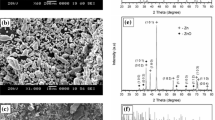
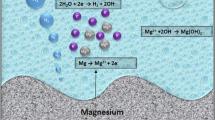
Abstract
Magnesium alloys with suitable corrosion behaviour and good mechanical properties are desired for biodegradable materials. In the current study, novel Mg–Li-based metallic glasses (MGs) demonstrate potential clinical applications as implantable biodegradable materials. The amorphous structure of MGs provides suitable elastic modulus with human bone. The enhanced corrosion resistance of MGs realises a uniform corrosion process, as well as maintains a stable acid-based environment, and increases cell proliferation. A schematic model is proposed to illustrate the corrosion mechanisms of MGs. Adding Li significantly improves the corrosion resistance of MGs. Both the indirect cytotoxicity and direct cell culture assays are conducted using transfected osteoblasts (hFOB) cells. Results show that the novel Mg–Li–Zn–Ca MGs have good biocompatibility.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang DY, Jie Y, Sang KW et al (2014) The effects of microstructural factors on the corrosion behaviour of Mg–5Sn–xZn (x = 1, 3 wt%) extrusions. Corros Sci 90(16):597–605
Ha HY, Kang JY, Chang DY et al (2014) Role of hydrogen evolution rate in determining the corrosion rate of extruded Mg–5Sn–(1–4 wt%)Zn alloys. Corros Sci 89:275–285
Zheng YF, Gu XN, Witte F (2014) Biodegradable metals. Mater Sci Eng Rep 77(2):1–34
Witte F, Kaese V, Haferkamp H, Switzer E, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Wirth CJ et al (2005) In vivo corrosion of four magnesium alloys and the associated bone response. Biomaterials 26:3557–3563
Lin X, Tan L, Wang Q et al (2013) In vivo, degradation and tissue compatibility of ZK60 magnesium alloy with micro-arc oxidation coating in a transcortical model. Mater Sci Eng C 33(7):3881–3888
Xue-Nan GU, Zheng YF (2010) A review on magnesium alloys as biodegradable materials. Chin Inst High Learn Acad Abstr Mater Sci 4(2):111–115
Sigel H (1973) Metal ions in biological systems, vol 2. Dekker, pp 124–126
Kannan MB, Raman RK (2008) In vitro degradation and mechanical integrity of calcium-containing magnesium alloys in modified-simulated body fluid.[J]. Biomaterials 29(15):2306–2314
Zhang S, Zhang X, Zhao C et al (2010) Research on an Mg–Zn alloy as a degradable biomaterial. Acta Biomater 6(2):626–640
Wan Y, Xiong G, Luo H et al (2008) Preparation and characterization of a new biomedical magnesium–calcium alloy. Mater Des 29(10):2034–2037
Sun Y, Kong MX, Jiao XH (2011) In-vitro evaluation of Mg–4.0Zn–0.2Ca alloy for biomedical application. Transact Nonferrous Metals Soc China 21(31):s252–s257
Kubásek J, Vojtěch D, Jablonská E, Pospíšilová I, Lipov J, Ruml T (2016) Structure, mechanical characteristics and in vitro degradation, cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and mutagenicity of novel biodegradable Zn–Mg alloys. Mater Sci Eng C 58(1):24–35
Song G, Atrens A (1999) Corrosion mechanisms of magnesium alloys. Adv Eng Mater 1(1):11–33
Li Z, Gu X, Lou S, Zheng Y (2008) The development of binary Mg–Ca alloys for use as biodegradable materials within bone [J]. Biomaterials 29:1329–1344
Song GL (2007) Control of biodegradation of biocompatible magnesium alloys. Corros Sci 49:1696–1701
Mao L, Yuan GY, Niu JL, Zong Y, Ding WJ (2013) In vitro degradation behavior and biocompatibility of Mg–Nd–Zn–Zr alloy by hydrofluoric acid treatment. Mater Sci Eng C 33:242–250
Zhang E, Yang L, Xu J et al (2010) Microstructure, mechanical properties and bio-corrosion properties of Mg–Si(–Ca, Zn) alloy for biomedical application. Acta Biomater 6(5):1756–1762
Scully JR, Gebert A, Payer JH (2007) Corrosion and related mechanical properties of bulk metallic glasses. J Mater Res 22:302–313
Wang WH, Dong C, Shek CH (2004) Bulk metallic glasses. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 44(2–3):45–89
Gebert A, Wolff U, John A, Eckert J, Schultz L (2001) Stability of the bulk glass-forming Mg65Y10Cu25 alloy in aqueous electrolytes. Mater Sci Eng A 299:125–135
Zberg B, Uggowitzer PJ, Loffler JF (2009) MgZnCa glasses without clinically observable hydrogen evolution for biodegradable implants. Nat Mater 8:887–891
Li H, Pang S, Liu Y et al (2015) Biodegradable Mg–Zn–Ca–Sr bulk metallic glasses with enhanced corrosion performance for biomedical applications. Mater Des 67:9–19
Haferkamp H, Jaschik C, Juchmann P et al (2001) Entwicklung und Eigenschaften von Magnesium–Lithium–Legierungen. Material wissen schaft Und Werkstofftechnik 32(1):25–30
Zeng RC, Sun L, Zheng YF et al (2014) Corrosion and characterisation of dual phase Mg–Li–Ca alloy in Hank’s solution: the influence of microstructural features. Corros Sci 79(79):69–82
Witte F, Fischer J, Nellesen J et al (2006) In vitro and in vivo corrosion measurements of magnesium alloys [J]. Biomaterials 27(7):1013–1018
Fischer J, Feyerabend F, Hort N, Kainer KU, Schreyer A, Willumeit R (2009) Cytotoxic and immunological effects of magnesium alloy elements on cells. In: Kainer KU (ed) Proceeding of 8th international conference on magnesium alloys and their applications. Wiley-VCH, DGM, Weinheim, pp 1175–1181
Sahoo B, Kuncser V, Keune W, Pieper J (2005) Mössbauer spectroscopical investigation of amorphous Fe–Y alloy ribbons prepared by melt spinning. Hyperfine Interact 165:175–181
Schuh CA, Nieh TG (2003) A nanoindentation study of serrated flow in bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater 51(1):87–99
Chinh NQ, Horváth G, Kovács Z et al (2005) Kinematic and dynamic characterization of plastic instabilities occurring in nano- and microindentation tests. Mater Sci Eng A 409(1–2):100–107
Zhang YJ, Yan CW, Wang FH, Li WF (2005) Electrochemical behavior of anodized Mg alloy AZ91D in chloride containing aqueous solution. Corros Sci 47:2816–2831
Morlidge JR, Skeldon P, Thompson GE, Habazaki H, Shimizu K, Wood GC (1999) Gel formation and the efficiency of anodic film growth on aluminium. Electrochim Acta 44:2423–2435
Song GL (2009) Effect of tin modification on corrosion of AM70 magnesium alloy. Corros Sci 51:2063–2070
Tan ALK, Soutar AM, Annergren IF, Liu YN (2005) Multilayer sol-gel coating for corrosion protection of magnesium. Surf Coat Technol 198:478–482
Brett CMA, Dias L, Trindabe B, Fischer R, Mies S (2006) Characterisation by EIS of ternary Mg alloys synthesised by mechanical alloying [J]. Electrochim Acta 51:1752–1760
Gu X, Zheng Y (2010) Corrosion of, and cellular responses to Mg–Zn–Ca bulk metallic glasses. Biomaterials 31(6):1093–1103
Zeng R, Guo X, Liu C et al (2011) Study on corrosion of medical Mg–Ca And Mg–Li–Ca alloys. Acta Metall Sin Chin Edit 47(11):1477–1482
Bialobrzeski A, Saja K, Zmudzińska M (2011) Studies of corrosion behaviour in alkaline environment of binary Mg–Li alloys for plastic forming. Arch Foundry Eng 11(SI 3):21–24
Zeng R, Kainer KU, Blawert C et al (2011) Corrosion of an extruded magnesium alloy ZK60 component—the role of microstructural features. J Alloy Compd 509(13):4462–4469
News STB (2007) CRC handbook of chemistry and physics, a ready-reference book of chemical and physical data, 88th edn. Scitech Book News, Portland
Nordlien JH, Ono S, Masuko N et al (1997) A TEM investigation of naturally formed oxide films on pure magnesium. Corros Sci 39(8):1397–1414
Meyer-Lindenberg A, Windhagen H, Witte F, et al (2004) medical implant for the human or animal body: US, US 2004 0241036 A1[P]
Song Y, Shan D, Chen R et al (2009) Investigation of surface oxide film on magnesium lithium alloy. J Alloy Compd 484(1):585–590
Liu JX, Zhu YX, Gao F (2011) Chemistry of Nonorganic Elements, 2nd edn. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Kokubo T (1996) Formation of biologically active bone-like apatite on metals and polymers by a biomimetic process. Thermochim Acta S280–S281(95):479–490
Ramya M, Sarwat SG, Udhayabanu V, Subramanian S, Raj B, Ravi KR (2015) Role of partially amorphous structure and alloying elements on the corrosion behavior of Mg–Zn–Ca bulk metallic glass for biomedical applications. Mater Des 86:829–835
Wang Jingfeng, Huang Song, Li Yang, Wei Yiyun, Xi Xingfeng, Cai Kaiyong (2013) Effects of Y on the Microstructure, microstructure, mechanical and bio-corrosion properties of Mn-doped Mg–Zn–Ca bulk metallic glass composites. Mater Sci Eng C 33(7):3832–3838
Wu Y, He G, Zhang Y et al (2016) Unique antitumor property of the Mg–Ca–Sr alloys with addition of Zn. Sci Rep 6:21736–21748
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation, China (Grant Nos. 51771120 and 51304136), project supported by Shanghai Key Technology Support Program (Shanghai Science and Technology Ministry China. Grant No. 16060502400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meifeng, H., Hao, W., Kunguang, Z. et al. Effects of Li addition on the corrosion behaviour and biocompatibility of Mg(Li)–Zn–Ca metallic glasses. J Mater Sci 53, 9928–9942 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2323-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2323-3