Abstract
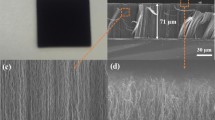
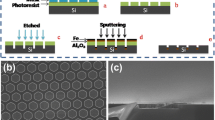
Vertically aligned carbon nanotube (VACNT) emitters were synthesized directly on stainless steel substrate using DC plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Remarkable field emission (FE) properties, such as low turn-on electric field (ETO = 1.40 V/μm) and low threshold electric field (ETH = 2.31 V/μm), were observed from VACNT arrays with long length and moderate density. The FE performance was significantly enhanced by a uniquely bundled structure of VACNTs formed through a simple water treatment process. The FE properties of VACNTs were further improved by coating the exterior of CNTs with a uniform layer of crystalline SnO2 nanoparticles; the ETO and ETH were reduced to 1.18 and 2.01 V/μm, respectively. The enhancement of FE properties by SnO2 coating can be attributed to the morphological change of VACNTs caused by the solution phase coating process. The coated samples also exhibited an improved FE stability which is attributed to the enhancement of the mechanical strength and chemical stability of the VACNTs after the SnO2 coating. The VACNT emitters with characteristic features such as a conductive substrate, low contact resistance between the VACNTs and the substrate, uniform coating, and bundled morphology can be ideal candidates for FE devices.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qian D, Wagner GJ, Liu WK, Yu MF, Ruoff RS (2002) Mechanics of carbon nanotubes. Appl Mech Rev 55(6):495–533
Hone J, Llaguno MC, Biercuk MJ, Johnson AT, Batlogg B, Benes Z et al (2002) Thermal properties of carbon nanotubes and nanotube-based materials. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 74(3):339–343
Bockrath M, Cobden DH, McEuen PL, Chopra NG, Zettl A, Thess A et al (1997) Single-electron transport in ropes of carbon nanotubes. Science 275(5308):1922–1925
Poudel YR, Li W (2018) Synthesis, properties, and applications of carbon nanotubes filled with foreign materials: a review. Mater Today Phys 7:7–34
Choi WB, Chung DS, Kang JH, Kim HY, Jin YW, Han IT et al (1999) Fully sealed, high-brightness carbon-nanotube field-emission display. Appl Phys Lett 75(20):3129–3131
Baughman RH, Zakhidov AA, De Heer WA (2002) Carbon nanotubes—the route toward applications. Science 297(5582):787–792
Yue GZ, Qiu Q, Gao B, Cheng Y, Zhang J, Shimoda H et al (2002) Generation of continuous and pulsed diagnostic imaging x-ray radiation using a carbon-nanotube-based field-emission cathode. Appl Phys Lett 81(2):355–357
Milne WI, Teo KBK, Minoux E, Groening O, Gangloff L, Hudanski L et al (2006) Aligned carbon nanotubes/fibers for applications in vacuum microwave amplifiers. J Vacuum Sci Technol B Microelectron Nanometer Struct 24(1):345–348
Li J, Papadopoulos C, Xu J (1999) Growing Y-junction carbon nanotubes. Nature 402:253–254
Morassutto M, Tiggelaar RM, Smithers M, Gardeniers JG (2016) Vertically aligned carbon nanotube field emitter arrays with Ohmic base contact to silicon by Fe-catalyzed chemical vapor deposition. Mater Today Commun 7:89–100
Talapatra S, Kar S, Pal SK, Vajtai R, Ci L, Victor P et al (2006) Direct growth of aligned carbon nanotubes on bulk metals. Nat Nanotechnol 1(2):112–116
Neupane S, Yang Y, Li W, Gao Y (2014) Synthesis and enhanced electron field emission of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes grown on stainless steel substrate. J Nanosci Lett 4:14–20
Bonard JM, Weiss N, Kind H, Stöckli T, Forró L, Kern K, Chatelain A (2001) Tuning the field emission properties of patterned carbon nanotube films. Adv Mater 13(3):184–188
Kim D, Lim SH, Guilley AJ, Cojocaru CS, Bourée JE, Vila L et al (2008) Growth of vertically aligned arrays of carbon nanotubes for high field emission. Thin Solid Films 516(5):706–709
Hazra KS, Rai P, Mohapatra DR, Kulshrestha N, Bajpai R, Roy S et al (2009) Dramatic enhancement of the emission current density from carbon nanotube based nanosize tips with extremely low onset fields. ACS Nano 3(9):2617–2622
Gupta BK, Kedawat G, Gangwar AK, Nagpal K, Kashyap PK, Srivastava S et al (2018) High-performance field emission device utilizing vertically aligned carbon nanotubes-based pillar architectures. AIP Adv 8(1):015117
Wang K-Y, Liao C-Y, Cheng H-C (2016) Field-emission characteristics of the densified carbon nanotube pillars array. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 5(9):M99–M103
Li Z, Yang X, He F, Bai B, Zhou H, Li C et al (2015) High current field emission from individual non-linear resistor ballasted carbon nanotube cluster array. Carbon 89:1–7
Li X, Niu J, Zhang J, Li H, Liu Z (2003) Labeling the defects of single-walled carbon nanotubes using titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 107:2453–2458
Green JM, Dong L, Gutu T, Jiao J, Conley JF, Ono Y (2006) ZnO-nanoparticle-coated carbon nanotubes demonstrating enhanced electron field-emission properties. J Appl Phys 99(9):1–4
Chen C-A, Lee K-Y, Chen Y-M, Chi J-G, Lin S-S, Huang Y-S (2010) Field emission properties of RuO2 thin film coated on carbon nanotubes. Vacuum 84(12):1427–1429
Chakrabarti S, Pan L, Tanaka H, Hokushin S, Nakayama Y (2007) Stable field emission property of patterned MgO coated carbon nanotube arrays. Jpn J Appl Phys 46(7R):4364–4369
Sreekanth M, Ghosh S, Barman SR, Sadhukhan P, Srivastava P (2018) Field emission properties of indium-decorated vertically aligned carbon nanotubes: an interplay between type of hybridization, density of states and metal thickness. Appl Phys A 124(8):528–536
Sridhar S, Tiwary C, Vinod S, Taha-Tijerina JJ, Sridhar S, Kalaga K et al (2014) Field emission with ultralow turn on voltage from metal decorated carbon nanotubes. ACS Nano 8(8):7763–7770
Suriani A, Dalila A, Mohamed A, Mamat M, Malek M, Soga T et al (2016) Fabrication of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes–zinc oxide nanocomposites and their field electron emission enhancement. Mater Des 90:185–195
Thapa A, Neupane S, Guo R, Jungjohann KL, Pete D, Li W (2018) Direct growth of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes on stainless steel by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Diam Relat Mater 90:144–153
Han W-Q, Zettl A (2003) Coating single-walled carbon nanotubes with tin oxide. Nano Lett 3(5):681–683
Masarapu C, Wei B (2007) Direct growth of aligned multiwalled carbon nanotubes on treated stainless steel substrates 23(17):9046–9049
Bower C, Zhou O, Zhu W, Werder DJ, Jin S (2000) Nucleation and growth of carbon nanotubes by microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition. Appl Phys Lett 77(17):2767–2769
Chhowalla M, Teo KBK, Ducati C, Rupesinghe NL, Amaratunga GAJ, Ferrari AC et al (2001) Growth process conditions of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes using plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. J Appl Phys 90(10):5308–5317
Abadi PPSS, Maschmann MR, Hodson SL, Fisher TS, Baur JW, Graham S et al (2017) Mechanical behavior of carbon nanotube forests grown with plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition: pristine and conformally coated. J Eng Mater Technol 139(3):034502
Arjmand M, Chizari K, Krause B, Pötschke P, Sundararaj U (2016) Effect of synthesis catalyst on structure of nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes and electrical conductivity and electromagnetic interference shielding of their polymeric nanocomposites. Carbon 98:358–372
Jang JW, Lee CE, Lyu SC, Lee TJ, Lee CJ (2004) Structural study of nitrogen-doping effects in bamboo-shaped multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Appl Phys Lett 84(15):2877–2879
Lau KK, Bico J, Teo KB, Chhowalla M, Amaratunga GA, Milne WI et al (2003) Superhydrophobic carbon nanotube forests. Nano Lett 3(12):1701–1705
Mashayekhi A, Hosseini SM, Amiri MH, Namdar N, Sanaee Z (2016) Plasma-assisted nitrogen doping of VACNTs for efficiently enhancing the supercapacitor performance. J Nanopart Res 18(6):154–168
Pandey A, Prasad A, Moscatello J, Ulmen B, Yap YK (2010) Enhanced field emission stability and density produced by conical bundles of catalyst-free carbon nanotubes. Carbon 48(1):287–292
Zhang K, Li T, Ling L, Lu H, Tang L, Li C et al (2017) Facile synthesis of high density carbon nanotube array by a deposition-growth-densification process. Carbon 114:435–440
Rudloff-Grund J, Brenker F, Marquardt K, Kaminsky F, Schreiber A (2016) STEM EDX nitrogen mapping of nanoinclusions in milky diamonds from Juina, Brazil, using a windowless silicon drift detector system. Anal Chem 88(11):5804–5808
Barros E, Souza Filho A, Lemos V, Mendes Filho J, Fagan SB, Herbst M et al (2005) Charge transfer effects in acid treated single-wall carbon nanotubes. Carbon 43(12):2495–2500
Wang Z, Chen G, Xia D (2008) Coating of multi-walled carbon nanotube with SnO2 films of controlled thickness and its application for Li-ion battery. J Power Sources 184(2):432–436
Fan W, Gao L, Sun J (2006) Tin oxide nanoparticle-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes by the vapor phase method. J Am Ceram Soc 89(8):2671–2673
Jonge N, Allioux M, Doytcheva M, Kaiser M, Teo KBK, Lacerda RG et al (2004) Characterization of the field emission properties of individual thin carbon nanotubes. Appl Phys Lett 85(9):1607–1609
Doytcheva M, Kaiser M, Verheijen MA, Reyes-Reyes M, Terrones M, de Jonge N (2004) Electron emission from individual nitrogen-doped multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem Phys Lett 396(1–3):126–130
Brodie I, Spindt C (1992) Vacuum microelectronics. In: Hawkes PW (ed) Advances in electronics and electron physics. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–106
Gao R, Pan Z, Wang ZL (2001) Work function at the tips of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Appl Phys Lett 78(12):1757–1759
Kurilich MR, Thapa A, Moilanen A, Miller JL, Li W, Neupane S (2019) Comparative study of electron field emission from randomly-oriented and vertically-aligned carbon nanotubes synthesized on stainless steel substrates. J Vacuum Sci Technol B Nanotechnol Microelectron Mater Process Meas Phenom 37(4):041202
Pandey A, Prasad A, Moscatello JP, Yap YK (2010) Stable electron field emission from PMMA− CNT matrices. ACS Nano 4(11):6760–6766
Chhowalla M, Ducati C, Rupesinghe NL, Teo KBK, Amaratunga GAJ (2001) Field emission from short and stubby vertically aligned carbon nanotubes. Appl Phys Lett 79(13):2079–2081
Patra R, Ghosh S, Sharma H, Vankar VD (2013) High stability field emission from zinc oxide coated multiwalled carbon nanotube film. Adv Mater Lett 4(11):849–855
Xu J, Xu P, Ou-Yang W, Chen X, Guo P, Li J et al (2015) Outstanding field emission properties of wet-processed titanium dioxide coated carbon nanotube based field emission devices. Appl Phys Lett 106(7):073501
Crespi VH, Chopra NG, Cohen ML, Zettl A, Louie SG (1996) Anisotropic electron-beam damage and the collapse of carbon nanotubes. Phys Rev B 54(8):5927–5931
Zhang K, Stocks GM, Zhong J (2007) Melting and premelting of carbon nanotubes. Nanotechnology 18(28):285703
Doytcheva M, Kaiser M, Jonge N (2006) In situ transmission electron microscopy investigation of the structural changes in carbon nanotubes during electron emission at high currents. Nanotechnology 17(13):3226–3233
Bocharov G, Eletskii A (2013) Theory of carbon nanotube (CNT)-based electron field emitters. Nanomaterials 3(3):393–442
Chen G, Neupane S, Li W, Chen L, Zhang J (2013) An increase in the field emission from vertically aligned multiwalled carbon nanotubes caused by NH3 plasma treatment. Carbon 52:468–475
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Science Foundation under grant DMR-1506640. This work was performed, in part, at the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies, an Office of Science User Facility operated for the US Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science. Sandia National Laboratories is a multi-mission laboratory managed and operated by National Technology and Engineering Solutions of Sandia, LLC., a wholly owned subsidiary of Honeywell International, Inc., for the US DOE’s National Nuclear Security Administration under contract DE-NA-0003525. This paper describes objective technical results and analysis. Any subjective views or opinions that might be expressed in the paper do not necessarily represent the views of the US Department of Energy or the US Government. The authors would also like to acknowledge the support from Advanced Materials Engineering Research Institutes (AMERI) at Florida International University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thapa, A., Jungjohann, K.L., Wang, X. et al. Improving field emission properties of vertically aligned carbon nanotube arrays through a structure modification. J Mater Sci 55, 2101–2117 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-04156-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-04156-6