Abstract
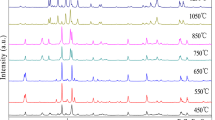
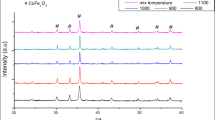
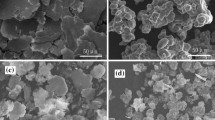
Ferrite/carbon composite powder was prepared by hydrothermal reaction of glucose solution and BaZn2Fe16O27 powder (BZFO) synthesized by the solid-state method. The XRD, SEM were used to analyze the structure and the morphology of the composite powder. The vector network analyzer was used to test the electromagnetic performance of the composite absorbent at different hydrothermal reaction times. The results showed that glucose was carbonized after hydrothermal reaction, and the produced carbon was grafted on the surface of flake ferrite. The BZFO/carbon micro-nano composite absorbent was obtained. At the frequency range from 2 to 18 GHz, with the increase of hydrothermal reaction time, the magnetic loss of composite materials was slightly changed, but the dielectric loss was obviously increased. When the reaction time is 2 h, the magnetic loss reaches the maximum 0.591 at 9.68 GHz; When the hydrothermal reaction time was 4 h, the dielectric loss reached the maximum 0.2737 at about 11.76 GHz, and the reflection loss reaches the minimum −27.10 dB at 11.44 GHz, even more, it obtains a higher 10 dB of RL ranging from 7.6 to 14.96 GHz, with the 3.2 mm thickness.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.L. Xia, S.K. Liu, C.G. Jin, S.B. Su, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 23, 4166 (2013). doi:10.1007/s10854-013-1377-x
S.R. Jigajeni, M.M. Sutar, S.M. Salunkhe, P.B. Joshi, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 23, 1678 (2012). doi:10.1007/s10854-012-0646-4
X.G. Huang, J. Zhang, S.R. Xiao, G.S. Chen, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 97(5), 1363–1366 (2014). doi:10.1111/jace.12909
M. Bayat, H. Yang, F.K. Ko, D. Michelson, A. Mei, Polymer 55, 936–943 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2013.12.042
J. Zhang, L.X. Wang, Q.T. Zhang. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 25, 5601–5605 (2014). doi:10.1007/s10854-014-2349-5
D.G. Li, C. Chen, W. Rao, W.H. Lu, Y.H. Xiong, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25(1), 76–81 (2014). doi:10.1007/s10854-013-1551-1
G.J.H. Melvin, Q.Q. Ni, T. Natsuki, J. Alloy. Compd. 615, 84–90 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.06.191
C. Poochai, T. Pongprayoon, Colloids Sur. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 456, 67–74 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.05.009
M.Z. Xu, X.L. Shi, X.Q. Zou, H. Pan, M.D. Liu, K. Jia, X.B. Liu, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 371, 20–28 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.07.002
D. Sarkar, A. Bhattacharya, P. Nandy, S. Das, Mater. Lett. 120, 259–262 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2014.01.089
S. Vinayasree, M.A. Soloman, V. Sunny, P. Mohanan, P. Kurian, P.A. Joy, M.R. Anantharaman, J. Appl. Phys. 2(116), 024902 (2014). doi:10.1063/1.4886382
J. Zhang, L.X. Wang, M.P. Liang, Q.T. Zhang, T. Nonferr, Met. Soc. 24(1), 131–135 (2014). doi:10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63038-7
X.G. Huang, J. Zhang, S.R. Xiao, T.Y. Sang, G.S. Chen, Mater. Lett. 124, 126–128 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2014.03.049
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (51202111), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Provincial Universities (14KJB430019), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20141000), National Natural Science Foundation of China (51402154), and Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Wang, L. & Zhang, Q. Hydrothermal carbonization synthesis of BaZn2F16O27/carbon composite microwave absorbing materials and its electromagnetic performance. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26, 2538–2543 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-2720-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-2720-1