Abstract
Selective electron beam melting (SEBM) has been recently employed for additive manufacturing (AM) Al alloys but showing comparatively low hardness and strength. In this work, SEBM technique was employed to additive manufacture an in-situ TiB2 particle reinforced AlSi10Mg composite. With optimized processing parameters, the SEBM TiB2/AlSi10Mg composite showed good surface quality and a high relative density. The as-printed composite exhibited a refined equiaxed grain structure with an average size of 27.7 µm. The eutectic Si phase was mostly spherical and uniformly distributed in the Al matrix, while the nano-sized TiB2 particles were partly agglomerated. The resultant microstructure was associated with the combined effect of the rapid solidification and annealing-like process during SEBM. Additionally, TiB2 particles facilitated grain refinement by enhancing the heterogeneous nucleation and retarding grain growth. The SEBM TiB2/AlSi10Mg composite presented a yield strength (YS) and ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 103.6 MPa and 165.4 MPa, respectively, with an appreciable elongation of 15% at as-printed state. After a T6-like treatment, the YS and UTS of the composite were further improved to 225 MPa and 316 MPa, respectively, and an elongation of 12% was maintained. This paper shows the potency of SEBM in AM metal matrix composites (MMCs) with both agreeable strength and ductility.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data supporting the findings of the current study are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
References
Gokuldoss PK, Kolla S, Eckert J (2017) Additive manufacturing processes: selective laser melting, electron beam melting and binder jetting-selection guidelines. Mater 10:672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10060672
Li XP, Ji G, Chen Z et al (2017) Selective laser melting of nano-TiB2 decorated AlSi10Mg alloy with high fracture strength and ductility. Acta Mater 129:183–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2017.02.062
Zhang J, Song B, Wei Q, Bourell D, Shi Y (2019) A review of selective laser melting of aluminum alloys: processing, microstructure, property and developing trends. J Mater Sci Technol 35:270–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2018.09.004
Ma S, Li Y, Kan W et al (2022) Enhancement of grain refinement and heat resistance in TiB2-reinforced Al-Cu-Mg-Fe-Ni matrix composite additive manufactured by electron beam melting. J Alloys Compd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166395
Gu DD, Meiners W, Wissenbach K, Poprawe R (2012) Laser additive manufacturing of metallic components: materials, processes and mechanisms. Int Mater Rev 57:133–164. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743280411Y.0000000014
Zhang H, Zhu H, Nie X, Yin J, Hu Z, Zeng X (2017) Effect of Zirconium addition on crack, microstructure and mechanical behavior of selective laser melted Al-Cu-Mg alloy. Scr Mater 134:6–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2017.02.036
Brice CA, Tayon WA, Newman JA, Kral MV, Bishop C, Sokolova A (2018) Effect of compositional changes on microstructure in additively manufactured aluminum alloy 2139. Mater Charact 143:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2018.04.002
Kenevisi MS, Lin F (2020) Selective electron beam melting of high strength Al2024 alloy microstructural characterization and mechanical properties. J Alloys Compd 843:155866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155866
Murr LE, Gaytan SM, Ramirez DA et al (2012) Metal fabrication by additive manufacturing using laser and electron beam melting technologies. J Mater Sci Technol 28:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1005-0302(12)60016-4
Sun S, Zheng L, Peng H, Zhang H (2016) Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Fe-V-Si aluminum alloy produced by electron beam melting. Mater Sci Eng A Struct Mater 659:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.02.053
Buchbinder D, Schleifenbaum H, Heidrich S, Meiners W, Bültmann J (2011) High power selective laser melting (HP SLM) of aluminum parts. Phys Procedia 12:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2011.03.035
Louvis E, Fox P, Sutcliffe CJ (2011) Selective laser melting of aluminium components. J Mater Process Technol 211:275–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.09.019
Feng Z, Tan H, Fang Y, Lin X, Huang W (2022) Selective laser melting of TiB2/AlSi10Mg composite: Processability, microstructure and fracture behavior. J Mater Process Technol 299:117386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117386
Xiao YK, Bian ZY, Wu Y et al (2019) Effect of nano-TiB2 particles on the anisotropy in an AlSi10Mg alloy processed by selective laser melting. J Alloys Compd 798:644–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.05.279
Galarraga H, Lados DA, Dehoff RR, Kirka MM, Nandwana P (2016) Effects of the microstructure and porosity on properties of Ti-6Al-4V ELI alloy fabricated by electron beam melting (EBM). Addit Manuf 10:47–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2016.02.003
Galarraga H, Warren RJ, Lados DA, Dehoff RR, Kirka MM, Nandwana P (2017) Effects of heat treatments on microstructure and properties of Ti-6Al-4V ELI alloy fabricated by electron beam melting (EBM). Mater Sci Eng A Struct Mater 685:417–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.01.019
Murr LE, Gaytan SM, Ceylan A et al (2010) Characterization of titanium aluminide alloy components fabricated by additive manufacturing using electron beam melting. Acta Mater 58:1887–1894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2009.11.032
Murr LE, Martinez E, Pan XM et al (2013) Microstructures of Rene 142 nickel-based superalloy fabricated by electron beam melting. Acta Mater 61:4289–4296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2013.04.002
Strondl A, Palm M, Gnauk J, Frommeyer G (2011) Microstructure and mechanical properties of nickel based superalloy IN718 produced by rapid prototyping with electron beam melting (EBM). Mater Sci Technol 27:876–883. https://doi.org/10.1179/026708309X12468927349451
Kuwabara K, Shiratori H, Fujieda T, Yamanaka K, Koizumi Y, Chiba A (2018) Mechanical and corrosion properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy fabricated with selective electron beam melting. Addit Manuf 23:264–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.06.006
Xiao B, Jia W, Tang H, Wang J, Zhou L (2022) Microstructure and mechanical properties of WMoTaNbTi refractory high-entropy alloys fabricated by selective electron beam melting. J Mater Sci Technol 108:54–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.07.041
Gockel J, Beuth J, Taminger K (2014) Integrated control of solidification microstructure and melt pool dimensions in electron beam wire feed additive manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V. Addit Manuf 1–4:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2014.09.004
Tan S, Wang Y, Liu W, Wang H, Jia P, Ding Y (2022) Anisotropy reduction of additively manufactured AlSi10Mg for metal mirrors. J Mater Sci 57:11934–11948. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07080-4
Tradowsky U, White J, Ward RM, Read N, Reimers W, Attallah MM (2016) Selective laser melting of AlSi10Mg: Influence of post-processing on the microstructural and tensile properties development. Mater Des 105:212–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.05.066
Wang L, Jiang X, Zhu Y, Ding Z, Zhu X, Sun J, Yan B (2018) Investigation of performance and residual stress generation of AlSi10Mg processed by selective laser melting. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2018:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7814039
Hadadzadeh A, Amirkhiz BS, Li J, Mohammadi M (2018) Columnar to equiaxed transition during direct metal laser sintering of AlSi10Mg alloy: effect of building direction. Addit Manuf 23:121–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.08.001
Bian H, Aoyagi K, Zhao Y, Maeda C, Mouri T, Chiba A (2020) Microstructure refinement for superior ductility of Al–Si alloy by electron beam melting. Addit Manuf 32:100982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.100982
Li W, Li S, Liu J et al (2016) Effect of heat treatment on AlSi10Mg alloy fabricated by selective laser melting: Microstructure evolution, mechanical properties and fracture mechanism. Mater Sci Eng A Struct Mater 663:116–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.03.088
Ma K, Wen H, Hu T et al (2014) Mechanical behavior and strengthening mechanisms in ultrafine grain precipitation-strengthened aluminum alloy. Acta Mater 62:141–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2013.09.042
Tjong SC, Ma ZY (2000) Microstructural and mechanical characteristics of in situ metal matrix composites. Mater Sci Eng R Rep: A Rev J 29:49–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-796X(00)00024-3
Fan Z, Wang Y, Zhang Y et al (2015) Grain refining mechanism in the Al/Al–Ti–B system. Acta Mater 84:292–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.10.055
Hu L, Chen D (2015) Field activated and pressure assisted bonding mechanism of ultra-hard materials of AlMgB 14 to metal. Ferroelectrics 482:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1080/00150193.2015.1081533
Schaffer PL, Miller DN, Dahle AK (2007) Crystallography of engulfed and pushed TiB2 particles in aluminium. Scr Mater 57:1129–1132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2007.08.009
Kapoor R, Kumar N, Mishra RS, Huskamp CS, Sankaran KK (2010) Influence of fraction of high angle boundaries on the mechanical behavior of an ultrafine grained Al–Mg alloy. Mater Sci Eng A Struct Mater 527:5246–5254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.04.086
Ma SM, Zhang P, Ji G et al (2014) Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir processed Al–Mg–Si alloys dispersion-strengthened by nanosized TiB2 particles. J Alloys Compd 616:128–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.07.092
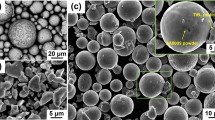
Chen M, Li X, Ji G et al (2017) Novel composite powders with uniform TiB2 nano-particle distribution for 3D printing. Appl Sci 7:250. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7030250
Xiao YK, Chen H, Bian ZY et al (2022) Enhancing strength and ductility of AlSi10Mg fabricated by selective laser melting by TiB2 nanoparticles. J Mater Sci Technol 109:254–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.08.030
Bösch D, Pogatscher S, Hummel M, Fragner W, Uggowitzer PJ, Göken M, Höppel HW (2015) Secondary Al-Si-Mg high-pressure die casting alloys with enhanced ductility. Metall Mater Trans A 46:1035–1045. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2700-8
Chen S, Tan Q, Gao W et al (2022) Effect of heat treatment on the anisotropy in mechanical properties of selective laser melted AlSi10Mg. Mater Sci Eng A Struct Mater 858:144130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2022.144130
Han Y, Liu X, Bian X (2002) In situ TiB2 particulate reinforced near eutectic Al-Si alloy composites. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manufact 33:439–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-835X(01)00124-5
Yan W, Ge W, Qian Y et al (2017) Multi-physics modeling of single/multiple-track defect mechanisms in electron beam selective melting. Acta Mater 134:324–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2017.05.061
Antonysamy AA, Meyer J, Prangnell PB (2013) Effect of build geometry on the β-grain structure and texture in additive manufacture of Ti-6Al-4V by selective electron beam melting. Mater Charact 84:153–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2013.07.012
Herzog D, Seyda V, Wycisk E, Emmelmann C (2016) Additive manufacturing of metals. Acta Mater 117:371–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.07.019
Dong QIU, Zhang M-X (2014) The nucleation crystallography and wettability of Mg grains on active Al2Y inoculants in an Mg-10 wt% Y Alloy. J Alloys Compd 586:39–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.10.042
Greer AL, Bunn AM, Tronche A, Evans PV, Bristow DJ (2000) Modelling of inoculation of metallic melts: application to grain refinement of aluminium by Al–Ti–B. Acta Mater 48:2823–2835. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(00)00094-X
Liu YJ, Li SJ, Wang HL et al (2016) Microstructure, defects and mechanical behavior of beta-type titanium porous structures manufactured by electron beam melting and selective laser melting. Acta Mater 113:56–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.04.029
Xiao H, Zhang C, Zhu H (2023) Effect of direct aging and annealing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AlSi10Mg fabricated by selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyp J 29:118–127. https://doi.org/10.1108/RPJ-03-2022-0085
Goh CS, Wei J, Lee LC, Gupta M (2007) Properties and deformation behaviour of Mg-Y2O3 nanocomposites. Acta Mater 55:5115–5121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2007.05.032
Gao C, Wu W, Shi J, Xiao Z, Akbarzadeh AH (2020) Simultaneous enhancement of strength, ductility, and hardness of TiN/AlSi10Mg nanocomposites via selective laser melting. Addit Manuf 34:101378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101378
Sanaty-Zadeh A (2012) Comparison between current models for the strength of particulate-reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites with emphasis on consideration of Hall-Petch effect. Mater Sci Eng A Struct Mater 531:112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.10.043
Lin T-C, Cao C, Sokoluk M et al (2019) Aluminum with dispersed nanoparticles by laser additive manufacturing. Nat Commun 10:4124–4129. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12047-2
Sekine H, Rong C (1995) A combined microstructure strengthening analysis of SiCp/Al metal matrix composites. Composites 26:183–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-4361(95)91381-E
Girelli L, Tocci M, Gelfi M, Pola A (2019) Study of heat treatment parameters for additively manufactured AlSi10Mg in comparison with corresponding cast alloy. Mater Sci Eng A Struct Mater 739:317–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.10.026
Cheng W, Liu Y, Xiao X, Huang B, Zhou Z, Liu X (2022) Microstructure and mechanical properties of a novel (TiB2+TiC)/AlSi10Mg composite prepared by selective laser melting. Mater Sci Eng A Struct Mater 834:142435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.142435
Xie X, Chen C, Chen Z et al (2021) Effect of annealing treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of cold sprayed TiB2/AlSi10Mg composites. Surf. Interfaces 26:101341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2021.101341
Hadadzadeh A, Baxter C, Amirkhiz BS, Mohammadi M (2018) Strengthening mechanisms in direct metal laser sintered AlSi10Mg: comparison between virgin and recycled powders. Addit Manuf 23:108–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.07.014
Körner C (2016) Additive manufacturing of metallic components by selective electron beam melting - a review. Int Mater Rev 61:361–377. https://doi.org/10.1080/09506608.2016.1176289
Geng J, Hong T, Shen Y et al (2017) Microstructural stability of in-situ TiB2/Al composite during solution treatment. Mater Charact 124:50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2016.11.032
Ma S, Wang Y, Wang X (2020) Microstructures and mechanical properties of an Al-Cu-Mg-Sc alloy reinforced with in-situ TiB2 particulates. Mater Sci Eng A Struct Mater 788:139603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.139603
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Nos. 51971137, 52071207] and Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (China, Grant No. 22ZR1432800). The authors would like to acknowledge the facility support from Tianjin Qbeam-3d Technology Co. Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KW done investigation, formal analysis, data curation, and writing—original draft preparation; SM done writing—reviewing & editing, data curation; XF performs validation; YL performed investigation; WK helped in resources, methodology; HW contributed to supervision; MW performed validation and data curation; JL performed investigation and methodology; ZC contributed to conceptualization, supervision, writing—review & and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Catalin Croitoru.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, K., Ma, S., Fang, X. et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of an in-situ TiB2 particle reinforced AlSi10Mg composite additive manufactured by selective electron beam melting. J Mater Sci 58, 7915–7929 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-023-08516-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-023-08516-1