Abstract
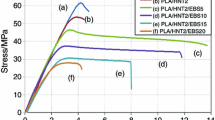
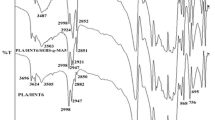
In this work, ternary nanocomposites of poly(lactic acid)/ethylene-co-vinyl-acetate (PLA/EVA, 70:30) containing varying concentrations (0.4–9.1 wt%) of halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) were prepared through melt compounding. Enhanced tensile modulus and impact strength demonstrated the strengthening and toughening effects of halloysite in the nanocomposites, simultaneously. The impact-fractured surface morphologies and halloysite-induced morphological changes of the nanocomposites were evaluated using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), respectively. FT-IR investigation revealed interactions between HNT and PLA. Glass transition behavior of the nanocomposites, as shown by dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), presents strong evidence in favor of phase interaction and the reinforcing effect of halloysite. Enhanced tensile strength and elongation-at-break demonstrated the toughening effect of halloysite.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Silva R, Pasbakhsh P, Goh K, Chai SP, Chen J (2014) Synthesis and characterisation of poly (lactic acid)/halloysite bionanocomposite films. J Compos Mater 48(30):3705–3717
Hashima K, Nishitsuji S, Inoue T (2010) Structure-properties of super-tough PLA alloy with excellent heat resistance. Polymer 51(17):3934–3939
Raquez J-M, Habibi Y, Murariu M, Dubois P (2013) Polylactide (PLA)-based nanocomposites. Prog Polym Sci 38(10):1504–1542
Liu M, Jia Z, Jia D, Zhou C (2014) Recent advance in research on halloysite nanotubes-polymer nanocomposite. Prog Polym Sci 39(8):1498–1525
De Silva RT, Pasbakhsh P, Lee SM, Kit AY (2015) ZnO deposited/encapsulated halloysite–poly (lactic acid)(PLA) nanocomposites for high performance packaging films with improved mechanical and antimicrobial properties. Appl Clay Sci 111:10–20
Ma P, Hristova-Bogaerds D, Goossens J, Spoelstra A, Zhang Y, Lemstra P (2012) Toughening of poly (lactic acid) by ethylene-co-vinyl acetate copolymer with different vinyl acetate contents. Eur Polym J 48(1):146–154
Shi Y, Li Y, Wu J, Huang T, Chen C, Peng Y (2011) Toughening of poly (l-lactide)/multiwalled carbon nanotubes nanocomposite with ethylene-co-vinyl acetate. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 49(4):267–276
Singla RK, Maiti SN, Ghosh AK (2016) Fabrication of super tough poly(lactic acid)/ethylene-co-vinyl-acetate blends via melt recirculation approach: static-short term mechanical and morphological interpretation. RSC Adv 6:14580–14588
Anderson KS, Hillmyer MA (2004) The influence of block copolymer microstructure on the toughness of compatibilized polylactide/polyethylene blends. Polymer 45(26):8809–8823
Oyama HT (2009) Super-tough poly (lactic acid) materials: reactive blending with ethylene copolymer. Polymer 50(3):747–751
Ojijo V, Ray SS (2015) Super toughened biodegradable polylactide blends with non-linear copolymer interfacial architecture obtained via facile in situ reactive compatibilization. Polymer 80:1–17
Shi YY, Du XC, Yang JH, Huang T, Zhang N, Wang Y (2014) Super toughened poly (l-lactide)/thermoplastic polyurethane blends achieved by adding dicumyl peroxide. Polym Plast Technol Eng 53(13):1344–1353
Zhou Y, Xiu H, Dai J, Bai H, Zhang Q, Fu Q (2015) Largely reinforced polyurethane via simultaneous incorporation of poly (lactic acid) and multiwalled carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv 5(39):30912–30919
Feng Y, Hu Y, Yin J, Zhao G, Jiang W (2013) High impact poly (lactic acid)/poly (ethylene octene) blends prepared by reactive blending. Polym Eng Sci 53(2):389–396
Ma P, Spoelstra AB, Schmit P, Lemstra PJ (2013) Toughening of poly (lactic acid) by poly (b-hydroxybutyrate-co-b-hydroxyvalerate) with high b-hydroxyvalerate content. Eur Polym J 49(6):1523–1531
Jiang L, Zhang J, Wolcott MP (2007) Comparison of polylactide/nano-sized calcium carbonate and polylactide/montmorillonite composites: reinforcing effects and toughening mechanisms. Polymer 48(26):7632–7644
Singh S, Ghosh AK, Maiti SN, Raha S, Gupta RK, Bhattacharya S (2012) Morphology and rheological behavior of polylactic acid/clay nanocomposites. Polym Eng Sci 52(1):225–232
Aghjeh MR, Nazari M, Khonakdar HA, Jafari SH, Wagenknecht U, Heinrich G (2015) In depth analysis of micro-mechanism of mechanical property alternations in PLA/EVA/clay nanocomposites: a combined theoretical and experimental approach. Mater Des 88:1277–1289
Liu W, Wei J, Chen Y, Huo P, Wei Y (2013) Electrospinning of poly (l-lactide) nanofibers encapsulated with water-soluble fullerenes for bioimaging application. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(3):680–685
Pluta M, Jeszka J, Boiteux G (2007) Polylactide/montmorillonite nanocomposites: structure, dielectric, viscoelastic and thermal properties. Eur Polym J 43(7):2819–2835
Hapuarachchi TD, Peijs T (2010) Multiwalled carbon nanotubes and sepiolite nanoclays as flame retardants for polylactide and its natural fibre reinforced composites. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 41(8):954–963
Fukushima K, Tabuani D, Camino G (2009) Nanocomposites of PLA and PCL based on montmorillonite and sepiolite. Mater Sci Eng C 29(4):1433–1441
Su Z, Li Q, Liu Y, Hu GH, Wu C (2009) Multiple melting behavior of poly (lactic acid) filled with modified carbon black. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 47(20):1971–1980
Balakrishnan H, Masoumi I, Yussuf A, Imran M, Hassan A, Wahit MU (2012) Ethylene copolymer toughened polylactic acid nanocomposites. Polym Plast Technol Eng 51(1):19–27
Wu TM, Wu CY (2006) Biodegradable poly (lactic acid)/chitosan-modified montmorillonite nanocomposites: preparation and characterization. Polym Degrad Stab 91(9):2198–2204
Balakrishnan H, Hassan A, Wahit MU, Yussuf AA, Razak SBA (2010) Novel toughened polylactic acid nanocomposite: mechanical, thermal and morphological properties. Mater Des 31(7):3289–3298
Rancan F, Papakostas D, Hadam S, Hackbarth S, Delair T, Primard C (2009) Investigation of polylactic acid (PLA) nanoparticles as drug delivery systems for local dermatotherapy. Pharm Res 26(8):2027–2036
Zhang L, Webster TJ (2009) Nanotechnology and nanomaterials: promises for improved tissue regeneration. Nano Today 4(1):66–80
Prashantha K, Lacrampe M, Krawczak P (2011) Processing and characterization of halloysite nanotubes filled polypropylene nanocomposites based on a masterbatch route: effect of halloysites treatment on structural and mechanical properties. Express Polym Lett 5(4):295–307
Liu M, Zhang Y, Zhou C (2013) Nanocomposites of halloysite and polylactide. Appl Clay Sci 75:52–59
Dong Y, Marshall J, Haroosh HJ, Mohammadzadehmoghadam S, Liu D, Qi X (2015) Polylactic acid (PLA)/halloysite nanotube (HNT) composite mats: influence of HNT content and modification. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 76:28–36. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.05.011
Cavallaro G, Lazzara G, Milioto S (2013) Sustainable nanocomposites based on halloysite nanotubes and pectin/polyethylene glycol blend. Polym Degrad Stab 98(12):2529–2536
Lvov Y, Wang W, Zhang L, Fakhrullin R (2016) Halloysite clay nanotubes for loading and sustained release of functional compounds. Adv Mater 28(6):1227–1250
Liu HY, Du L, Zhao YT, Tian WQ (2015) In vitro hemocompatibility and cytotoxicity evaluation of halloysite nanotubes for biomedical application. J Nanomater. doi:10.1155/2015/685323
Lvov Y, Aerov A, Fakhrullin R (2014) Clay nanotube encapsulation for functional biocomposites. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 207:189–198
Luo BH, Hsu CE, Li JH, Zhao LF, Liu MX, Wang XY (2013) Nano-composite of poly (l-lactide) and halloysite nanotubes surface-grafted with l-lactide oligomer under microwave irradiation. J Biomed Nanotechnol 9(4):649–658
Hughes AD, King MR (2010) Use of naturally occurring halloysite nanotubes for enhanced capture of flowing cells. Langmuir 26(14):12155–12164
Ma P, Hristova-Bogaerds DG, Schmit P, Goossens JGP, Lemstra PJ (2012) Tailoring the morphology and properties of poly(lactic acid)/poly(ethylene)-co-(vinyl acetate)/starch blends via reactive compatibilization. Polym Int 61(8):1284–1293
Sharma R, Maiti SN (2014) Effects of crystallinity of PP and flexibility of SEBS-g-MA copolymer on the mechanical properties of PP/SEBS-g-MA blends. Polym Plast Technol Eng 53(3):229–238
Harris AM, Lee EC (2008) Improving mechanical performance of injection molded PLA by controlling crystallinity. J Appl Polym Sci 107(4):2246–2255
Li Y, Liu L, Shi Y, Xiang F, Huang T, Wang Y (2011) Morphology, rheological, crystallization behavior, and mechanical properties of poly (l-lactide)/ethylene-co-vinyl acetate blends with different VA contents. J Appl Polym Sci 121(5):2688–2698
Singla RK, Maiti SN, Ghosh AK (2016) Crystallization, morphological, and mechanical response of poly (lactic acid)/lignin-based biodegradable composites. Polym Plast Technol Eng 55(5):475–485
Rasal RM, Janorkar AV, Hirt DE (2009) Poly(lactic acid) modifications. Prog Polym Sci 35(3):338–356
Chow WS, Lok SK (2009) Thermal properties of poly(lactic acid)/organo-montmorillonite nanocomposites. J Therm Anal Calorim 95:627–632
Gorrasi G, Senatore V, Vigliotta G, Belviso S, Pucciariello R (2014) PET—halloysite nanotubes composites for packaging application: preparation, characterization and analysis of physical properties. Eur Polym J 61:145–156
Costache MC, Jiang DD, Wilkie CA (2005) Thermal degradation of ethylene–vinyl acetate copolymer nanocomposites. Polymer 46(18):6947–6958
Fortunati E, Puglia D, Kenny JM, Minhaz-Ul Haque M, Pracella M (2013) Effect of ethylene-co-vinyl acetate-glycidylmethacrylate and cellulose microfibers on the thermal, rheological and biodegradation properties of poly(lactic acid) based systems. Polym Degrad Stab 98(12):2742–2751
Liu M, Jia Z, Liu F, Jia D, Guo B (2010) Tailoring the wettability of polypropylene surfaces with halloysite nanotubes. J Colloid Interface Sci 350(1):186–193
Murariu M, Dechief A-L, Paint Y, Peeterbroeck S, Bonnaud L, Dubois P (2012) Polylactide (PLA)—halloysite nanocomposites: production, morphology and key-properties. J Polym Environ 20(4):932–943
Shi Y, Li Y, Xiang F, Huang T, Chen C, Peng Y (2012) Carbon nanotubes induced microstructure and mechanical properties changes in cocontinuous poly (l-lactide)/ethylene-co-vinyl acetate blends. Polym Adv Technol 23(4):783–790
Shen Y, Zhang TT, Yang JH, Zhang N, Huang T, Wang Y (2015) Selective localization of reduced graphene oxides at the interface of PLA/EVA blend and its resultant electrical resistivity. Polym Compos. doi:10.1002/pc.23769
Li Y, Wang Y, Liu L, Han L, Xiang F, Zhou Z (2009) Crystallization improvement of poly (L-lactide) induced by functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 47(3):326–339
Du M, Guo B, Jia D (2010) Newly emerging applications of halloysite nanotubes: a review. Polym Int 59(5):574–582
Wang XF, Zhang ZX, Yang JH, Wang Y, Zhang JH (2015) Largely improved fracture toughness of an immiscible poly (l-lactide)/ethylene-co-vinyl acetate blend achieved by adding carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv 5(85):69522–69533
Ma P, Hristova-Bogaerds DG, Goossens JGP, Spoelstra AB, Zhang Y, Lemstra PJ (2011) Toughening of poly (lactic acid) by ethylene-co-vinyl acetate copolymer with different vinyl acetate contents. Eur Polym J 48(1):146–154
Rashmi B, Prashantha K, Lacrampe M, Krawczak P (2015) Toughening of poly (lactic acid) without sacrificing stiffness and strength by melt-blending with polyamide 11 and selective localization of halloysite nanotubes. Express Polym Lett 9(8):721–735
Shi YY, Yang JH, Huang T, Zhang N, Chen C, Wang Y (2013) Selective localization of carbon nanotubes at the interface of poly (l-lactide)/ethylene-co-vinyl acetate resulting in lowered electrical resistivity. Compos Part B Eng 55:463–469
Akbari A, Jawaid M, Hassan A, Balakrishnan H (2014) Epoxidized natural rubber toughened polylactic acid/talc composites: mechanical, thermal, and morphological properties. J Compos Mater 48(7):769–781
Petinakis E, Yu L, Edward G, Dean K, Liu H, Scully AD (2009) Effect of matrix—particle interfacial adhesion on the mechanical properties of poly (lactic acid)/wood-flour micro-composites. J Polym Environ 17(2):83–94
Chartoff RP, Menczel JD, Dillman SH (2009) Dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA). Thermal analysis of polymers: fundamentals and applications. p 387–495. doi: 10.1002/9780470423837.ch5
Ornaghi HL, Bolner AS, Fiorio R, Zattera AJ, Amico SC (2010) Mechanical and dynamic mechanical analysis of hybrid composites molded by resin transfer molding. J Appl Polym Sci 118(2):887–896
Mofokeng J, Luyt A (2015) Dynamic mechanical properties of PLA/PHBV, PLA/PCL, PHBV/PCL blends and their nanocomposites with TiO2 as nanofiller. Thermochim Acta 613:41–53
Hassan E, Wei Y, Jiao H, Muhuo Y (2013) Dynamic mechanical properties and thermal stability of poly (lactic acid) and poly (butylene succinate) blends composites. J Fiber Bioeng Inf 6(1):85–94
Sewda K, Maiti S (2011) Effect of bark flour on viscoelastic behavior of high density polyethylene. J Compos Mater 45(9):1007–1016
Landel RF, Nielsen LE (1993) Mechanical properties of polymers and composites. CRC Press, Boston
Klein N, Marom G, Pegoretti A, Migliaresi C (1995) Determining the role of interfacial transcrystallinity in composite materials by dynamic mechanical thermal analysis. Composites 26(10):707–712
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Indian Institute of Technology Delhi and University Grant commission for providing research facilities and financial assistance to one of the authors (Rajendra Kumar Singla).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singla, R.K., Maiti, S.N. & Ghosh, A.K. Mechanical, morphological, and solid-state viscoelastic responses of poly(lactic acid)/ethylene-co-vinyl-acetate super-tough blend reinforced with halloysite nanotubes. J Mater Sci 51, 10278–10292 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0255-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0255-3