Abstract
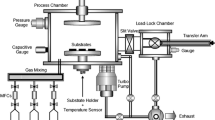
Hydrogenated nanocrystalline silicon (nc-Si:H) thin films were deposited on glass substrate by inductively coupled plasma chemical vapor deposition technique in this paper. The structural, optical, and morphological properties of samples were investigated and found to be strongly dependent on the substrate temperature. X-ray diffraction patterns show silicon film deposited at 25 °C is almost entirely amorphous, however, as the substrate temperature increased from 100 to 300 °C, the grain size of samples increases from 4.1 to 14.6 nm indicates improved crystalline quality. Raman spectroscopy revealed the nc-Si:H films contain crystalline, amorphous and an intermediate structure, and the crystallinity of sample deposited at 300 °C reaching a maximum value of 56 %. The optical absorption spectra of nc-Si:H films show hydrogen content and quantum confinement effect have strong influence on the optical band gap. Atomic force microscopy images show good coincidence with above results.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.P. Zhou, D.Y. Wei, S. Xu, S.Q. Xiao, L.X. Xu, S.Y. Huang, Y.N. Guo, W.S. Yan, M. Xu, J. Appl. Phys. 110, 023517 (2011)
G.B. Tong, Z. Aspanut, M.R. Muhamad, S.A. Rahman, Vacuum 86, 1195–1202 (2012)
P. Dutta, S. Paul, D. Galipeau, V. Bommisetty, Thin Solid Films 518, 6811–6817 (2010)
A. Banerjee, F.S. Liu, D. Beglau, S. Tining, G. Pietka, J. Yang, S. Guha, IEEE J. Photovolt. 2, 104–108 (2012)
L. Zhang, H.L. Shen, X.F. Jiang, B. Qian, Z.D. Han, H.H. Hou, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24, 4209–4212 (2013)
A.A.D.T. Adikaari, N.K. Mudugamuwa, S.R.P. Silva, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 92, 634–638 (2008)
J.H. Shim, S. Im, Y.J. Kim, N.H. Cho, Thin Solid Films 503, 55–59 (2006)
B.T. Goh, C.K. Wah, Z. Aspanut, S.A. Rahman, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 25, 286–296 (2014)
S.E. Lee, Y.C. Park, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 65, 651–656 (2014)
N.A. Bakr, A.M. Funde, V.S. Waman, M.M. Kamble, R.R. Hawaldar, D.P. Amalnerkar, V.G. Sathe, S.W. Gosavi, S.R. Jadkar, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 72, 685–691 (2011)
Y. Sakawa, N. Koshikawa, T. Shoji, Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 1695–1696 (1996)
S. Xu, K.N. Ostrikov, Y. Li, E.L. Tsakadze, I.R. Jones, Phys. Plasmas 8, 2549–2557 (2001)
B.Y. Moon, J.H. Youn, S.H. Won, J. Jang, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 69, 139–145 (2001)
A. Radhakrishnan, P. Rejani, B. Beena, Int. J. Nano Dimens. 5, 519–524 (2014)
H.B. Jeong, K.N. Kim, N.E. Lee, G.Y. Yeom, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 63, 1140–1145 (2013)
X.Y. Gao, J.T. Zhao, Y.F. Liu, Q.G. Lin, Y.S. Chen, J.H. Gu, S.E. Yang, J.X. Lu, Acta Phys. Polon. A 115, 738–741 (2009)
S. Mukhopadhyay, C. Das, S. Ray, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 37, 1736–1741 (2004)
W. Yu, L. Zhang, B.Z. Wang, W.B. Lu, L.W. Wang, G.S. Fu, Chin. Phys. Soc. 55, 1936–1941 (2006)
S.B. Amor, M. Atyaoui, R. Bousbih, I. Haddadi, W. Dimassi, H. Ezzaouia, Sol. Energy 108, 126–134 (2014)
S.J. Lee, S.H. Kim, D.W. Kim, K.H. Kim, B.K. Kim, J. Jang, Cells 95, 81–83 (2011)
C. Das, S. Ray, Thin Solid Films 403–404, 81–85 (2002)
N. Budini, P.A. Rinaldi, J.A. Schmidt, R.D. Arce, R.H. Buitrago, Thin Solid Films 518, 5349–5354 (2010)
A. Remolina, B.M. Monroy, M.F. García-Sánchez, A. Ponce, M. Bizarro, J.C. Alonso, A. Ortiz, G. Santana, Nanotechnology 20, 245604 (2009)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Sichuan Province Science and Technology Supporting Program (2015GZ0194) and Shuangliu County Science and Technology Achievements Incubator Program (13H012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, D., Zhu, X., Sun, H. et al. Effects of substrate temperature on structural, optical and morphological properties of hydrogenated nanocrystalline silicon thin films prepared by inductively coupled plasma chemical vapor deposition. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26, 7790–7796 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3426-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3426-0