Abstract
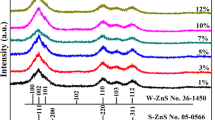
Wurtzite-type Zn0.99−xCdxMn0.01S quantum dots (QDs) were synthesized facilely by the one-step solvothermal method. The as-prepared QDs had an average diameter of 4.0 ± 1.0 nm. The composition of the QDs was adjusted by controlling the Zn/Cd molar ratios. The successive shift of the XRD and PL patterns indicated that the QDs obtained were not a mixture of ZnS and CdS, but the Zn1−xCdxS solid solution. The red emission peak (coming from the cadmium vacancies), the yellow–orange emission peak (coming from the Mn2+ ions), and the green emission peak (coming from the intrinsic near band edge) were observed in the PL spectra, the intensity and position of which can be turned by controlling the Zn/Cd molar ratios effectively.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Gur et al., Science 310, 462–465 (2005)
G. Konstantatos et al., Naure 442, 180–183 (2006)
M.Z. Wang et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 213111–213115 (2013)
A.J. Waldau et al., Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 95, 1509–1517 (2011)
Z. Qahtani et al., Mat. Sci. Semicond. Process. 20, 68–73 (2014)
P.P. Ingole et al., J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 7376–7383 (2013)
N.S. Karan et al., J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 1, 2863–2866 (2010)
L. Liu et al., Chem. Phys. Lett. 539, 112–117 (2012)
Z.X. Pan et al., ACS Nano 6, 3982–3991 (2012)
R.M. Xing et al., Nanoscale 4, 3135–3140 (2012)
H.Q. Huang et al., J. Lumin. 132, 1003–1009 (2012)
S. Zu et al., J. Alloys Compd. 476, 689–692 (2009)
S. Biswas et al., J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 3617–3624 (2009)
G. Deroubaix et al., Surf. Interface Anal. 18, 39–46 (1992)
D.S. Kim et al., J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 10861–10868 (2007)
J.Y. Ji et al., J. Mater. Chem. 21, 14498–14501 (2011)
Y. Chen et al., J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 2263–2266 (2009)
Z. Yang et al., CrystEngComm 14, 4298–4305 (2012)
J. Cao et al., J. Alloys Compd. 486, 890–894 (2009)
G. Murali, et al. J. Alloys Compd. 581, 849–855 (2013)
Acknowledgment
This work was financially supported by the National Programs for High Technology Research and Development of China (863) (Item No. 2013AA032202), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61008051, 61178074, 11204104, 11254001, 61378085, 61308095).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, D., Cao, J., Yang, S. et al. Structure and optical properties of Zn0.99−xCdxMn0.01S quantum dots. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26, 2205–2209 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-2669-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-2669-0