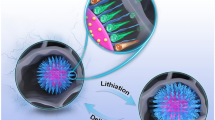
Abstract
Mg-ion batteries (MIBs) possess promising advantages over monovalent Li-ion battery. However, the exploitation of desirable cathode materials encounters the dilemma of sluggish reaction kinetics caused by strong coulomb interaction between Mg2+ and cathode. Reasonable electrode structure design is of great importance for achieving fast Mg2+ intercalation kinetics. Herein, a novel configuration composed of sub-5 nm amorphous V2O5 quantum dots and nitrogen-doping carbon nanofibers (a-V2O5-QDs@NCNFs) was elaborately designed and fabricated. Sub-5 nm QDs provide shorter diffusion path and more storage sites for Mg2+. Simultaneously, a large range of disorder states in amorphous structure can provide more open diffusion channels for Mg2+ transport. In addition, NCNFs play a crucial part in relieving the volumetric strains of V2O5 and maintaining the structural integrity during Mg2+ insertion/extraction. Reflecting in MIBs, a-V2O5-QDs@NCNFs deliver ultra-long cycling life (5000 cycles at 5 A g−1) and outstanding rate performance (52 mAh g−1 at 20 A g−1). This design conception opens up a new route for exploiting high-performance cathode for MIBs.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data and code availability
Not Applicable.
References
Hou S, Ji X, Gaskell K, Wang PF, Wang LN, Xu JJ, Sun RM, Borodin O, Wang CS (2021) Solvation sheath reorganization enables divalent metal batteries with fast interfacial charge transfer kinetics. Science 374:172–178
Zhao YM, Du AB, Dong SM, Jiang F, Guo ZY, Ge XS, Qu XL, Zhou XH, Cui GL (2021) A bismuth-based protective layer for magnesium metal anode in noncorrosive electrolytes. ACS Energy Lett 6:2594–2601
Li XG, Gao T, Han FD, Ma ZH, Fan XL, Hou S, Eidson N, Li WS, Wang CS (2017) Reducing Mg anode overpotential via ion conductive surface layer formation by iodine additive. Adv Energy Mater 8:1701728
Liu FF, Wang TT, Liu XB, Jiang N, Fan LZ (2021) High-performance heterojunction Ti3C2/CoSe2 with both intercalation and conversion storage mechanisms for magnesium batteries. Chem Eng J 426:130747
Chen Z, Yang Q, Wang DH, Chen A, Li XL, Huang ZD, Liang GJ, Wang Y, Zhi CY (2022) Tellurium: a high-performance cathode for magnesium ion batteries based on a conversion mechanism. ACS Nano 16:5349–5357
Mao ML, Lin ZJ, Tong YX, Yue JM, Zhao CL, Lu JZ, Zhang QH, Gu L, Suo LM, Hu YS, Li H, Huang XJ, Chen LQ (2020) Iodine vapor transport-triggered preferential growth of chevrel Mo6S8 nanosheets for advanced multivalent batteriesm. ACS Nano 14:1102–1110
Zhu YP, Huang G, Yin J, Lei YJ, Emwas AH, Yu X, Mohammed OF, Alshareef HN (2020) Hydrated MgxV5O12 cathode with improved Mg2+ storage performance. Adv Energy Mater 10:2002128
Liang YL, Feng RJ, Yang SQ, Ma H, Liang J, Chen J (2011) Rechargeable Mg batteries with graphene-like MoS2 cathode and ultrasmall Mg nanoparticle anode. Adv Mater 23:640–643
Wang YR, Liu ZT, Wang CX, Yi X, Chen RP, Ma LB, Hu Y, Zhu GY, Chen T, Tie ZX, Ma J, Liu J, Jin Z (2018) Highly branched VS4 nanodendrites with 1D atomic-chain structure as a promising cathode material for long-cycling magnesium batteries. Adv Mater 30:1802563
Deng XW, Xu YN, An QY, Xiong FY, Tan SS, Wu LM, Mai LQ (2019) Manganese ion pre-intercalated hydrated vanadium oxide as a high-performance cathode for magnesium ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 7:10644–10650
Son SB, Gao T, Harvey SP, Steirer KX, Stokes A, Norman A, Wang CS, Cresce A, Xu K, Ban CM (2018) An artificial interphase enables reversible magnesium chemistry in carbonate electrolytes. Nature Chem 10:532–539
Xu YN, Deng XW, Li QD, Zhang GB, Xiong FY, Tan SS, Wei QL, Lu J, Li JT, An QY, Mai LQ (2019) Vanadium oxide pillared by interlayer Mg2+ ions and water as ultralong-life cathodes for magnesium-ion batteries. Chem 5:1194–1209
Andrews JL, Mukherjee A, Yoo HD, Parija A, Marley PM, Fakra S, Prendergast D, Cabana J, Klie RF, Banerjee S (2018) Reversible Mg-ion insertion in a metastable one-dimensional polymorph of V2O5. Chem 4:1–22
Liu ZW, Han K, Li PW, He DL, Tan QW, Wang LY, Li Y, Qin ML, Qu XH (2019) Tuning metallic Co0.85Se quantum dots/carbon hollow polyhedrons with tertiary hierarchical structure for high-performance potassium ion batteries. Nano-Micro Lett 11:1–14
Zhao KN, Zhang L, Xia R, Dong YF, Xu WW, Niu CJ, He L, Yan MY, Qu LB, Mai LQ (2016) SnO2 quantum dots@graphene oxide as a high-rate and long-life anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Small 12:588–594
Zhang GH, Zhu J, Zeng W, Hou SC, Gong FL, Li F, Li CC, Duan HG (2022) Tin quantum dots embedded in nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers as excellent anode for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Nano 16:5349–5357
Gao H, Zhou TF, Zheng Y, Zhang Q, Liu YQ, Chen J, Liu HK, Guo ZP (2017) CoS quantum dot nanoclusters for high-energy potassium-ion batteries. Adv Funct Mater 27:1702634
Ha CH, Yan MY, Mai LQ, Tian XC, Xu L, Xu X, An QY, Zhao YL, Ma XY, Xie JL (2013) V2O5 quantum dots/graphene hybrid nanocomposite with stable cyclability for advanced lithium batteries. Nano Energy 2:916–922
Huang ZX, Liu B, Kong DZ, Wang Y, Yan HY (2018) SnSe2quantum dot/rGO composite as high performing lithium anode. Energy Storage Mater 10:92–101
Li HX, Jiang LL, Feng QX, Huang ZY, Zhou HH, Gong Y, Hou ZH, Yang WJ, Fu CP, Kuang YF (2019) Ultra-fast transfer and high storage of Li+/Na+ in MnO quantum dots@carbon hetero-nanotubes: appropriate quantum dots to improve the rate. Energy Storage Mater 17:157–166
Meng RJ, Huang JM, Feng YT, Zu LH, Peng CX, Zheng LR, Zheng L, Chen ZB, Liu GL, Chen BJ, Mi YL, Yang JH (2018) Black phosphorus quantum Dot/Ti3C2 mxene nanosheet composites for efficient electrochemical lithium/sodium-ion storage. Adv Energy Mater 8:1801514
Wang XJ, Liu YC, Wang YJ, Jiao LF (2016) CuO quantum dots embedded in carbon nanofibers as binder-free anode for sodium ion batteries with enhanced properties. Small 12:4865–4872
Guo QB, Ma YF, Chen TT, Xia QY, Yang M, Xia H, Yu Y (2017) Cobalt sulfide quantum dot embedded N/S-doped carbon nanosheets with superior reversibility and rate capability for sodium-ion batteries. ACS Nano 11:12658–12667
Chao DL, Block RD, Lai CH, Wei QL, Dunn B, Fan HJ (2021) Amorphous VO2: a pseudocapacitive platform for high-rate symmetric batteries. Adv Mater 33:2103736
Liu YL, Xu YH, Han XG, Pellegrinelli C, Zhu YJ, Zhu HL, Wan JY, Chung AC, Vaaland O, Wang CS, Hu LB (2012) Porous amorphous FePO4 nanoparticles connected by single-wall carbon nanotubes for sodium ion battery cathodes. Nano lett 12:5664–5668
Qin ZZ, Lv CD, Pei J, Yan CS, Hu YY, Chen G (2020) A 1D honeycomb-like amorphous zincic vanadate for stable and fast sodium-ion storage. Small 16:1906214
Jin SX, Li N, Cui H, Wang CX (2013) Growth of the vertically aligned graphene@ amorphous GeOx sandwich nanoflakes and excellent Li storage properties. Nano Energy 2:1128–1136
Wang MS, Peng AM, Xu H, Yang ZL, Zhang L, Zhang J, Yang H, Chen JC, Huang Y, Li X (2020) Amorphous SnSe quantum dots anchoring on graphene as high performance anodes for battery/capacitor sodium ion storage. J Power Sources 469:228414
Tu ZM, Yang GZ, Song HW, Wang CX (2017) Amorphous ZnO quantum dots (QDs)/mesoporous carbon bubble composites for high-performance lithium-ion battery anode. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:439–446
Ye HL, Wang L, Deng S, Zeng XQ, Nie KQ, Duchesne PN, Wang B, Liu SM, Zhou JH, Zhao FP, Han N, Zhang P, Zhong J, Sun XH, Li TY, Li YG, Lu J (2017) Amorphous MoS3 infiltrated with carbon nanotubes as an advanced anode material of sodium-ion batteries with large gravimetric, areal, and volumetric capacities. Adv Energy Mater 7:1601602
Wang JG, Liu HY, Liu HZ, Hua W, Shao MH (2018) Interfacial constructing flexible V2O5@polypyrrole core-shell nanowire membrane with superior supercapacitive performance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:18816–18823
Zhang DD, Cao J, Yue YL, Pakornchote T, Bovornratanaraks T, Han JT, Zhang XY, Qin JQ, Huang YH (2021) Two birds with one stone: boosting zinc-ion insertion/extraction kinetics and suppressing vanadium dissolution of V2O5 via La3+ incorporation enable advanced zinc-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:38416–38424
Chen LL, Yang ZH, Cui F, Meng JL, Chen HZ, Zeng X (2020) Enhanced rate and cycling performances of hollow V2O5 nanospheres for aqueous zinc ion battery cathode. Appl Surf Sci 507:145137
Din YC, Peng YQ, Chen WY, Niu YJ, Wu SG, Zhang XX, Hu LH (2019) V-MOF derived porous V2O5 nanoplates for high performance aqueous zinc ion battery. Appl Surf Sci 493:368–374
He TQ, Li JH, Luo ZZ, Zhang YQ, Zhao YY, Zhang XT, Chen YJ (2022) MIL-47(V) derived V2O5@carbon core-shell microcuboids with oxygen vacancies as advanced conversion cathodes for high-performance zinc-ion batteries. ChemElectroChem 9:e202200
Yan CS, Chen G, Zhou X, Sun JX, Lv CD (2016) Template-based engineering of carbon-doped Co3O4 hollow nanofibers as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Adv Funct Mater 26:1428–1436
Jin QZ, Li W, Wang KL, Feng PY, Li HM, Gu TT, Zhou M, Wang W, Cheng SJ, Jiang K (2019) Experimental design and theoretical calculation for sulfur-doped carbon nanofibers as a high performance sodium-ion battery anode. J Mater Chem A 7:10239–10245
Cheng XL, Li DJ, Liu FF, Xu R, Yu Y (2019) Binding nanosized cobalt chalcogenides in B, N-codoped graphene for enhanced sodium storage. Small Methods 3:1800170
Kong HB, Lv CD, Wu YS, Yan CS, Chen G (2021) Integration of cobalt selenide nanocrystals with interlayer expanded 3D Se/N Co-doped carbon networks for superior sodium-ion storage. J Energy Chem 55:169–175
Tepavcevic S, Liu YZ, Zhou DH, Lai B, Maser J, Zuo XB, Chan H, Král P, Johnson CS, Stamenkovic V, Markovic NM, Rajh T (2015) Nanostructured layered cathode for rechargeable mg-ion batteries. ACS Nano 9:8194–8205
Drosos C, Jia CL, Mathew S, Palgrave RG, Moss B, Kafizas A, Vernardou D (2018) Aerosol-assisted chemical vapor deposition of V2O5 cathodes with high rate capabilities for magnesium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 384:355–359
Attias R, Salama M, Hirsch B, Gofer Y, Aurbach D (2018) Solvent effects on the reversible intercalation of Mg ions into V2O5 electrodes. ChemElectroChem 5:3514–3524
Zhang K, Park M, Zhou LM, Lee GH, Li WJ, Kang YM, Chen J (2016) Urchin-like CoSe2 as a high-performance anode material for sodium-ion batteries. Adv Funct Mater 26:6728–6735
Chen CJ, Wen YW, Hu XL, Ji XL, Yan MY, Mai LQ, Hu P, Shan B, Huang YH (2015) Na+ intercalation pseudocapacitance in graphene-coupled titanium oxide enabling ultra-fast sodium storage and long-term cycling. Nat Commun 6:6929
Lou PL, Cui ZH, Jia ZQ, Sun JY, Tan YB, Guo XX (2017) Monodispersed carbon-coated cubic NiP2 nanoparticles anchored on carbon nanotubes as ultra-long-life anodes for reversible lithium storage. ACS Nano 11:3705–3715
Yang C, Zhang YL, Zho JH, Lin CF, Lv F, Wang K, Feng JR, Xu ZK, Li JB, Guo SJ (2018) Hollow Si/SiOx nanosphere/nitrogen-doped carbon superstructure with a double shell and void for high-rate and long-life lithium-ion storage. J Mater Chem A 6:8039–8046
Kong HB, Cui W, Yan CS, Kong Y, Lv CD, Chen G (2021) Interface engineering on cobalt selenide composites enables superior alkali-ion storage. Chem Eng J 419:129490
Wang QF, Huang Y, Miao J, Zhao Y, Wang Y (2013) Synthesis and electrochemical characterizations of Ce doped SnS2 anode materials for rechargeable lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 93:120–130
Cui Y, Zhao XL, Guo RS (2010) Improved electrochemical performance of La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 and carbon co-coated LiFePO4 synthesized by freeze-drying process. Electrochim Acta 55:922–926
Fang GZ, Wang QC, Zhou J, Lei YP, Chen ZX, Wang ZQ, Pan AQ, Liang SQ (2019) Metal organic framework-templated synthesis of bimetallic selenides with rich phase boundaries for sodium-ion storage and oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Nano 13:5635–5645
Ngo DT, Le HT, Kim C, Lee JY, Fisher JG, Kim ID, Park CJ (2015) Mass-scalable synthesis of 3D porous germanium-carbon composite particles as an ultra-high rate anode for lithium ion batteries. Energy Environ Sci 8:3577–3588
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22302072), Natural Science Foundation of Xiamen, China (3502Z20227029), Scientific Research Starting Foundation of Huaqiao University (No. 21BS115). We acknowledge the support from the Instrumental Analysis Center of Huaqiao University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HK and YC contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Ethical approval
Not Applicable.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Jean-Francois Gohy.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10853_2023_9313_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary materials (SEM images of as-spun nanofiber, a-V2O5-QDs@NCNFs, c-V2O5-NPs@NCNFs and c-V2O5-NDs, CV curves of c-V2O5-NPs@NCNFs and c-V2O5-NDs, charge–discharge profiles of c-V2O5-NPs@NCNFs and c-V2O5-NDs, Kinetics analysis of the electrochemical behavior toward Mg2+ for the c-V2O5-NPs@NCNFs and c-V2O5-NDs.)
Supplementary file1 (DOCX 5465 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, H., Chen, Y., Wen, Y. et al. Amorphous quantum dots enable V2O5 with superior Mg storage. J Mater Sci 59, 1526–1536 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-023-09313-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-023-09313-6