Abstract
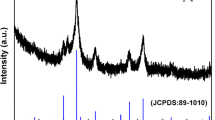
Template-free method is used to facilely synthesize TiO2 hollow microspheres via one-step hydrothermal method. Interestingly, the TiO2 hollow microspheres have porous shell with thickness of about 450 nm. The formation mechanism of the hollow@porous TiO2 microspheres involves the formation and aggregation of TiO2 nanoparticles followed by oriented growth, etching of HF, and then Ostwald ripening and transformation process. The prepared TiO2 microspheres show a reversible capacity of ~170 mAh g−1 after 150 cycles at a current density of 0.6 C and also exhibit a good rate capability of 40.8 mAh g−1 at a current density of 24 C due to the unique hollow@porous structure, which can offer more sites for the storage and insertion of Li ions, and accelerate electrolyte diffusion and Li ions transport. The results also indicate that the as-prepared TiO2 material possesses excellent electrochemical performances, which may be an ideal anode material for lithium ion battery.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang HE, Jin J, Cai Y et al (2014) Facile and fast synthesis of porous TiO2 spheres for use in lithium ion batteries. J Colloid Interface Sci 417:144–151
Zhang P, Zhang J, Xie A, Li S, Song J, Shen Y (2015) Hierarchical flower-like Bi2WO6 hollow microspheres: facile synthesis and excellent catalytic performance. RSC Adv 5:23080–23085
Yan Z, Liu L, Guo H et al (2014) One-pot synthesis of FCNTs-wired TiO2 nanocomposites as anode materials for high-rate lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 123:551–559
Trang NT, Ali Z, Kang DJ (2015) Mesoporous TiO2 spheres interconnected by multiwalled carbon nanotubes as an anode for high-performance lithium ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:3676–3683
Zhao C, Liu L, Zhang Q, Rogers J, Zhao H, Li Y (2015) Synthesis of carbon-TiO2 nanocomposites with enhanced reversible capacity and cyclic performance as anodes for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 155:288–296
Wang Z, Lou XW (2012) TiO(2) nanocages: fast synthesis, interior functionalization and improved lithium storage properties. Adv Mater 24:4124–4129
Xiao L, Cao M, Mei D et al (2013) Preparation and electrochemical lithium storage features of TiO2 hollow spheres. J Power Sources 238:197–202
Zhang G, Wu HB, Song T, Paik U, Lou XW (2014) TiO2 hollow spheres composed of highly crystalline nanocrystals exhibit superior lithium storage properties. Angew Chem 53:12590–12593
Ren H, Yu R, Wang J et al (2014) Multishelled TiO2 hollow microspheres as anodes with superior reversible capacity for lithium ion batteries. Nano Lett 14:6679–6684
Yi J, Lu D, Li X, Hu S, Li W, Lei J, Wang Y (2011) Preparation and performance of porous titania with a trimodal pore system as anode of lithium ion battery. J Solid State Electrochem 16:443–448
Xia T, Zhang W, Murowchick J, Liu G, Chen X (2013) Built-in electric field-assisted surface-amorphized nanocrystals for high-rate lithium-ion battery. Nano Lett 13:5289–5296
Madej E, Ventosa E, Klink S, Schuhmann W, La Mantia F (2014) Aging effects of anatase TiO2 nanoparticles in Li-ion batteries. Phys Chemistry Chem Phys 16:7939–7945
Yu J, Zhang J (2010) A simple template-free approach to TiO2 hollow spheres with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Dalton Trans 39:5860–5867
Shi Q, Li Y, Zhan E, Ta N, Shen W (2014) Anatase TiO2 hollow nanosheets: dual roles of F−, formation mechanism and thermal stability. CrystEngComm 16:3431–3437
Lv K, Cheng B, Yu J, Liu G (2012) Fluorine ions-mediated morphology control of anatase TiO2 with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:5349–5362
Yang HG, Zeng HC (2004) Preparation of hollow anatase TiO2 nanospheres via Ostwald ripening. J Phys Chem B 108:3492–3495
Yu J, Xiang Q, Ran J, Mann S (2010) One-step hydrothermal fabrication and photocatalytic activity of surface-fluorinated TiO2 hollow microspheres and tabular anatase single micro-crystals with high-energy facets. CrystEngComm 12:872–879
Wang X, Wang Y, Yang L, Wang K, Lou X, Cai B (2014) Template-free synthesis of homogeneous yolk–shell TiO2 hierarchical microspheres for high performance lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 262:72–78
Wang S, Xing Y, Su H, Zhang S (2014) MnO nanoparticles interdispersed in 3D porous carbon framework for high performance lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:12713–12718
Jadhav HS, Kalubarme RS, Park CN, Kim J, Park CJ (2014) Facile and cost effective synthesis of mesoporous spinel NiCo2O4 as an anode for high lithium storage capacity. Nanoscale 6:10071–10076
Wu F, Huang R, Mu D, Wu B, Chen S (2014) New synthesis of a foamlike Fe3O4/C composite via a self-expanding process and its electrochemical performance as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:19254–19264
Wen CJ, Ho C, Boukamp BA, Raistrick ID, Weppner W, Huggins RA (1981) Use of electrochemical methods to determine chemical-diffusion coefficients in alloys: application to ‘LiAl’. Int Metals Rev 5:253–268
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (21173001 and 21371003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Zhang, C., Xie, A. et al. Novel template-free synthesis of hollow@porous TiO2 superior anode materials for lithium ion battery. J Mater Sci 51, 3448–3453 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9662-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9662-0