Abstract
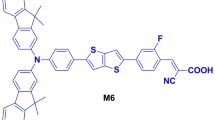
Several novel indoline dyes configured with donor–acceptor–bridge–acceptor (D–A–π–A) structures were designed and applied to organic dye-sensitized solar cells. These D–A–π–A dye molecules are composed of indoline (electron donating group), benzothiadiazole (BDT) (auxiliary acceptor), two furan rings (π-conjugated group), and 2-cyanoacrylic acid (electron accepting group). The influence of position of auxiliary acceptor in D–A–π–A organic sensitizer on the performance of photosensitize is investigated in detail. Calculated results show that the sensitizer could achieve a red-shifted absorption in long-wavelength region and a stronger absorption in short-wavelength region when the position of auxiliary acceptor changes from the donor to the acceptor. Moreover, among these dyes, WS-12, whose auxiliary acceptor nearing the 2-cyanoacrylic acid, possesses the better performance in terms of the charge transfer characteristics, lifetime of excited state as well as the vertical dipole moment when compared with WS-1 and WS-11. We hope that the present results could provide theoretical guidance for designing photosensitizes with higher efficiencies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yella A, Lee H-W, Tsao HN, Yi C, Chandiran AK, Nazeeruddin MK, Diau EW-G, Yeh C-Y, Zakeeruddin SM, Grätzel M (2011) Porphyrin-sensitized solar cells with cobalt (II/III)—based redox electrolyte exceed 12 percent efficiency. Science 334(6056):629–634
Yu G, Gao J, Hummelen J, Wudl F, Heeger A (1995) Polymer photovoltaic cells: enhanced efficiencies via a network of internal donor-acceptor heterojunctions. Science 270(5243):1789–1790
Lee MM, Teuscher J, Miyasaka T, Murakami TN, Snaith HJ (2012) Efficient hybrid solar cells based on meso-superstructured organometal halide perovskites. Science 338(6107):643–647
Jung J, Pang X, Feng C, Lin Z (2013) Semiconducting conjugated polymer–inorganic tetrapod nanocomposites. Langmuir 29(25):8086–8092
Pang X, Zhao L, Feng C, Lin Z (2011) Novel amphiphilic multiarm, starlike coil-rod diblock copolymers via a combination of click chemistry with living polymerization. Macromolecules 44(18):7176–7183
O’regan B, Grfitzeli M (1991) A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized. Nature 353:737–740
Mathew S, Yella A, Gao P, Humphry-Baker R, Curchod BF, Ashari-Astani N, Tavernelli I, Rothlisberger U, Nazeeruddin MK, Grätzel M (2014) Dye-sensitized solar cells with 13% efficiency achieved through the molecular engineering of porphyrin sensitizers. Nature Chem 6(3):242–247
Holliman PJ, Al-Salihi KJ, Connell A, Davies ML, Jones EW, Worsley DA (2014) Development of selective, ultra-fast multiple co-sensitization to control dye loading in dye-sensitized solar cells. RSC Adv 4(5):2515–2522
Piatkowski P, Martin C, di Nunzio MR, Cohen B, Pandey SS, Hayase S, Douhal A (2014) Complete photodynamics of the efficient YD2-o-C8-Based Solar Cell. J Phys Chem C 118(51):29674–29687
Chaitanya K, Ju X-H, Heron BM (2014) Theoretical study on the light harvesting efficiency of zinc porphyrin sensitizers for DSSCs. RSC Adv 4(51):26621–26634
Zhang J-Z, Zhang J, Li H-B, Wu Y, Xu H-L, Zhang M, Geng Y, Su Z-M (2014) Modulation on charge recombination and light harvesting toward high-performance benzothiadiazole-based sensitizers in dye-sensitized solar cells: a theoretical investigation. J Power Sources 267:300–308
Perera IR, Daeneke T, Makuta S, Yu Z, Tachibana Y, Mishra A, Bäuerle P, Ohlin CA, Bach U, Spiccia L (2015) Application of the tris (acetylacetonato) iron (III)/(II) redox couple in p-type dye-sensitized solar cells. Angew Chem Int Ed 54(12):3758–3762
Li M, Kou L, Diao L, Zhang Q, Li Z, Wu Q, Lu W, Pan D (2015) Theoretical study of acene-bridged dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells. J Phys Chem A 119(13):3299–3309
Yuan W, Zhao H, Baker GL (2014) Low glass transition temperature hole transport material in enhanced-performance solid-state dye-sensitized solar cell. Org Electron 15(11):3362–3369
Yuan W, Zhao H, Hu H, Wang S, Baker GL (2013) Synthesis and characterization of the hole-conducting silica/polymer nanocomposites and application in solid-state dye-sensitized solar cell. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(10):4155–4161
Hagfeldt A, Boschloo G, Sun L, Kloo L, Pettersson H (2010) Dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem Rev 110(11):6595–6663
Sánchez-de-Armas R, San-Miguel MA, Oviedo J, Sanz JF (2012) Molecular modification of coumarin dyes for more efficient dye sensitized solar cells. J Chem Phys 136(19):194702
Koops SE, Barnes PR, O’Regan BC, Durrant JR (2010) Kinetic competition in a coumarin dye-sensitized solar cell: injection and recombination limitations upon device performance. J Phys Chem C 114(17):8054–8061
Wang J, Li M, Qi D, Shen W, He R, Lin SH (2014) Exploring photophysical properties of metal-free coumarin sensitizers: an efficient strategy to improve the performance of dye-sensitized solar cells. RSC Adv 4(96):53927–53938
Liu B, Wang B, Wang R, Gao L, Huo S, Liu Q, Li X, Zhu W (2014) Influence of conjugated π-linker in D-D–π–A indoline dyes: towards long-term stable and efficient dye-sensitized solar cells with high photovoltage. J Mater Chem A 2(3):804–812
Kuang D, Uchida S, Humphry-Baker R, Zakeeruddin SM, Grätzel M (2008) Organic dye-sensitized ionic liquid based solar cells: remarkable enhancement in performance through molecular design of indoline sensitizers. Angew Chem Int Ed 47(10):1923–1927
Huang J-F, Liu J-M, Tan L-L, Chen Y-F, Shen Y, Xiao L-M, Kuang D-B, Su C-Y (2015) Novel carbazole based sensitizers for efficient dye-sensitized solar cells: role of the hexyl chain. Dyes Pigm 114:18–23
Koumura N, Wang Z-S, Miyashita M, Uemura Y, Sekiguchi H, Cui Y, Mori A, Mori S, Hara K (2009) Substituted carbazole dyes for efficient molecular photovoltaics: long electron lifetime and high open circuit voltage performance. J Mater Chem 19(27):4829–4836
Kim S, Choi H, Kim D, Song K, Kang SO, Ko J (2007) Novel conjugated organic dyes containing bis-dimethylfluorenyl amino phenyl thiophene for efficient solar cell. Tetrahedron 63(37):9206–9212
Choi H, Baik C, Kang SO, Ko J, Kang MS, Nazeeruddin MK, Grätzel M (2008) Highly efficient and thermally stable organic sensitizers for solvent-free dye-sensitized solar cells. Angew Chem 120(2):333–336
Kozma E, Concina I, Braga A, Borgese L, Depero LE, Vomiero A, Sberveglieri G, Catellani M (2011) Metal-free organic sensitizers with a sterically hindered thiophene unit for efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. J Mater Chem 21(36):13785–13788
Sakong C, Kim HJ, Kim SH, Namgoong JW, Park JH, Ryu J-H, Kim B, Ko MJ, Kim JP (2012) Synthesis and applications of new triphenylamine dyes with donor–donor–(bridge)–acceptor structure for organic dye-sensitized solar cells. New J Chem 36(10):2025–2032
Wan Z, Jia C, Zhang J, Duan Y, Lin Y, Shi Y (2012) Triphenylamine-based starburst dyes with carbazole and phenothiazine antennas for dye-sensitized solar cells. J Power Sources 199:426–431
Jiang X, Karlsson KM, Gabrielsson E, Johansson EM, Quintana M, Karlsson M, Sun L, Boschloo G, Hagfeldt A (2011) Highly efficient solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells based on triphenylamine dyes. Adv Funct Mater 21(15):2944–2952
Zhu W, Wu Y, Wang S, Li W, Li X, Chen J, Zs Wang, Tian H (2011) Organic D-A-π-A solar cell sensitizers with improved stability and spectral response. Adv Funct Mater 21(4):756–763
Lee DH, Lee MJ, Song HM, Song BJ, Seo KD, Pastore M, Anselmi C, Fantacci S, De Angelis F, Nazeeruddin MK (2011) Organic dyes incorporating low-band-gap chromophores based on π-extended benzothiadiazole for dye-sensitized solar cells. Dyes Pigm 91(2):192–198
Tian H, Yang X, Chen R, Zhang R, Hagfeldt A, Sun L (2008) Effect of different dye baths and dye-structures on the performance of dye-sensitized solar cells based on triphenylamine dyes. J Phys Chem C 112(29):11023–11033
Zhu H, Li W, Wu Y, Liu B, Zhu S, Li X, Ågren H, Zhu W (2014) Insight into benzothiadiazole acceptor in D-A-π-A configuration on photovoltaic performances of dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2(4):1026–1034
Frisch M, Trucks G, Schlegel H, Scuseria G, Robb M, Cheeseman J Jr, Montgomery J, Vreven T, Kudin K, Burant J (2009) Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT, Gaussian 09 (Revision-A. 01). Gaussian. Inc., Pittsburgh
Lipparini F, Barone V (2011) Polarizable force fields and polarizable continuum model: a fluctuating charges/PCM approach. 1. theory and implementation. J Chem Theory Comput 7(11):3711–3724
Hay PJ, Wadt WR (1985) Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for K to Au including the outermost core orbitals. J Chem Phys 82(1):299–310
Ding W-L, Wang D-M, Geng Z-Y, Zhao X-L, Xu W-B (2013) Density functional theory characterization and verification of high-performance indoline dyes with D-A–π-A architecture for dye-sensitized solar cells. Dyes Pigm 98(1):125–135
Lu T, Chen F (2012) Multiwfn: a multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J Comput Chem 33(5):580–592
Ciofini I, Le Bahers T, Adamo C, Odobel F, Jacquemin D (2012) Through-space charge transfer in rod-like molecules: lessons from theory. J Phys Chem C 116(22):11946–11955
Li L-L, Diau EW-G (2013) Porphyrin-sensitized solar cells. Chem Soc Rev 42(1):291–304
Fitri A, Benjelloun AT, Benzakour M, Mcharfi M, Hamidi M, Bouachrine M (2014) Theoretical investigation of new thiazolothiazole-based D-π-A organic dyes for efficient dye-sensitized solar cell. Spectrochim Acta Part A 124:646–654
Guo M, He R, Dai Y, Shen W, Li M, Zhu C, Lin SH (2012) Electron-deficient pyrimidine adopted in porphyrin sensitizers: a theoretical interpretation of π-spacers leading to highly efficient photo-to-electric conversion performances in dye-sensitized solar cells. J Phys Chem C 116(16):9166–9179
Chen S-L, Yang L-N, Li Z-S (2013) How to design more efficient organic dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells? Adding more sp 2-hybridized nitrogen in the triphenylamine donor. J Power Sources 223:86–93
Yang L-N, Sun Z-Z, Chen S-L, Li Z-S (2013) The effects of various anchoring groups on optical and electronic properties of dyes in dye-sensitized solar cells. Dyes Pigm 99(1):29–35
Ding W-L, Wang D-M, Geng Z-Y, Zhao X-L, Yan Y-F (2013) Molecular engineering of indoline-based D-A-π-A organic sensitizers toward high efficiency performance from first-principles calculations. J Phys Chem C 117(34):17382–17398
Feng J, Jiao Y, Ma W, Nazeeruddin MK, Grätzel M, Meng S (2013) First principles design of dye molecules with ullazine donor for dye sensitized solar cells. J Phys Chem C 117(8):3772–3778
Katoh R, Furube A, Yoshihara T, Hara K, Fujihashi G, Takano S, Murata S, Arakawa H, Tachiya M (2004) Efficiencies of electron injection from excited N3 dye into nanocrystalline semiconductor (ZrO2, TiO2, ZnO, Nb2O5, SnO2, In2O2) films. J Phys Chem B 108(15):4818–4822
Marinado T, Nonomura K, Nissfolk J, Karlsson MK, Hagberg DP, Sun L, Mori S, Hagfeldt A (2009) How the nature of triphenylamine-polyene dyes in dye-sensitized solar cells affects the open-circuit voltage and electron lifetimes. Langmuir 26(4):2592–2598
Wu J, Liao Y, Wu S-X, Li H-B, Su Z-M (2012) Phenylcarbazole and phosphine oxide/sulfide hybrids as host materials for blue phosphors: effectively tuning the charge injection property without influencing the triplet energy. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14(5):1685–1693
Kasha M (1950) Characterization of electronic transitions in complex molecules. Discuss Faraday Soc 9:14–19
Asbury JB, Wang Y-Q, Hao E, Ghosh HN, Lian T (2001) Evidences of hot excited state electron injection from sensitizer molecules to TiO2 nanocrystalline thin films. Res Chem Intermed 27(4):393–406
Luo J-H, Li Q-S, Yang L-N, Sun Z-Z, Li Z-S (2014) Theoretical design of porphyrazine derivatives as promising sensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cells. RSC Adv 4(39):20200–20207
Wu Y, Zhu W (2013) Organic sensitizers from D-π-A to D-A-π-A: effect of the internal electron-withdrawing units on molecular absorption, energy levels and photovoltaic performances. Chem Soc Rev 42(5):2039–2058
Rühle S, Greenshtein M, Chen S-G, Merson A, Pizem H, Sukenik CS, Cahen D, Zaban A (2005) Molecular adjustment of the electronic properties of nanoporous electrodes in dye-sensitized solar cells. J Phys Chem B 109(40):18907–18913
Chen P, Yum JH, Angelis FD, Mosconi E, Fantacci S, Moon S-J, Baker RH, Ko J, Nazeeruddin MK, Grätzel M (2009) High open-circuit voltage solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells with organic dye. Nano Lett 9(6):2487–2492
Zhang J, Li H-B, Sun S-L, Geng Y, Wu Y, Su Z-M (2012) Density functional theory characterization and design of high-performance diarylamine-fluorene dyes with different π spacers for dye-sensitized solar cells. J Mater Chem 22(2):568–576
R Sánchez-de-Armas, Oviedo López J, San-Miguel MA, Sanz JF, Ordejón P, Pruneda M (2010) Real-time TD-DFT simulations in dye sensitized solar cells: the electronic absorption spectrum of alizarin supported on TiO2 nanoclusters. J Chem Theory Comput 6(9):2856–2865
Kim S, Lim H, Kim K, Kim C, Kang TY, Ko MJ, Kim K, Park N-G (2010) Synthetic strategy of low-bandgap organic sensitizers and their photoelectron injection characteristics. IEEE J Quantum Electron 16(6):1627–1634
Acknowledgement
We acknowledge the generous financial support from Natural Science Foundation of China (21173169, 20803059), Chongqing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (cstc2013jcyjA90015), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. XDJK2013A008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, P., Zhang, F., Li, M. et al. Influence of position of auxiliary acceptor in D–A–π–A photosensitizes on photovoltaic performances of dye-sensitized solar cells. J Mater Sci 50, 7333–7342 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9290-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9290-8