Abstract
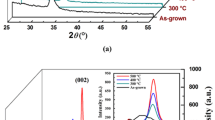
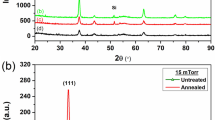
In this work, we present the substrate temperature induced change in the structural, optical, vibrational and luminescence properties of mixed NiO:WO3 (95:5) thin films deposited on glass substrates by rf magnetron sputtering technique. X-ray diffraction analysis revealed the onset of crystallization of the films occurred at 300 °C. The average optical transmittance of the films varied between 91 and 97 % in the visible region. The refractive index and extinction coefficient of films are found to decrease with increasing substrate temperature. It was observed that the dispersion data obeyed the single oscillator of the Wemple-DiDomenico model, from which the dielectric constants, ratio between free carrier density and free carrier effective mass, plasma frequency, oscillator energy, oscillator strength, and dispersion energy parameters of NiO:WO3 films were calculated and reported for the first time due to variation in substrate temperature during deposition by rf magnetron sputtering. The micro-Raman result shows two broad peaks corresponding to one-phonon LO mode at 570 cm−1 and two-phonon LO mode at 1,100 cm−1 due to the vibrations of Ni–O bonds and the peak found at 870 cm−1 belongs to the W–O mode. Room temperature photoluminescence (RTPL) study exhibits two characteristic emission peaks at 3.32 eV (374 nm) and 2.93 eV (423 nm), which corresponding to the transition of 3d8 Ni2+ ions. We have made an attempt to discuss and correlate these results with the light of possible mechanisms underlying the phenomena.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Subramanian, M. Mohamed Ibrahim, V. Senthilkumar, K.R. Murali, V.S. Vidhya, C. Sanjeeviraja, M. Jayachandran, Optoelectronic and electrochemical properties of nickel oxide (NiO) films deposited by DC reactive magnetron sputtering. Phys. B 403, 4104–4110 (2008)
M.M. Hasan, A.S.M.A. Haseeb, H.H. Masjuki, Structural and mechanical properties of nano structured tungsten oxide thin films. Sur. Eng. 28, 778–785 (2012)
M. Yin, H.P. Li, S.H. Tang, W. Ji, Determination of nonlinear absorption and refraction by single Z-scan method. Appl. Phys. B: Lasers Opt. 70, 587–591 (2000)
P.K. Shen, J. Syed-Bokhari, A.C.C. Tseung, The performance of electrochromic tungsten trioxide films doped with cobalt or nickel. J. Electrochem. Soc. 138, 2778–2783 (1991)
S.V. Green, E. Pehlivan, C.G. Granqvist, G.A. Niklasson, Electrochromism in sputter deposited nickel-containing tungsten oxide films. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 99, 339–344 (2012)
S.H. Lee, S.K. Joo, Electrochromic behavior of Ni-W oxide electrodes. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 39, 155–166 (1995)
S.-H. Lee, H.M. Cheong, N.-G. Park, C.E. Tracy, A. Mascarenhas, D.K. Benson, S.K. Deb, Raman spectroscopic studies of Ni-W oxide thin films. Solid State Ionics 140, 135–139 (2001)
B. Sasi, K.G. Gopchandran, P.K. Manoj, P. Koshy, P.P. Rao, V.K. Vaidyan, Preparation of transparent and semiconducting NiO films. Vacuum 68, 149–154 (2002)
T. Seike, J. Nagai, Electrochromism of 3d transition metal oxides. Sol. Energy Mater. 22, 107–117 (1991)
P.K. Pandey, N.S. Bhave, R.B. Kharat, Preparation and characterization of nanostructured NiO thin films by reactive-pulsed laser ablation technique. Electrochim. Acta 51, 4659–4664 (2006)
B. Sasi, K.G. Gopchandran, Preparation and characterization of nanostructured NiO thin films by reactive-pulsed laser ablation technique Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 91, 1505–1509 (2007)
S.V. Green, A. Kuzmin, J. Purans, C.G. Granqvist, G.A. Niklasson, Structure and composition of sputter-deposited nickel-tungsten oxide films. Thin Solid Films 519, 2062–2066 (2011)
H.L. Chen, Y.M. Lu, W.S. Hwang, Thickness dependence of electrical and optical properties of sputtered Nickel oxide films. Thin Solid Films 514, 361–365 (2006)
A. Mendoza-Galvan, M.A. Vidales-Hurtado, A.M. Lopez-Beltran, Comparison of the optical and structural properties of nickel oxide-based thin films obtained by chemical bath and sputtering. Thin Solid Films 517, 3115–3120 (2009)
M.C. Rao, O.M. Hussain, Optical properties of vacuum evaporated WO3 thin films. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 1, 76–80 (2011)
H.R. Fallah, M. Ghasemi, A. Hassanzadeh, Influence of heat treatment on structural, electrical, impedance and optical properties of nanocrystalline ITO films grown on glass at room temperature prepared by electron beam evaporation. Physica E 39, 69–74 (2007)
J.I. Pankove, Optical Process in Semiconductors (Prentice Hall, Inc., New Jersey, 1971), pp. 34
E. Burstein, Anomalous optical absorption limit in InSb. Phys. Rev. 93, 632–633 (1954)
T.S. Moss, The interpretation of the properties of Indium antimonide. Proc. Phys. Soc. London, Sect. B 67, 775–782 (1954)
M.A. Hassan, C.A. Hogarth, A study of the structural, electrical and optical properties of copper tellurium oxide glasses. J. Mater. Sci. 23, 2500–2504 (1988)
N.F. Mott, E.A. Davis, Electronic Processes in Non-Crystalline Materials (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1979)
Dirk Poelman, Philippe Frederic Smet, methods for the determination of the optical constants of thin films from single transmission measurements: a critical review. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 36, 1850–1857 (2003)
N.A. Subrahamanyam, A Textbook of Optics, 9th edn. (Brj Laboratory, India, 1977)
A.A. Al-Ghamdi, W.E. Mahmoud, S.J. Yaghmour, F.M. AlMarzouki, Structure and optical properties of nanocrystalline NiO thin film synthesized by sol-gel spin-coating method. J. Alloys Compd. 486, 9–13 (2009)
J. Singh, Optical Properties of Condensed Matter and Applications (John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, 2006)
P.J.L. Herve, L.K.J. Vandamme, Empirical temperature dependence of the refractive index of semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. 77, 5476–5477 (1995)
W.L. Bragg, A.B. Pippard, The form birefringence of macromolecules. Acta Crystallogr. 6, 865–867 (1953)
H.A. Macleod, Structure related optical properties of thin films. J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 4, 418–422 (1986)
Optical Properties of Solids, edited by F. Abeles (North-Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam, London, 1972)
J.I. Pankove, Optical Processes in Semiconductors (Dover Publications Inc., New York, 1975), p. 91
T.S. Moss, G.J. Burrell, E. Ellis, Semiconductor Opto-Electronics (Butterworth’s Scientific Publication LTD, London, 1973)
M. Abdel-Baki, F.A. Abdel, F. Wahab, El-Diasty, optical characterization of xTiO2–(60 − x)SiO2–40Na2O glasses: I. Linear and nonlinear dispersion properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 96, 201–210 (2006)
M. Caglar, S. Ilican, Y. Calgan, Y. Sahin, F. Yakuphanoglu, D. Hur, A spectro electrochemical study on single-oscillator model and optical constants of sulfonated polyaniline film. Spectrochimica Acta A 71, 621–627 (2008)
S.H. Wemple, M. DiDomenco, Behavior of the electronic dielectric constant in covalent and ionic materials. Phys. Rev. B 3, 1338–1342 (1971)
D.K. Madhup, D.P. Subedi, A. Huczko, Influence of doping on optical properties of ZnO Nanofilms, Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. Rapid Commun. 4, 1582–1586 (2010)
S.H. Wample, Material dispersion in optical fibers. Appl. Opt. 18, 31–35 (1979)
T. Wagner, M. Krbal, T. Kohoutek, V. Peina, M. Vlek, M. Frumar, Kinetics of optically- and thermally-induced diffusion and dissolution of silver in spin-coated As33S67 amorphous films; their properties and structure. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 326, 233–237 (2003)
A. Kuzmin, J. Purans, R. Kalendarev, Local structure and vibrational dynamics in NiWO4. Ferroelectrics 258, 21–30 (2001)
R. Sivakumar, C. Sanjeeviraja, M. Jayachandran, R. Gopalakrishnan, S.N. Sarangi, D. Paramanik, T. Som, Modification of WO3 thin films by MeV N+-ion beam irradiation. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 19, 186204–186213 (2007)
C. Diaz-Guerra, A. Remon, J. Garcia, J. Piqueras, Cathodoluminescence and photoluminescence spectroscopy of NiO. Phys. Stat. Sol. (a) 163, 497–503 (1997)
Yude Wang, Chunlai Ma, Xiaodan Sun, Hengde Li, Preparation and photoluminescence properties of organic–inorganic nanocomposite with a mesolamellar nickel oxide. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 71, 99–102 (2004)
D. Adler, J. Feinleib, Electrical and optical properties of narrow-band materials. Phys. Rev. B 2, 3112–3134 (1970)
S.M.M. Zawawi, R. Yahya, A. Hassan, H.N.M. Ekramul Mahmud, M.N. Daud, Structural and optical characterization of metal tungstates (MWO4; M = Ni, Ba, Bi) synthesized by a sucrose-templated method. Chem. Cent. J. 7, 80–90 (2013)
E.G. Lee, M.D. Kim, D. Lee, Effect of the carrier capture process on the photoluminescence intensity and the decay time of semiconductor quantum dots. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 48, 1228–1232 (2006)
T.S. Shyju, S. Anandhi, R. Sivakumar, S.K. Garg, R. Gopalakrishnan, Investigation on structural, optical, morphological and electrical properties of thermally deposited lead selenide (PbSe) nanocrystalline thin films. J. Cryst. Growth 353, 47 (2012)
Acknowledgments
One of the authors (K. S. Usha) gratefully acknowledges the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India for the financial assistance rendered through Innovation in Science Pursuit for Inspired Research (INSPIRE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Usha, K.S., Sivakumar, R. & Sanjeeviraja, C. Effect of substrate temperature on structural and optical properties of nickel tungsten oxide thin films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26, 1033–1044 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2501-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2501-2