Abstract
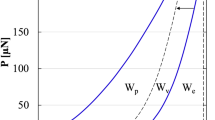
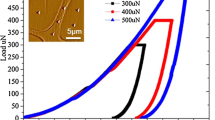
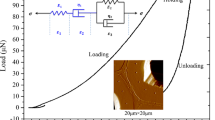
Micromechanical properties of individual phases within wood tissues are crucially important for the processing and utilization of this biomass material. The quasi-static nanoindentation and dynamic modulus mapping techniques were employed to study the micromechanical properties of wood cell walls and their interface regions. Nanoindentation results showed that the reduced modulus of secondary cell walls (18 GPa) was twice that of interface compound middle lamella (CML) (7 GPa). Modulus mapping, with advantages of high resolution and undamaged test over conventional nanoindentation, was able to analyse the subtle variations in micromechanical properties of individual phases within the whole wood tissues, especially interface layers. The variation tendency across adjacent cell walls was similar to that tested by nanoindentation, and the secondary cell walls exhibited maxima in the middle of the secondary wall and slightly reduction approaching to the S1 and S3 layers. Moreover, the storage modulus of interface region CML showed “W” distribution, which meant that the modulus first fell and then rose from the central area to edge regions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnett JR, Bonham VA (2004) Cellulose microfibril angle in the cell wall of wood fibres. Biol Rev 79:461–472
Mishnaevsky L, Qing H (2008) Micromechanical modelling of mechanical behaviour and strength of wood: state-of-the-art review. Comput Mater Sci 44:363–370
Wimmer R, Lucas BN, Tsui TY, Oliver WC (1997) Longitudinal hardness and Young’s modulus of spruce tracheid secondary walls using nanoindentation technique. Wood Sci Technol 31:131–141
Yu Y, Fei B, Wang H, Tian G (2011) Longitudinal mechanical properties of cell wall of Masson pine (Pinus massoniana Lamb) as related to moisture content: a nanoindentation study. Holzforschung 65:121–126
Wu Y, Wang S, Zhou D, Xing C, Zhang Y, Cai Z (2010) Evaluation of elastic modulus and hardness of crop stalks cell walls by nano-indentation. Bioresour Technol 101:2867–2871
Wimmer R, Lucas BN (1997) Comparing mechanical properties of secondary wall and cell comer middle lamella in spruce wood. IAWA J 18:77–88
Tze WTY, Wang S, Rials TG, Pharr GM, Kelley SS (2007) Nanoindentation of wood cell walls: continuous stiffness and hardness measurements. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 38:945–953
Gindl W, Gupta HS, Schöberl T, Lichtenegger HC, Fratzl P (2004) Mechanical properties of spruce wood cell walls by nanoindentation. Appl Phys A 79:2069–2073
Konnerth J, Gierlinger N, Keckes J, Gindl W (2009) Actual versus apparent within cell wall variability of nanoindentation results from wood cell walls related to cellulose microfibril angle. J Mater Sci 44:4399–4406. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3665-7
Konnerth J, Valla A, Gindl W (2007) Nanoindentation mapping of a wood-adhesive bond. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 88:371–375
Barick AK, Tripathy DK (2010) Thermal and dynamic mechanical characterization of thermoplastic polyurethane/organoclay nanocomposites prepared by melt compounding. Mater Sci Eng A 527:812–823
Ryou H, Pashley DH, Tay FR, Arola D (2013) A characterization of the mechanical behavior of resin-infiltrated dentin using nanoscopic dynamic mechanical analysis. Dent Mater 29:719–728
Sahin O, Erina N (2008) High-resolution and large dynamic range nanomechanical mapping in tapping-mode atomic force microscopy. Nanotechnology 19:445717
Lashgari HR, Chen Z, Liao XZ, Chu D, Ferry M, Li S (2015) Thermal stability, dynamic mechanical analysis and nanoindentation behavior of FeSiB (Cu) amorphous alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 626:480–499
Lee G, Kim JY, Burek MJ, Greer JR, Tsui TY (2011) Plastic deformation of indium nanostructures. Mater Sci Eng A 528:6112–6120
Králík V, Němeček J (2014) Comparison of nanoindentation techniques for local mechanical quantification of aluminium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 618:118–128
Shilo D, Drezner H, Dorogoy A (2008) Investigation of interface properties by nanoscale elastic modulus mapping. Phys Rev Lett 100:35505
Balooch G, Marshall GW, Marshall SJ, Warren OL, Asif SAS, Balooch M (2004) Evaluation of a new modulus mapping technique to investigate microstructural features of human teeth. J Biomech 37:1223–1232
Wilkinson TM, Zargari S, Prasad M, Packard CE (2015) Optimizing nano-dynamic mechanical analysis for high-resolution, elastic modulus mapping in organic-rich shales. J Mater Sci 50:1041–1049. doi:10.1007/s10853-014-8682-5
Gershon AL, Bruck HA, Xu S, Sutton MA, Tiwari V (2010) Multiscale mechanical and structural characterizations of Palmetto wood for bio-inspired hierarchically structured polymer composites. Mater Sci Eng C 30:235–244
Uskokovic PS, Tang CY, Tsui CP, Ignjatovic N, Uskokovic DP (2007) Micromechanical properties of a hydroxyapatite/poly-l-lactide biocomposite using nanoindentation and modulus mapping. J Eur Ceram Soc 27:1559–1564
Prošek Z, Králík V, Topič J, Nežerka V, Indrová K, Tesárek P (2015) Microstructure description and micromechanical properties of spruce wood. Acta Polytech 55:39–49
Oliver WC, Pharr GM (1992) An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J Mater Res 7:1564–1583
Asif SAS, Wahl KJ, Colton RJ (1999) Nanoindentation and contact stiffness measurement using force modulation with a capacitive load–displacement transducer. Rev Sci Instrum 70:2408–2413
Asif SAS, Wahl KJ, Colton RJ, Warren OL (2001) Quantitative imaging of nanoscale mechanical properties using hybrid nanoindentation and force modulation. J Appl Phys 90:1192–1200
Shangguan W, Ren H, Lv J, Fei B, Chen Z, Zhao R, Zhao Y (2014) Cell wall property changes of white rot larch during decay process. BioResources 9:4297–4310
Cave ID, Hutt L (1968) The anisotropic elasticity of the plant cell wall. Wood Sci Technol 2:268–278
Jakes JE, Frihart CR, Beecher JF, Moon RJ, Resto PJ, Melgarejo ZH, Surez OM, Baumgart H, Elmustafa AA, Stone DS (2009) Nanoindentation near the edge. J Mater Res 24:1016–1031
Jakes JE, Frihart CR, Beecher JF, Moon RJ, Stone DS (2008) Experimental method to account for structural compliance in nanoindentation measurements. J Mater Res 23:1113–1127
Bergander A, Salmén L (2002) Cell wall properties and their effects on the mechanical properties of fibers. J Mater Sci 37:151–156. doi:10.1023/A:1013115925679
Gindl W, Schöberl T (2004) The significance of the elastic modulus of wood cell walls obtained from nanoindentation measurements. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 35:1345–1349
Dokukin ME, Sokolov I (2012) On the measurements of rigidity modulus of soft materials in nanoindentation experiments at small depth. Macromolecules 45:4277–4288
Dokukin ME, Sokolov I (2012) Quantitative mapping of the elastic modulus of soft materials with HarmoniX and PeakForce QNM AFM modes. Langmuir 28:16060–16071
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial supports from the Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 31370012). The authors would also like to thank Fengqin Dong from the Institute Botany, the Chinese Academy of Sciences for her assistance in sample preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, L., Lin, L., Fu, F. et al. Micromechanical properties of wood cell wall and interface compound middle lamella using quasi-static nanoindentation and dynamic modulus mapping. J Mater Sci 53, 549–558 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1185-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1185-4