Abstract
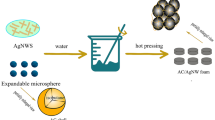
Carbon foam filled with silver particles was fabricated by a powder molding process using polyurethane as pore former, novolac resin as binder, coal-tar pitch as densification additive, and silver foils as a filler. High-temperature treatment at 1200 °C, transformed the silver into spherical particles covered with in situ grown Ag nanowires. Their microstructure, electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding effectiveness (SE), and shielding mechanism was investigated. It was found that the micron-sized silver foils converted into particles during heat treatment and strongly bonded in carbon matrix. The addition of silver significantly enhanced both conductivity and SE. Carbon foam containing 1.5 wt% silver exhibited very impressive total SE and dielectric loss tangent owing to the more conductive network of silver particles providing fast electron-transport channels. A maximum specific EMI SE value of 58.21 dB g−1 cm3 at 12 GHz was achieved in the carbon foam at 1.5 wt% Ag loading. The dominant mechanism was absorption with only 6–10 % reflectance, resulting from the multiple reflections at interfaces inside the foam. Due to controlled attachment of silver particles and in situ reactions, this novel substrate has unique opportunities for future surface tailoring required in various commercial and aerospace fields.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Z, Xu C, Ma C, Ren W, Cheng H-M (2013) Lightweight and flexible graphene foam composites for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv Mater 25(9):1296–1300
Ameli A, Jung PU, Park CB (2013) Electrical properties and electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of polypropylene/carbon fiber composite foams. Carbon 60:379–391
Das NC, Chaki TK, Khastgir D, Chakraborty A (2001) Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of conductive carbon black and carbon fiber-filled composites based on rubber and rubber blends. Adv Polym Technol 20(3):226–236
Li N, Huang Y, Du F, He X, Lin X, Gao H et al (2006) Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding of single-walled carbon nanotube epoxy composites. Nano Lett 6(6):1141–1145
Wang L-L, Tay B-K, See K-Y, Sun Z, Tan L-K, Lua D (2009) Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of carbon-based materials prepared by screen printing. Carbon 47(8):1905–1910
Yan DX, Ren PG, Pang H, Fu Q, Yang MB, Li ZM (2012) J Mater Chem 22:18772–18774
Gelves GA, Al-Saleh MH, Sundararaj U (2011) J Mater Chem 21:829–836
Kwon S, Ma R, Kim U, Choi HR, Baik S (2014) Carbon 68:118–124
Ling JQ, Zhai WT, Feng WW, Shen B, Zhang JF, Zheng WG (2013) Facile preparation of lightweight microcellular polyetherimide/graphene composite foams for electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:2677–2684
Li N, Huang Y, Du F, He XB, Lin X, Gao HJ et al (2006) Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding of single-walled carbon nanotube epoxy composites. Nano Lett 6:1141–1145
Cao MS, Wang XX, Cao WQ, Yuan J (2015) Ultrathin graphene: electrical properties and highly efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. J Mater Chem C 3:6589–6599
Farhan S, Wang RM, Jiang H, Ul-Haq N (2014) Preparation and characterization of carbon foam derived from pitch and phenolic resin using a soft templating method. J Anal App Pyrol 110:229–234
Mei H, Farhan S, Han DY, Liu GX, Wang Z, Zhao GK (2016) Mechanical, structural and oxidation resistance enhancement of carbon foam by in situ grown SiC nanowires. Ceram Int 42:4723–4733
Farhan S, Wang RM (2015) Thermal, mechanical and self-destruction properties of aluminium reinforced carbon foam. J Porous Mater 22:897–906
Farhan S et al (2016) A novel combination of simple foaming and freeze-drying processes for making carbon foam containing multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Ceram Int. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.01.131
Fang ZG, Li CS, Sun JY, Zhang HT, Zhang JS (2007) The electromagnetic characteristics of carbon foams. Carbon 45:2873–2879
Liu Q, Gu J, Zhang W, Miyamoto Y, Chen Z, Zhang D (2012) Biomorphic porous graphitic carbon for electromagnetic interference shielding. J Mater Chem 22:21183–21188
Kumar R, Dhakate SR, Saini P, Mathur RB (2013) Improved electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of light weight carbon foam by ferrocene accumulation. RSC Adv 3:4145–4151
Yang J, Shen Z, Hao Z (2004) Preparation of highly microporous and mesoporous carbon from the mesophase pitch and its carbon foams with KOH. Carbon 42 (8–9):1872–1875
Wang C, Xiang CS, Liu Q, Pan YB, Guo JK (2008) Ordered mesoporous carbon/fused silica composites. Adv Funct Mater 18:2995–3002
Zhou JH, He JP, Li GX, Wang T, Sun D, Ding XC, Zhao JQ, Wu SC (2010) Direct incorporation of magnetic constituents within ordered mesoporous carbon-silica nanocomposites for highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorbers. J Phys Chem C 114:7611–7617
Moglie F, Micheli D, Laurenzi S, Marchetti M, Mariani Primiani V (2012) Electromagnetic shielding performance of carbon foams. Carbon 50(5):1972–1980
Blacker JM, Plucinski JW (2001) Electrically graded carbon foam. US 7,867, 608 B2
Kuzhir PP, Paddubskaya AG, Maksimenko SA (2012) Highly porous conducting carbon foams for electromagnetic application. In: International symposium on electromagnetic compatibility (EMC Europe)
Zhang L, Wang LB, See KY, Ma J (2013) Effect of carbon nanofiber reinforcement on electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of syntactic foam. J Mater Sci 48:7757–7763
Farhan S, Wang RM, Jiang H (2015) A novel method for the processing of carbon foam containing in situ grown nano-materials and silicon nanowires. Mater Lett 159:439–442
Tsuji M, Maeda Y, Hikino S, Kumagae H, Matsunaga M, Matsuo R, Tang XL, Ogino M, Jiang P (2009) Shape evolution of octahedral and triangular platelike silver nanocrystals from cubic and right bipyramidal seeds in DMF. Cryst Growth Des 9:4700–4705
Oliveira CCS, Ando RA, Camargo PHC (2013) Size-controlled synthesis of silver micro/nanowires as enabled by HCL oxidative etching. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15:1887–1893
Ma J, Wang K, Zhan M (2015) A comparative study of structure and electromagnetic interference shielding performance for silver nanostructure hybrid polyimide foams. RSC Adv 5:65283–65296
Yu YH, Ma CCM, Teng CC, Huang YL, Lee SH, Wang I, Wei MH (2012) Mater Chem Phys 136:334–340
Arjmand M, Moud AA, Li Y, Sundararaj U (2015) Outstanding electromagnetic interference shielding of silver nanowires: comparison with carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv 5:56590–56598
Al-Ghamdi AA, Al-Hartomy OA, El-Tantawy F, Yakuphanoglu F (2014) Novel polyvinyl alcohol/silver hybrid nanocomposites for high performance electromagnetic wave shielding effectiveness. Microsyst Technol 21(4):1–10
Hu MJ, Gao JF, Dong YC, Li K, Shan GC, Yang SL, Li RKY (2012) Flexible transparent PES/silver nanowires/PET sandwich-structured film for high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding. Langmuir 28:7101–7106
Karumuri AK, Oswal DP, Hostetler HA, Mukhopadhyay SM (2013) Silver nanoparticles attached to porous carbon substrates: robust materials for chemical-free water disinfection. Mater Lett 109:83–87
Sevilla M (2006) Catalytic graphitization of templated mesoporous carbons. Carbon 44(3):468–474
Kasahara N, Shiraishi S, Oya A (2003) Heterogeneous graphitization of thin carbon fiber derived from phenol-formaldehyde resin. Carbon 41:1654–1656
Chen LQ, Yin XW, Fan XM, Chen M, Ma XK, Cheng LF, Zhang LT (2015) Mechanical and electromagnetic shielding properties of carbon fiber reinforced silicon carbide matrix composites. Carbon 95:10–19
Sutter EA, Sutter PW (2011) Giant carbon solubility in Au nanoparticles. J Mater Sci 46:7090–7097
Harris PJF (2005) New perspectives on the structure of graphitic carbons. Crit Rev Solid State Mater Sci 30:235–253
Duarte F, Maldonado-Hodar FJ, Perez-Cadenas AF, Madeira LM (2009) Fenton-like degradation of azo-dye Orange II catalyzed by transition metals on carbon aerogels. Appl Catal B Environ 85:139–147
Strano MS, Zydney AL, Barth H, Wooler G, Agarwal H, Foley HC (2002) Ultrafiltration membrane synthesis by nanoscale templating of porous carbon. J Membr Sci 198(2):173–186
Tondi G, Fierro V, Pizzi A, Celzard A (2009) Tannin-based carbon foam. Carbon 47:1480–1492
Cao MS, Song WL, Hou ZL, Wen B, Yuan J (2012) The effects of temperature and frequency on the dielectric properties, electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave-absorption of short carbon fiber/silica composites. Carbon 48:788–796
Wang C, Han X, Xu P, Zhang X, Du Y, Hu S, Wang J, Wang X (2011) The electromagnetic property of chemically reduced graphene oxide and its application as microwave absorbing material. Appl Phys Lett 98(7):072906–072909
Chen DZ, Wang GS, He S, Liu J, Guo L, Cao MS (2013) Controllable fabrication of mono-dispersed RGO–hematite nanocomposites and their enhanced wave absorption properties. J Mater Chem A 1:5996–6003
Li Q, Yin XW, Duan WY, Kong L, Hao BL, Ye F (2013) Electrical, dielectric and microwave-absorption properties of polymer derived SiC ceramics in X band. J Alloy Compd 565:66–72
Wen MS, Cao ZL, Hou WL, Song L, Zhang MM, Lu HB, Jin XY, Fang WZ, Wang JY (2013) Temperature dependent microwave attenuation behavior for carbon-nanotube/silica composites. Carbon 65:124–139
Yin XW, Xue YY, Zhang LT, Cheng LF (2012) Dielectric, electromagnetic absorption and interference shielding properties of porous yttria-stabilized zirconia/silicon carbide composites. Ceram Int 38(3):2421–2427
Al-Saleh MH, Sundararaj U (2013) X-band EMI shielding mechanisms and shielding effectiveness of high structure carbon black/polypropylene composites. J Phys D Appl Phys 46:035304
Liu QL, Zhang D, Fan TX, Gu JJ, Miyamoto Y, Chen ZX (2008) Amorphous carbon-matrix composites with interconnected carbon nano-ribbon networks for electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 46(3):461–465
Hao X, Yin XW, Zhang LT, Cheng LF (2013) Dielectric, electromagnetic interference shielding and absorption properties of Si3N4-PyC composite ceramics. J Mater Sci Technol 29:249–254
Cao MS, Wang XX, Cao WQ, Yuan J (2015) Ultrathin graphene: electrical properties and highly efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. J Mater Chem C 3(26):6589–6599
Yin XW, Kong L, Zhang LT, Cheng LF, Travitzky N, Greil P (2014) Electromagnetic properties of Si–C–N based ceramics and composites. Int Mater Rev 59(6):326–355
Huynen I, Quievy N, Bailly C, Bollen P, Detrembleur C, Eggermont S et al (2011) Multifunctional hybrids for electromagnetic absorption. Acta Mater 59:3255–3266
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support (CX201627) of Innovation Foundation for Doctor Dissertation of Northwestern Polytechnical University and National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant No. 51472202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farhan, S., Wang, R. & Li, K. Carbon foam decorated with silver particles and in situ grown nanowires for effective electromagnetic interference shielding. J Mater Sci 51, 7991–8004 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0068-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0068-4