Abstract
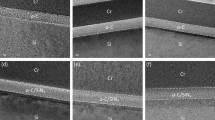
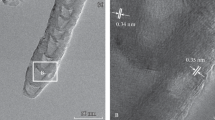
We used a multiwall carbon nanotube (MWNT) as a minute heater and studied structural changes in amorphous silicon (a-Si) supported on the surface of the MWNT heater during its Joule heating by in situ transmission electron microscopy combined with an optical spectroscopy system. During Joule heating of the MWNT at a temperature higher than 1690 K, thermal radiation spectra which follow Planck’s blackbody radiation law started to be measured, and it was demonstrated that the MWNT heater could reach a maximum temperature of approximately 2135 K. The increase in temperature caused the crystallization of a-Si and subsequent reaction of crystallized Si with carbon in the outer layers of the MWNT to form Si carbide nanoparticles. At elevated temperatures between 2040 and 2135 K, the formed Si carbide nanoparticles thermally decomposed to generate carbon nanocapsules consisting of multilayered graphene shells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei BQ, Vajtai R, Ajayan PM (2001) Reliability and current carrying capacity of carbon nanotubes. Appl Phys Lett 79:1172–1174
Kim P, Shi L, Majumdar A, McEuen PL (2001) Thermal transport measurements of individual multiwalled nanotubes. Phys Rev Lett 87:215502
Miyamoto Y, Berber S, Yoon M, Rubio A, Tománek D (2002) Onset of nanotube decay under extreme thermal and electronic excitations. Phys B 323:78–85
Begtrup GE, Ray KG, Kessler BM, Yuzvinsky TD, Garcia H, Zettl A (2007) Probing nanoscale solids at thermal extremes. Phys Rev Lett 99:155901
Zhang M, Fang S, Zakhidov AA, Lee SB, Aliev AE, Williams CD, Atkinson KR, Baughman RH (2005) Strong, transparent, multifunctional, carbon nanotube sheets. Science 309:1215–1219
Jang H-S, Jeon SK, Nahm SH (2011) The manufacture of a transparent film heater by spinning multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 49:111–116
Huang JY (2007) In situ observation of quasimelting of diamond and reversible graphite–diamond phase transformations. Nano Lett 7:2335–2340
Chen S, Huang JY, Wang Z, Kempa K, Chen G, Ren ZF (2005) High-bias-induced structure and the corresponding electronic property changes in carbon nanotubes. Appl Phys Lett 87:263107
Asaka K, Karita M, Saito Y (2011) Graphitization of amorphous carbon on a multiwall carbon nanotube surface by catalyst-free heating. Appl Phys Lett 99:091907
Xiong F, Liao A, Pop E (2009) Inducing chalcogenide phase change with ultra-narrow carbon nanotube heaters. Appl Phys Lett 95:243103
Zhang R, Hummelgård M, Olin H (2010) Carbon nanocages grown by gold templating. Carbon 48:424–430
Wei X, Wang M-S, Bando Y, Golberg D (2011) Thermal stability of carbon nanotubes probed by anchored tungsten nanoparticles. Sci Technol Adv Mater 12:044605
Li P, Jiang K, Liu M, Li Q, Fan S (2003) Polarized incandescent light emission from carbon nanotubes. Appl Phys Lett 82:1763–1765
Cai X, Akita S, Nakayama Y (2004) Current induced light emission from a multiwall carbon nanotube. Thin Solid Films 464–465:364–367
Aliev AE, Kuznetsov AA (2008) The origin of polarized blackbody radiation from resistively heated multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Phys Lett A 372:4938–4942
Zhang Y, Ichihashi T, Landree E, Nihey F, Iijima S (1999) Heterostructures of single-walled carbon nanotubes and carbide nanorods. Science 285:1719–1722
Asaka K, Nakahara H, Saito Y (2008) Nanowelding of a multiwalled carbon nanotube to metal surface and its electron field emission properties. Appl Phys Lett 92:023114
Asaka K, Terada T, Saito Y (2014) Transformation of silicon nanoparticles on a carbon nanotube heater into hollow graphitic nanocapsules via silicon carbide. Diam Relat Mater 50:49–54
Greene JE, Mei L (1976) High temperature metal-induced crystallization of r.f. sputtered amorphous Si thin films. Thin Solid Films 37:429–440
Gonzalez-Hernandez J, Martin D, Chao SS, Tsu R (1984) Crystallization temperature of ultrahigh vacuum deposited silicon films. Appl Phys Lett 45:101–103
Hirasawa M, Orii T, Seto T (2006) Size-dependent crystallization of Si nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett 88:093119
Kamino T, Tagushi T, Saka H (1994) In situ study of chemical reaction between silicon and graphite at 1,400°C in a high resolution/analytical electron microscope. J Electron Microsc 43:104–110
Man D, Kato YK, Kinkhabwala A, Cao E, Wang X, Zhang L, Wang Q, Guo J, Dai H (2007) Electrically driven thermal light emission from individual single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nat Nanotechnol 2:33–38
Liu Z, Bushmarker A, Aykol M, Cronin SB (2011) Thermal emission spectra from individual suspended carbon nanotubes. ACS Nano 5:4634–4640
Acknowledgements
This study was partly supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 25390015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asaka, K., Terada, T. & Saito, Y. High-temperature reaction of amorphous silicon with carbon on a multiwall carbon nanotube heater and temperature measurement by thermal radiation spectra. J Mater Sci 52, 7232–7238 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-0960-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-0960-6