical properties. RSC Adv. 3, 6132–6140 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA22405H
S. Shukla, W. Joel, Q. Ager, T. Xiong, Sritharan, Scientific and technological assessment of iron pyrite for use in solar devices. Energy Technol. 6, 8–20 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/ente.201700638
M.G. Gong, A. Kirkeminde, N. Kumar, H. Zhao, S.Q. Ren, Ionic-passivated FeS2 photocapacitors for energy coversion and storage. Chem. Commun. 49, 9260–9262 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CC45088K
S.L. Liu, M.M. Li, S. Li, H.L. Li, L. Yan, Synthesis and adsorption/photocatalysis performance of pyrite FeS2. Appl. Surf. Sci. 268, 213–217 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.12.061
E.J. Kim, B. Batchelor, Synthesis and characterization of pyrite (FeS2) using microwave irradiation. Mater. Res. Bull. 44, 1553–1558 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2009.02.006
G. Chatzitheodrou, S. Fiechter, M. Kunst, W. Jaegermann, H. Tributsch, Thin photoactive FeS2 (pyrite) films. Mater. Res. Bull. 21, 1481–1487 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-5408(86)90088-7
R.J. Soukup, P. Prabukanthan, N.J. Ianno, C.A. Kamler, D.G. Sekora, Formation of pyrite (FeS2) thin films by thermal sulfurization magnetron sputtered iron. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 29(1–5), 011001 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1116/1.3517739
D. Lichtenberger, K. Ellmer, R. Schieck, S. Fiechter, H. Tributsch, Structural, optical and electrical properties of polycrystalline iron pyrite layers deposited by reactive d.c. magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 246, 6–12 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-6090(94)90723-4
Q. Yu, S. Cai, Z. Jin, Z. Yan, Evolutions of composition, microstructure and optical properties of Mn doped pyrite (FeS2) films prepared by chemical bath deposition. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 3601–3606 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.05.074
S.D. Disale, S.S. Garje, Deposition of copper doped iron sulfide (CuxFe1–xS) thin films using aerosol-assisted chemical vapor deposition technique. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 24, 734–740 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.1676
S. Nakamura, A. Yamamoto, Electrcodeposition of pyrite (FeS2) thin films for photovoltaic cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 65, 79–85 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-0248(00)00080-5
N. Arbi, I. Ben Assaker, M. Gannouni, A. Kriaa, R. Chtourou, Effect of manganese concentration on physical and electrochemical properties of Mn2+ doped ZnS thin films deposited onto ITO-(glass) substrates by electordeposition techniques. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 4997–5005 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6155-0
Q. Fu, J. Chen, C. Shi, D. Ma, Room-temperature sol–gel derived molybdenum oxide thin films for efficient and stable solution-processed organic light-emitting diodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 6024–6029 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/am4007319
F. Martinez-Rojas, M. Hssein, Z. El Jouad, F. Armijo, L. Cattin, G. Louarn, N. Stephant, M.A. del Valle, M. Addou, J.P. Soto, J.C. Bernede, Mo(SxOy) thin films deposited by electrochemistry for application in organic photovoltaic cells. Mater. Chem. Phys. 201, 331–338 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.08.021
P. Prabukanthan, R.J. Soukup, N.J. Ianno, A. Sarkar, C.A. .Kamler, E.L. Extrom, J. Olejnicek, S.A. Darveau, Chemical bath deposition (CBD) of iron sulfide thin films for photovoltaic applications, crystallographic and optical properties. In Proceedings of the 35th Photovoltaics specialists Conference, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), pp. 002965–002969 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/PVSC.2010.5614465
P. Prabukanthan, G. Harichandran, Electrochemical deposition of n-type ZnSe thin film buffer layer for solar cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 14, D736–D741 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0261414jes
P. Prabukanthan, R. Dhanasekaran, Growth of CuGaS2 single crystals by chemical vapor Transport and characterization. Cryst. Growth Des. 7, 618–623 (2007) https://doi.org/10.1021/cg060450o
P. Prabukanthan, S. Thamaraiselvi, G. Harichandran, Structural, morphological, electrocatalytic activity and photocurrent properties of electrochemically deposited FeS2 thin films. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 11951–11963 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9297-4
B. Silwana, C. van der Horst, E. Iwuoha, V. Somerset, Synthesis, characterization and electrochemical evaluation of reduced grapheme oxide modified antimony nanoparticles. Thin Solid Films 592, 124 – 134 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2015.09.010
P. Prabukanthan, R. Lakshmi, G. Harichandran, T. Tatarchuk, Photovoltaic device performance of pure, manganese (Mn2+) doped and irradiated CuInSe2 thin films. New J. Chem. 42, 11642–11652 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NJ01056K
Z. Li, F. Gong, G. Zhou, Z.S. Wang, NiS2/reduced grapheme oxide nanocomposites for efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 6561–6566 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp401032c
X. Zuo, R. Zhang, B. Yang, G. Li, H. Tang, H. Zhang, M. Wu, Y. Ma, S. Jin, K. Zhu, NiS nanoparticles anchored on reduced grapheme oxide to enhance the performance of dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 8176–8181 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3478-1
Acknowledgements
One of the authors (P. Prabukanthan) wishes to acknowledge University Grant Commission (UGC), India, for the financial assistance through major research project (MRP) scheme [File No. 43-399/2014(SR)].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prabukanthan, P., Thamaraiselvi, S., Harichandran, G. et al. Single-step electrochemical deposition of Mn2+ doped FeS2 thin films on ITO conducting glass substrates: physical, electrochemical and electrocatalytic properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 3268–3276 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-00599-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-00599-w