Abstract
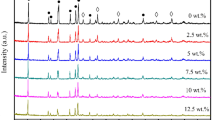
Relaxor based ternary (0.60 − x)Pb(In1/2Nb1/2)O3–0.40Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)–xPbTiO3 ((0.60 − x)PIN–0.40PMN–xPT) polycrystalline ceramics were synthesized by two-step columbite precursor method. The effects of PIN/PT content on phase structure, microstructure, density, and dielectric, piezoelectric, ferroelectric and pyroelectric properties of the ternary ceramics were systematically investigated. A morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) near x = 0.34 was identified by X-ray diffraction and further confirmed by their respective electrical properties. Piezoelectric, ferroelectric and pyroelectric properties were enhanced for compositions near the MPB. The 0.26PIN–0.40PMN–0.34PT ceramics show optimum electrical properties: piezoelectric coefficient d 33 = 505 pC/N, planar electromechanical coupling factor k p = 62.5 %, remnant polarization P r = 32.1 μC/cm2, coercive field E c = 8.8 kV/cm, and room temperature pyroelectric coefficient p = 0.050 μC/cm2 °C. In addition, the rhombohedral–tetragonal phase transition temperature T rt and Curie temperature T c of the ternary ceramics were identified by the temperature dependence of dielectric and pyroelectric measurements, which are much higher than those of binary PMN–PT ceramics, indicating the expanded temperature usage range of the ternary ceramics. The results show that this ternary system is a promising candidate for electromechanical applications with high performance and wide temperature usage range.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.E. Park, T.R. Shrout, Mater. Res. Innov. 1, 20 (1997)
F. Kochary, M.D. Aggarwal, A.K. Batra, R. Hawrami, D. Lianos, A. Burger, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 19, 1058 (2008)
S.J. Zhang, F. Li, J. Appl. Phys. 111, 031301 (2012)
E.W. Sun, W.W. Cao, Prog. Mater Sci. 65, 124 (2014)
Y. Hosono, Y. Yamashita, H. Sakamoto, N. Ichinose, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42, 535 (2003)
L.H. Liu, X. Wu, S. Wang, W.N. Di, D. Lin, X.Y. Zhao, H.S. Luo, J. Cryst. Growth 318, 856 (2011)
P. Finkel, H. Robinson, J. Stace, A. Amin, Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 122903 (2010)
X.Z. Liu, S.J. Zhang, J. Luo, T.R. Shrout, W.W. Cao, Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 012907 (2010)
Y. Chen, K.H. Lam, D. Zhou, W.F. Cheng, J.Y. Dai, H.S. Luo, H.L.W. Chan, Appl. Phys. A 108, 987 (2012)
D.B. Lin, Z.R. Li, F. Li, S.J. Zhang, Cryst. Eng. Comm. 15, 6292 (2013)
D.W. Wang, M.S. Cao, S.J. Zhang, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32, 433 (2012)
Z. Ren, Z.G. Ye, Ferroelectrics 464, 130 (2014)
S. Wongsaenmai, X.L. Tan, S. Ananta, R. Yimnirun, J. Alloys Compd. 454, 331 (2008)
S.J. Zhang, J. Luo, W. Hackenberger, N.P. Sherlock, R.J. Meyer Jr, T.R. Shrout, J. Appl. Phys. 105, 104506 (2009)
X.Z. Liu, S.J. Zhang, J. Luo, T.R. Shrout, W.W. Cao, J. Appl. Phys. 106, 074112 (2009)
K. Qian, B.J. Fang, Q.B. Du, J.N. Ding, X.Y. Zhao, H.S. Luo, Ferroelectrics 445, 74 (2013)
X. Liu, B.J. Fang, Z.H. Chen, J.N. Ding, X.Y. Zhao, H.Q. Xu, H.S. Luo, Ferroelectrics 467, 115 (2014)
P. Kumar, S. Sharma, S. Singh, O.P. Thakur, C. Prakash, T.C. Goel, Ferroelectrics 326, 55 (2005)
P. Kumar, S. Sharma, O.P. Thakur, C. Prakash, T.C. Goel, Ceram. Int. 30, 585 (2004)
S.T. Lau, C.H. Cheng, S.H. Choy, D.M. Lin, K.W. Kwok, H.L.W. Chan, J. Appl. Phys. 103, 104105 (2008)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) under Grant No. 2013CB632900, the National Science and Technology Support Program (Grant No. SQ2012BAJY3766), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and Program for Innovation Research of Science in Harbin Institute of Technology (Grant No. 01508451), and the State Key Laboratory of New Ceramic and Fine Processing Tsinghua University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Chang, Y., Yang, B. et al. Phase transitional behavior and electrical properties of Pb(In1/2Nb1/2)O3–Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3–PbTiO3 ternary ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26, 1874–1880 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2623-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2623-6