Abstract
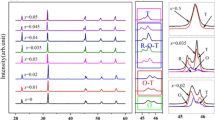
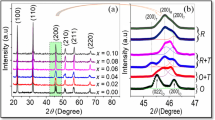
A series of barium zirconate modified potassium sodium niobate-based lead-free piezoelectric ceramics [(0.97-x)(K0.45Na0.55)(Nb0.97Sb0.03)O3-0.03Bi0.5K0.075Na0.425ZrO3-xBaZrO3, KNNS–BKNZ–xBZ, x = 0 ~ 0.02] were prepared by the traditional solid-state method. The effect of BZ on the phase structure and electrical properties was systematically studied. Rhombohedral–orthorhombic–tetragonal multiphase coexistence structure can be observed for the whole ceramic system while the addition of BZ leads to the reduction in the orthorhombic phase content and increase in the rhombohedral and tetragonal phase content. At the critical composition with x = 0.01, the ceramics show the optimized electrical properties with the piezoelectric constant d33 of 265 pC/N, unipolar strain Suni of 0.168%, inverse piezoelectric coefficient d33* of 480 pm/V, room-temperature dielectric constant εr of 1634, and Curie temperature TC of 282 °C. Moreover, enhanced temperature stability was achieved in the x = 0.01 ceramics, presenting the variation of d33 less than 15% within the temperature range of 20–100 °C and the Suni remained above 80% until the elevated temperature of 175 °C.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article and the raw data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Matsubara M, Yamaguchi T, Kikuta K, Hirano S (2005) Sintering and piezoelectric properties of potassium sodium niobate ceramics with newly developed sintering aid. Jpn J Appl Phys 44(1A):258–263
Panda PK, Sahoo B (2015) PZT to lead free piezo ceramics: a review. Ferroelectrics 474(1):128–143
Roedel J, Webber KG, Dittmer R, Jo W, Kimura M, Damjanovic D (2015) Transferring lead-free piezoelectric ceramics into application. J Eur Ceram Soc 35(6):1659–1681
Shrout TR, Zhang S (2007) Lead-free piezoelectric ceramics: Alternatives for PZT? J Electroceram 19(1):113–126
Shen Z-H, Liu H-X, Shen Y, Hu J-M, Chen L-Q, Nan C-W (2022) Machine learning in energy storage materials. Interdiscip Mater 1(2):175–195
Zheng P, Zhang J, Tan Y, Wang C (2012) Grain-size effects on dielectric and piezoelectric properties of poled BaTiO3 ceramics. Acta Mater 60(13–14):5022–5030
Sapkota P, Ueno S, Fujii I, Khanal GP, Kim S, Wada S (2019) Influence of grain size effect and Ba/Ti ratios on dielectric, ferroelectric, and piezoelectric properties of BaTiO3 ceramics. Jpn J Appl Phys 58(SL):SLLC05
Liu W, Ren X (2009) Large piezoelectric effect in Pb-free ceramics. Phys Rev Lett 103(25):257602
Zhao C, Wu H, Li F, Cai Y, Zhang Y, Song D, Jiagang W, Lyu X, Yin J, Xiao D, Zhu J, Pennycook Stephen J (2018) Practical high piezoelectricity in barium titanate ceramics utilizing multiphase convergence with broad structural flexibility. J Am Chem Soc 140(45):15252–15260
Zhou X, Jiang C, Luo H, Chen C, Zhou K, Zhang D (2016) Enhanced piezoresponse and electric field induced relaxor-ferroelectric phase transition in NBT-0.06BT ceramic prepared from hydrothermally synthesized nanoparticles. Ceram Int 42(16):18631–18640
Yin J, Tao H, Zhang Y, Han J, Huang Y, Li Z, Zhang X, Wu J (2020) Advances in tuning the “d33 ∝ 1/Td” bottleneck: simultaneously realizing large d33 and high Td in Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-based relaxor ferroelectrics. J Mater Chem A 8(18):9209–9217
Luo H, Liu H, Deng S, Shuxian Hu, Wang Lu, Gao B, Sun S, Ren Y, Qiao L, Chen J (2021) Simultaneously enhancing piezoelectric performance and thermal depolarization in lead-free (Bi, Na)TiO3–BaTiO3 via introducing oxygen-defect perovskites. Acta Mater 208:116711
Tellier J, Malic B, Dkhil B, Jenko D, Cilensek J, Kosec M (2009) Crystal structure and phase transitions of sodium potassium niobate perovskites. Solid State Sci 11(2):320–324
Roedel J, Jo W, Seifert KTP, Anton EM, Granzow T, Damjanovic D (2009) Perspective on the development of lead-free piezoceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 92(6):1153–1177
Guo Y, Kakimoto K, Ohsato H (2004) Phase transitional behavior and piezoelectric properties of (Na0.5K0.5)NbO3–LiNbO3 ceramics. Appl Phys Lett 85(18):4121–4123
Guo Y, Kakimoto K, Ohsato H (2005) (Na0.5K0.5)NbO3–LiTaO3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. Mater Lett 59(2–3):241–244
Saito Y, Takao H, Tani T, Nonoyama T, Takatori K, Homma T, Nagaya T, Nakamura M (2004) Lead-free piezoceramics. Nature 432(7013):84–87
Lv X, Zhu J, Xiao D, Zhang X-X, Wu J (2020) Emerging new phase boundary in potassium sodium-niobate based ceramics. Chem Soc Rev 49(3):671–707
Kuscer D, Kocjan A, Majcen M, Meden A, Radan K, Kovac J, Malic B (2019) Evolution of phase composition and microstructure of sodium potassium niobate -based ceramic during pressure-less spark plasma sintering and post-annealing. Ceram Int 45(8):10429–10437
Malic B, Koruza J, Hrescak J, Bernard J, Wang K, Fisher JG, Bencan A (2015) Sintering of lead-free piezoelectric sodium potassium niobate ceramics. Materials 8(12):8117–8146
Wang X, Wu J, Xiao D, Zhu J, Cheng X, Zheng T, Zhang B, Lou X, Wang X (2014) Giant piezoelectricity in potassium–sodium niobate lead-free ceramics. J Am Chem Soc 136(7):2905–2910
Xu K, Li J, Lv X, Wu J, Zhang XX, Xiao D, Zhu J (2016) Superior piezoelectric properties in potassium-sodium niobate lead-free ceramics. Adv Mater 28(38):8519–8852
Tao H, Wu H, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Wu J, Li F, Lyu X, Zhao C, Xiao D, Zhu J, Pennycook SJ (2019) Ultrahigh performance in lead-free piezoceramics utilizing a relaxor slush polar state with multiphase coexistence. J Am Chem Soc 141(35):13987–13994
Li P, Zhai J, Shen B, Zhang S, Li X, Zhu F, Zhang X (2018) Ultrahigh piezoelectric properties in textured (K, Na)NbO3 -based lead-free ceramics. Adv Mater 30(8):1705171
Wang K, Yao F, Jo W, Gobeljic D, Shvartsman VV, Lupascu DC, Li J, Roedel J (2013) Temperature-insensitive (K, Na)NbO3-based lead-free piezoactuator ceramics. Adv Funct Mater 23(33):4079–4086
Lv X, Wu J, Zhang XX (2020) Reduced degree of phase coexistence in KNN-based ceramics by competing additives. J Eur Ceram Soc 40(8):2945–2953
Li P, Fu Z, Wang F, Huan Y, Zhou Z, Zhai J, Shen B, Zhang S (2020) High piezoelectricity and stable output in BaHfO3 and (Bi0.5Na0.5)ZrO3 modified (K0.5Na0.5)(Nb0.96Sb0.04)O3 textured ceramics. Acta Mater 199:542–550
Lv X, Wu J, Zhang XX (2020) A new concept to enhance piezoelectricity and temperature stability in KNN ceramics. Chem Eng J 402:126215
Zhang H, Zhu Y, Fan P, Marwat MA, Ma W, Liu K, Liu H, Xie B, Wang K, Koruza J (2018) Temperature-insensitive electric-field-induced strain and enhanced piezoelectric properties of <001> textured (K,Na)NbO3-based lead-free piezoceramics. Acta Mater 156:389–398
Zheng T, Wu J (2020) Electric field compensation effect driven strain temperature stability enhancement in potassium sodium niobate ceramics. Acta Mater 182:1–9
Zheng T, Yu Y, Lei H, Li F, Zhang S, Zhu J, Wu J (2022) Compositionally graded KNN-based multilayer composite with excellent piezoelectric temperature stability. Adv Mater 34(8):2109175
Yao F, Wang K, Jo W, Webber KG, Comyn TP, Ding J-X, Xu B, Cheng L, Zheng M, Hou Y, Li J (2016) Diffused phase transition boosts thermal stability of high-performance lead-free piezoelectrics. Adv Funct Mater 26(8):1217–1224
Batra K, Sinha N, Kumar B (2020) Lead-free 0.95(K0.6Na0.4)NbO3-0.05(Bi0.5Na0.5)ZrO3 ceramic for high temperature dielectric, ferroelectric and piezoelectric applications. J Alloys Compd 818:152
Yang W, Wang Y, Li P, Wu S, Wang F, Shen B, Zhai J (2020) Improving electromechanical properties in KNANS-BNZ ceramics by the synergy between phase structure modification and grain orientation. J Mater Chem C 8(18):6149–6158
Zhou T, Zheng D, Peng G, Peng Z, Zhang N (2018) Effects of (Bi0.5Na0.5)ZrO3 addition on relaxation behavior and electrical properties of the KNN-LS ceramics. J Mater Sci-Mater Electron 29(2):1131–1138
Zhou C, Zhang J, Yao W, Wang X, Liu D, Sun X (2018) Piezoelectric performance, phase transitions, and domain structure of 0.96(K0.48Na0.52)(Nb0.96Sb0.04)O3–0.04(Bi0.50Na0.50)ZrO3 ceramics. J Appl Phys 124(16):164101
Qian S, Zhu K, Pang X, Liu J, Qiu J, Du J (2014) Phase transition, microstructure, and dielectric properties of Li/Ta/Sb co-doped (K, Na)NbO3 lead-free ceramics. Ceram Int 40(3):4389–4394
Yang ZP, Chang YF, Wei LL (2007) Phase transitional behavior and electrical properties of lead-free (K0.44Na0.52Li0.04)(Nb0.96−xTaxSb0.04)O3 piezoelectric ceramics. Appl Phys Lett 90(4):042911
Liu Q, Li J, Zhao L, Zhang Y, Gao J, Sun W, Wang K, Li L (2018) Niobate-based lead-free piezoceramics: a diffused phase transition boundary leading to temperature-insensitive high piezoelectric voltage coefficients. J Mater Chem C 6(5):1116–1125
Trainer M (2000) Ferroelectrics and the Curie–Weiss law. Eur J Phys 21(5):459
Catalan G, Seidel J, Ramesh R, Scott JF (2012) Domain wall nanoelectronics. Rev Mod Phys 84(1):119–156
Sun X, Li R, Zhao C, Lv X, Wu J (2021) One simple approach, two remarkable enhancements: Manipulating defect dipoles and local stress of (K, Na)NbO3-based ceramics. Acta Mater 221:117351
Li F, Cabral MJ, Xu B, Cheng Z, Dickey EC, LeBeau JM, Wang J, Luo J, Taylor S, Hackenberger W, Bellaiche L, Xu Z, Chen L-Q, Shrout TR, Zhang S (2019) Giant piezoelectricity of Sm-doped Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3–PbTiO3 single crystals. Science 364(6437):264–268
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2022YFB3807404); National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52172134). The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZD contributed to the writing—original draft, methodology, investigation, and formal analysis; XZ was involved in the writing—review and editing; YZ assisted in the writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition; DZ contributed to the project administration and funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Peiyao Zhao.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, Z., Zhou, X., Zhang, Y. et al. Temperature-insensitive electrical performance of the potassium sodium niobate-based ceramics modified by barium zirconate. J Mater Sci 59, 950–963 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-023-09270-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-023-09270-0