Abstract
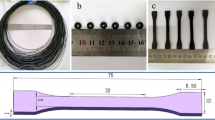
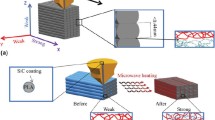
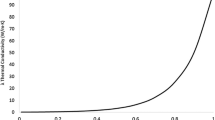
3D printing technology has attracted more and more interest in rapid manufacturing of components with complex shapes by pre-design. In the present work, various content of Li0.44Zn0.2Fe2.36O4 (LZFO) particles as reinforcement were added to polylactic acid (PLA) matrix for preparing 3D-printed composites by using fused deposition modeling (FDM). The structure and morphological characteristics were systematically examined by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and Scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Furthermore, mechanical, thermal and microwave absorption properties of 3D-printed LZFO/PLA composites with different contents were investigated in detail. Tensile strength and Young’s modulus of the LZFO/PLA composite with 10 wt% LZFO content were remarkably improved than that of original PLA. Thermal stability of the composite with 5 wt% LZFO content was the best among the test specimens. Microwave absorption property suggested that the reflection loss (RL) of the composite with 20 wt% LZFO can reach − 32.4 dB at 3.8 GHz and − 31.8 dB at 16.1 GHz with the thickness of 6 mm, and the effective bandwidth corresponding to RL (≤ − 10 dB) reaches 2.1 GHz (3.1–5.2 GHz) and 1.8 GHz (14–15.8 GHz). Therefore, 3D-printed LZFO/PLA composites prepared by FDM can be an incredibly promising novel 3D printable microwave absorption candidate with other comprehensive properties. Moreover, microwave absorbing materials prepared by 3D printing technology especially using FDM may become the development trend of this kind of materials in the future.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Standard A. F2792, Standard Terminology for Additive Manufacturing Technologies (ASTM International, West Conshohocken, 2012)
Y. He, Y. Wu, J. Fu, Q. Gao, J. Qiu, Developments of 3D printing microfluidics and applications in chemistry and biology: a review. Electroanalysis. 28, 1658–1678 (2016)
C. Zhu, T. Liu, F. Qian, T.Y.-J. Han, E.B. Duoss, J.D. Kuntz, C.M. Spadaccini, M.A. Worsley, Y. Li, Supercapacitors based on three-dimensional hierarchical graphene aerogels with periodic macropores. Nano Lett. 16, 3448–3456 (2016)
J. Zhong, M. Yi, H.H. Bau, Magneto hydrodynamic (MHD) pump fabricated with ceramic tapes. Sens. Actuators A 96, 59–66 (2002)
S.J. Leigh, R.J. Bradley, C.P. Purssell, D.R. Billson, D.A. Hutchins, A simple, lowcost conductive composite material for 3D printing of electronic sensors. PLoS ONE 7, e49365 (2012)
M.D. Symes, P.J. Kitson, J. Yan, C.J. Richmond, G.J.T. Cooper, R.W. Bowman, T. Vilbrandt, L. Cronin, Integrated 3D-printed reactionware for chemical synthesis and analysis. Nat. Chem. 4, 349–354 (2012)
G.N. Meloni, 3D printed and microcontrolled: the one hundred dollars scanningelectrochemical microscope. Anal. Chem. 89, 8643–8649 (2017)
A.P. West, S.P. Sambu, D.W. Rosen, A process planning method for improving build performance in stereolithography. Comput. Aided Des. 33, 65–79 (2001)
P. Dudek, FDM 3D printing technology in manufacturing composite elements. Arch. Metal. Mater. 58, 1415–1418 (2013)
J. Park, M.J. Tari, H.T. Hahn, Characterization of the laminated object manufacturing (LOM) process. Rapid Prototype J. 6, 36–50 (2000)
J.P. Krut, X. Wang, T. Laoui, L. Froyen, Lasers and materials in selective laser sintering. Assem. Autom. 23, 357–371 (2003)
C.L. Zhu, M.L. Zhang, Y.J. Qiao, G. Xiao, F. Zhang, Y.J. Chen, Fe3O4/TiO2 core/shell nanotubes: synthesis and magnetic and electromagnetic wave absorption characteristics. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 16229–16235 (2010)
H.J. Wu, G.L. Wu, L.D. Wang, Peculiar porous α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 nanospheres: facile synthesis and electromagnetic properties. Powder Technol. 269, 443–451 (2015)
K. Prashantha, F. Roger, Multifunctional properties of 3D printed poly(lactic acid)/graphene nanocomposites by fused deposition modeling. J. Macromol. Sci. 54, 24–29 (2017)
X. Wang, M. Jiang, Z.W. Zhou, J. Gou, D. Hui, 3D printing of polymer matrix composites: A review and prospective. Composite Part B 110, 442–458 (2017)
L.E. Murr, S.M. Gaytan, F. Medin, H. Lopez, E. Martinez, B.I. Machad, Next-generation biomedical implants using additive manufacturing of complex, cellular and functional mesh arrays. Philos. Trans. 368, 1999–2032 (2010)
F. Castles, D. Isakov, A. Lui, Q. Lei, C.E.J. Dancer, Microwave dielectric characterisation of 3D-printed BaTiO3/ABS polymer composites. Sci. Rep. 6, 22714 (2016)
E.C. Carola, G. Francesca, S. Francesca, F. Scalera, F. Montagna, A. Sannino, The feasibility of printing polylactic acid-nanohydroxyapatite composites using a low-cost fused deposition modeling 3D printer. J Appl. Polym. Sci. 134, 44656–44667 (2017)
M. Corey, R. Armando, T.P. Angel, C. Rocha, M. Liang, Mechanical, electromagnetic, and X-ray shielding characterization of a 3D printable tungsten–polycarbonate polymer matrix composite for space-based applications. J. Electron. Mater. 44, 2598–2607 (2015)
F.D. Ning, W.L. Cong, J.J. Qiu, J.H. Wei, S.R. Wang, Additive manufacturing of carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites using fused deposition modeling. Composite Part B 80, 369–378 (2015)
R. Matthew, M. Jake, A. Zeeshan, A.E. Miller, M.R. Hartings, The chemical, mechanical, and physical properties of 3D printed materials composed of TiO2-ABS nanocomposites. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 17, 89–97 (2016)
R.G. Yan, C.R. Zhang, Synthesis and characteristic of Li0.35Zn0.3Fe2.35O4 ferrite fiber using filter paper template. Mater Sci Eng B 189, 27–31 (2014)
R. Auras, B. Harte, S. Selke, An overview of polylactides as packaging materials. Macromol. Biosci. 4, 835–864 (2004)
D.G. Li, C. Chen, W. Rao, W.H. Lu, Y.H. Xiong, Preparation and microwave absorption properties of polyaniline/Mn0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 nanocomposite in 2–18 GHz. Mater. Sci. 25, 76–81 (2014)
P.J. Liu, Z.J. Yao, J.T. Zhou, Controllable synthesis and enhanced microwave absorption properties of silane-modified Ni0.4Zn0.4Co0.2Fe2O4 nanocomposites covered with reduced graphene oxide. Rsc Adv. 5, 93739–93748 (2015)
M. Khairy, Synthesis, characterization, magnetic and electrical properties of polyaniline/NiFe2O4 nanocomposite. Synth. Met. 189, 34–41 (2014)
J.T. Zhou, Z.J. Yao, Y.X. Chen, D.B. Wei, Y.B. Wu, T.S. Xu, Mechanical and thermal properties of graphene oxide/phenolic resin composite. Polym Compos. 34, 1245–1249 (2013)
S. Farah, D. Anderson, R. Langer, Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications-a comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 107, 367–392 (2016)
D.D.L. Chung, Composite Materials Science and Applications, 2nd edn. (Springer, London, 2010)
D. Gay, S. Hoa, S. Tsai, Composite Materials Design and Applications, 4th edn. (CRC, Boca Raton, 2003)
D. Kinet, P. Megret, K.W. Goossen, L. Qiu, D. Heider, C. Caucheteur, Fiber Bragg grating sensors toward structural health monitoring in composite materials: challenges and solutions. Sensors 14, 7394–7419 (2014)
Q.T. Shubhra, A. Alam, M.A. Quaiyyum, Mechanical properties of polypropylene composites: a review. J Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 26, 362–391 (2011)
V.M.F. Evora, A. Shukla, Fabrication, characterization, and dynamic behavior of polyester/TiO2 nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 361, 358–366 (2003)
S.P. Qian, K.C. .Sheng, PLA toughened by bamboo cellulose nanowhiskers: role of silane compatibilization on the PLA bionanocomposite properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 148, 59–69 (2017)
P.Sun,G. Liu, D. Lv, D.J. Wang, Effective activation of halloysite nanotubes by piranha solution for amine modification via silane coupling chemistry. Rsc Adv. 5, 52916–52925 (2015)
A. Elahi, A. Shakoor, M. Irfan, N.A. Niaz, K. Mahmood, M.S. Awan, Effect of loading ZnNiCrFe2O4 nanoparticles on structural and microwave absorption properties of polyaniline nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 9489–9495 (2016)
Z.X. Li, X.H. Li, Y. Zong, G.G. Tan, Y. Sun, Y.Y. Lan, Solvothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene decorated by superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their applications as enhanced synergistic microwave absorbers. Carbon 115, 493–502 (2017)
P.J. Liu, L. Li, Z.J. Yao, M.M. Du, T.T. Yao, Synthesis and excellent microwave absorption property of polyaniline nanorods coated Li0.435Zn0.195Fe2.37O4 nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 7776–7787 (2016)
H.J. Wu, G.L. Wu, Y.Y. Ren, L. Yang, L.D. Wang, X.H. Li, Co2+/Co3+ ratio dependence of electromagnetic wave absorption in hierarchical NiCo2O4–CoNiO2 hybrids. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 7677–7690 (2015)
Z. Wang, H. Bi, P. Wang, M. Wang, Z. Liu, L. Shen, X. Liu, Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of self-assemblies composed of core-shell cobalt-cobalt oxide nanocrystals. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 3796–3801 (2015)
J. Feng, Y. Zong, Y. Sun, Y. Zhang, X.H. Li, Optimization of porous FeNi3/N-GN composites with superior microwave absorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 345, 441–451 (2018)
P.J. Liu, Z.J. Yao, J.T. Zhou, Z.H. Yang, L.B. Kong, Small magnetic Co-doped NiZn ferrite/graphene nanocomposites and their dual-region microwave bsorption performance. J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 9738–9749 (2016)
H.J. Wu, S.H. Qu, K.J. Lin, Y.C. Qing, L.D. Wang, Y.C. Fan, Q.H. Fu, F.L. Zhang, Enhanced low-frequency microwave absorbing property of SCFs@TiO2 composite. Powder Technol. 333, 153–159 (2018)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Foundation of Graduate Innovation Center in NUAA (kfjj20170601), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51702158), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. NS2017036).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicting interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, Y., Yao, Z., Lin, H. et al. Mechanical and microwave absorption properties of 3D-printed Li0.44Zn0.2Fe2.36O4/polylactic acid composites using fused deposition modeling. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 19296–19307 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0056-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0056-3