Abstract
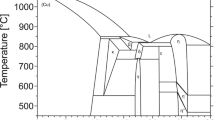
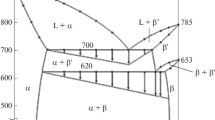
The solidification microstructures in three alloys from the Ag3Sn–Cu3Sn pseudo-binary section in the Ag–Cu–Sn system have been studied using a combination of X-ray diffraction, electron microscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, and quenching experiments. The three alloys have Ag:Cu ratios of 50:50, 40:60, and 30:70. In each case, the as-cast structures exhibit the equilibrium phases θ-Ag3Sn and ε1-Cu3Sn, with a little η-Cu6Sn5. There is no evidence of the metastable high-temperature phases that are so prevalent in as-cast structures of the corresponding binary alloys. The differential scanning calorimetry data obtained on heating the alloy samples are consistent with the transformations expected on the basis of the published ternary Ag–Cu–Sn diagrams. It is proposed that the solidification microstructures observed experimentally in such alloys must correspond to the nucleation of the high-temperature phases being kinetically limited upon cooling for these compositions. This leads to the direct formation of the equilibrium low-temperature phases by eutectic-type co-operative growth.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
It is important to note that the conventions used to define the axes in the D0a and long-period polymorphs are different. Thus, the b axis of the long-period structure lies parallel to c in the conventional description of the D0a structure, and b0 (superstructure) ≈ 10 c 0 (D0a).
References
Abtew M, Selvaduray G (2000) Lead-free solders in microelectronics. Mater Sci Eng R 27:95–141
Suganuma K (2001) Advances in lead-free electronics soldering. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 5:55–64
Yen YW, Chen SW (2004) Phase equilibria of the Ag-Sn-Cu ternary system. J Mater Res 19:2298–2305
Moon KW, Boettinger WJ (2004) Accurately determining eutectic compositions: the Sn-Ag-Cu ternary eutectic. J. Metals 56:22–27
Chang YA, Goldberg D, Neumann JP (1977) Phase diagrams and thermodynamic properties of ternary Cu-Ag Systems. J Phys Chem Ref Data 6:621–673
Fairhurst CW, Cohen JB (1972) The crystal structure of two compounds found in dental amalgam: Ag2Hg3 and Ag3Sn. Acta Cryst B28:371–378
Burkhardt W, Schubert K (1959) Über messingartige phasen mit A3-verwandter struktur. Z Metallkde 50:442–452
Brooks PL, Gillam E (1970) The ε-phase in the CuSn system. Acta Metal. 18:1181–1185
Watanabe Y, Fujinaga Y, Iwasaki H (1983) Lattice modulation in the long-period superstructure of Cu3Sn. Acta Cryst B39:306–311
Müller CJ, Lidin S (2014) Cu3Sn: Understanding the systematic absences. Acta Cryst B70:879–887
Xia Y, Xie X, Xie X, Lu C (2006) Intermetallic compounds evolution between lead-free solder and Cu-based lead frame alloys during isothermal aging. J Mater Sci 41:2359–2364. doi:10.1007/s10853-006-4501-y
Flandorfer H, Saeed U, Luef C, Sabbar A, Ipser H (2007) Interfaces in lead-free solder alloys: enthalpy of formation of binary Ag-Sn, Cu-Sn and Ni-Sn intermetallic compounds. Thermochim Acta 459:34–39
Shen J, Chan YC, Liu SY (2008) Growth mechanism of bulk Ag3Sn intermetallic compounds in Sn–Ag solder during solidification. Intermetallics 16:1142
Hsu C-M, Chen S-W (2013) Interfacial reactions with and without current stressing at Sn–Co/Ag and Sn–Co/Cu solder joints. J Mater Sci 48:6640–6646. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7464-9
Kang SK, Choi WK, Shih D-Y, Henderson DW, Gosselin T, Sarkhel A, Goldsmith C, Puttlitz KJ (2003) Ag3Sn plate formation in the solidification of near-ternary eutectic Sn-Ag-Cu. J Metals 55:61–65
Laurila T, Vuorinen V, Kivilahti JK (2005) Interfacial reactions between lead-free solders and common base materials. Mater Sci Eng R 49:1–60
Ma H (2009) Constitutive models of creep for lead-free solders. J Mater Sci 44:3841–3851. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3521-9
Mahler DB, Adey JD (1977) Microprobe analysis of a high Cu amalgam alloy. J Dental Res 56:379–384
Hooghan TK, Pinizzotto RF, Watkins JH, Okabe T (1996) Study of a low copper dental amalgam by analytical transmission electron microscopy. J Mater Res 11:2474–2485
Karakaya I, Thompson WT (1987) The Ag-Sn (Silver-Tin) system. Bull Alloy Phase Diagr 8:340–347
Saunders N, Miodownik AP (1990) The Cu-Sn (Copper-Tin) system. Bull Alloy Phase Diagr 11:278–287
Ghosh G (2004) Elastic properties, hardness, and indentation fracture toughness of intermetallics relevant to electronic packaging. J Mater Res 19:1439–1454
Fürtauer S, Li D, Cupid D, Flandorfer H (2013) The Cu-Sn phase diagram, part i: new experimental results. Intermetallics 34:142–147
Gangulee A, Das GC, Bever MB (1973) X-ray-diffraction and calorimetric investigation of compound Cu6Sn5. Met Trans 4:2063–2066
Carapella LA, Hultgren R (1942) The ferromagnetic nature of the beta-phase in the copper-manganese-tin system. Trans AIME 147:232–242
Kubaschewski O (1988) Silver–Copper–Tin; MSIT ternary evaluation program, in MSIT Workplace In: Effenberg G (ed) MSI, Materials Science International Services GmbH, Stuttgart, Document ID: 10.16022.1.20
Hari Kumar KC, Kubaschewski O (1988) Ag–Cu–Sn (Silver–Copper–Tin), in non-ferrous metal systems. Part 3 (Landolt-Börnstein: Group IV Physical Chemistry). In: Effenberg G, Ilyenko S (eds), vol 11C3. Materials Science International Services GmbH, Stuttgart, pp 47–62
Gebhardt E, Petzow G (1959) Über den Aufbau des Systems Silber-Kupfer-Zinn. Z Metallkd 50:597–605
Fedorov VN, Osintsev OE, Yushkina ET (1982) Ag–Cu–Sn, in phase diagrams of metallic systems. In: Ageev NV, Petrova LA (eds), vol 26. Acad. Sci. USSR, Moscow, pp 149–150
Acknowledgements
The microscopy studies were performed in the UConn/FEI Center for Advanced Microscopy and Materials Analysis (CAMMA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Sun, Y., Pamir Alpay, S. et al. Solidification microstructures in Ag3Sn–Cu3Sn pseudo-binary alloys. J Mater Sci 51, 6474–6487 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-9947-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-9947-y