Abstract
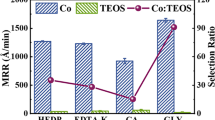
Cobalt (Co) has been applied as one of the most promising candidates of barrier metals for copper (Cu) interconnects. The present work describes the static etching and chemical mechanical polishing process of Cu and Co, which were conducted by potassium persulfate (K2S2O8) as an oxidizer at various pH values. It was found that compared with the conventional oxidizer hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-based slurries, the K2S2O8-based slurries exhibited a relatively high Co removal rate, as well as the diminished particulate contamination and excellent post-etching morphology. A slurry consisting of 3 vol% colloidal silica, 10 mM K2S2O8, and 5 mM benzotriazole (BTA) produced a Co removal rate of ~ 127 Å/min at pH 10, along with a removal rate selectivity of ~ 1 between Cu and Co films. Based on the data of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and nano-scratch depth tests, the interplaying mechanisms of chemical and mechanical on Cu and Co removal rates in K2S2O8-based slurries were investigated.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wong HSP (2005) Beyond the conventional transistor. Solid State Electron 49(5):755–762
T Nogami et al (2010) CVD Co and its application to Cu damascene interconnections. In: 2010 IEEE international interconnect technology conference IITC 2010, vol 111, pp 10–12
Yang CC et al (2012) Co capping layers for Cu/low-k interconnects. Microelectron Eng 92:79–82
Bekiaris N et al (2017) Cobalt fill for advanced interconnects. In: IITC 2017–2017 IEEE international interconnect technology conference. pp 1–3
Huang HY et al (2010) A new enhancement layer to improve copper interconnect performance. In: 2010 IEEE international interconnect technology conference, vol 3, pp 1–3
Li Z, Gordon RG, Farmer DB, Lin Y, Vlassak J (2005) Nucleation and adhesion of ALD copper on cobalt adhesion layers and tungsten nitride diffusion barriers. Electrochem Solid State Lett 8(7):G182–G185
Xu W-Z, Xu J-B, Lu H-S, Wang J-X, Hu Z-J, Qu X-P (2013) Direct copper plating on ultra-thin sputtered cobalt film in an alkaline bath. J Electrochem Soc 160(12):D3075–D3080
He M et al (2013) Mechanism of Co liner as enhancement layer for Cu interconnect gap-fill. J Electrochem Soc 160(12):D3040–D3044
CRC handbook of chemistry and physics: a ready-reference book of chemical and physical data. Choice Reviews Online, vol 29, no. 01. pp 29-0016–29-0016 (1988)
Jiang L, He Y, Li Y, Li Y, Luo J (2014) Synergetic effect of H2O2 and glycine on cobalt CMP in weakly alkaline slurry. Microelectron Eng 122:82–86
Popuri R et al (2017) Citric acid as a complexing agent in chemical mechanical polishing slurries for cobalt films for interconnect applications. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 6(9):P594–P602
Ranaweera CK, Baradanahalli NK, Popuri R, Seo J, Babu SV (2019) Ammonium persulfate and potassium oleate containing silica dispersions for chemical mechanical polishing for cobalt interconnect applications. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 8(5):P3001–P3008
Nishizawa H, Nojo H, Isobe A (2010) Fundamental study of chemical–mechanical polishing slurry of cobalt barrier metal for the next-generation interconnect process. Jpn J Appl Phys 49(5 PART 3):4–6
Peethala BC, Amanapu HP, Lagudu URK, Babu SV (2012) Cobalt polishing with reduced galvanic corrosion at copper/cobalt interface using hydrogen peroxide as an oxidizer in colloidal silica-based slurries. J Electrochem Soc 159(6):582–588
Lu H-S et al (2012) The effect of H2O2 and 2-MT on the chemical mechanical polishing of cobalt adhesion layer in acid slurry. Electrochem Solid State Lett 15(4):H97–H100
Sagi KV, Teugels LG, Van Der Veen MH, Struyf H, Alety SR, Babu SV (2017) Chemical mechanical polishing of chemical vapor deposited Co films with minimal corrosion in the Cu/Co/Mn/SiCOH patterned structures. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 6(5):P276–P283
Turk MC, Shi X, Gonyer DAJ, Roy D (2016) Chemical and mechanical aspects of a Co–Cu planarization scheme based on an alkaline slurry formulation. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 5(2):P88–P99
Tsai TH, Wu YF, Yen SC (2005) Glycolic acid in hydrogen peroxide-based slurry for enhancing copper chemical mechanical polishing. Microelectron Eng 77(3–4):193–203
Poddar MK et al (2019) Nanocatalyst-induced hydroxyl radical (OH) slurry for tungsten CMP for next-generation semiconductor processing. J Mater Sci
Cui H, Park JH, Park JG (2013) Effect of oxidizers on chemical mechanical planarization of ruthenium with colloidal silica based slurry. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 2(1):26–30
Lee WJ, Park HS (2004) Development of novel process for Ru CMP using ceric ammonium nitrate (CAN)-containing nitric acid. Appl Surf Sci 228(1–4):410–417
Kim IK et al (2008) Effect of sodium periodate in alumina-based slurry on Ru CMP for metal-insulator-metal capacitor. Electrochem Solid State Lett 11(6):150–153
Shirley DA (1972) High-resolution x-ray photoemission spectrum of the valence bands of gold. Phys Rev B 5(12):4709–4714
Foelske A, Strehblow HH (2000) Passivity of cobalt in borate buffer at pH 9.3 studied by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Surf Interface Anal 29(8):548–555
Sun Y et al (2013) Electrodeposited cobalt-sulfide catalyst for electrochemical and photoelectrochemical hydrogen generation from water. J Am Chem Soc 135(47):17699–17702
Ismail KM, Badawy WA (2000) Electrochemical and XPS investigations of cobalt in KOH solutions. J Appl Electrochem 30(11):1303–1311
Miller AC, Simmons GW (1993) Copper by XPS. Surf Sci Spectra 2(1):55–60
Galtayries A, Bonnelle J-P (1995) XPS and ISS studies on the interaction of H2S with polycrystalline Cu, Cu2O and CuO surfaces. Surf Interface Anal 23(3):171–179
Du T, Luo Y, Desai V (2004) The combinatorial effect of complexing agent and inhibitor on chemical–mechanical planarization of copper. Microelectron Eng 71(1):90–97
Lee WJ et al (2002) Adhesion and interface chemical reactions of Cu/polyimide and Cu/TiN by XPS. Appl Surf Sci 205(1–4):128–136
Varghese B, Yousheng Z, Ling D, Tan VBC, Chwee TL, Sow CH (2008) Structure-mechanical property of individual cobalt oxide nanowires. Nano Lett 8(10):3226–3232
Karimpoor AA, Erb U, Aust KT, Palumbo G (2003) High strength nanocrystalline cobalt with high tensile ductility. Scr Mater 49(7):651–656
Aledresse A, Alfantazi A (2004) A study on the corrosion behavior of nanostructured electrodeposited cobalt. J Mater Sci 39(4):1523–1526. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000013934.85378.40
Badawy WA, Al-Kharafi FM, Al-Ajmi JR (2000) Electrochemical behaviour of cobalt in aqueous solutions of different pH. J Appl Electrochem 30(6):693–704
Anipsitakis GP, Dionysiou DD (2003) Degradation of organic contaminants in water with sulfate radicals generated by the conjunction of peroxymonosulfate with cobalt. Environ Sci Technol 37(20):4790–4797
Yao Y, Xu C, Qin J, Wei F, Rao M, Wang S (2013) Synthesis of magnetic cobalt nanoparticles anchored on graphene nanosheets and catalytic decomposition of orange II. Ind Eng Chem Res 52(49):17341–17350
Ji Y, Dong C, Kong D, Lu J (2015) New insights into atrazine degradation by cobalt catalyzed peroxymonosulfate oxidation: kinetics, reaction products and transformation mechanisms. J Hazard Mater 285:491–500
Zhang L, Wang T, Lu X (2019) The effect of citric acid based cleaning solution on particle adhesion and removal during post-Cu CMP cleaning. Microelectron Eng 216:111090
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the financial support of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grand No. 51991374).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Wang, T. & Lu, X. Potassium persulfate as an oxidizer in chemical mechanical polishing slurries relevant for copper interconnects with cobalt barrier layers. J Mater Sci 55, 8992–9002 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04579-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04579-6