Abstract
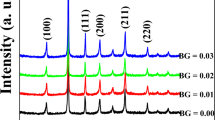
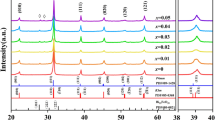
The role of BiFeO3 addition on the crystal structure, microstructure, and the electrical and electromechanical properties of high-sensitivity Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3–Bi0.5K0.5TiO3 ferroelectric ceramics for compositions at the morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) is investigated. A perovskite solid solution from nano-sized BiFeO3 and Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3–Bi0.5K0.5TiO3 powders is obtained, in which the persistence of a MPB in the ternary system is demonstrated. The structural characterization, along with the electrical properties, indicates the stabilization of intermediate domain configurations, associated with a decrease of the temperature for the development of the ferroelectric long-range order. As a consequence, high phase-change electromechanical response is found for certain small BiFeO3 additions. This result is very promising for the processing of textured ceramics taking advantage of the decomposition behaviour of BiFeO3. Ceramic texturing is demonstrated, a key technology for developing lead-free piezoelectrics that can replace Pb(Zr,Ti)O3.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haertling GH (1999) Ferroelectric ceramics: history and technology. J Am Ceram Soc 82:797–818
Cross E (2004) Lead-free at last. Nature 432:24–25
Rödel J, Jo W, Seifert KTP, Anton EM, Granzow T, Damjanovic D (2009) Perspective on the development of lead-free piezoceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 92:1153–1177
Leontsev SO, Eitel RE (2010) Progress in engineering high strain lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. Sci Technol Adv Mater 11:044302
Takenaka T, Nagata H, Hiruma Y, Yoshii Y, Matumoto K (2007) Lead-free piezoelectric ceramics based on perovskite structures. J Electroceram 19:259–265
Doshida Y, Kishimoto S, Ishii K, Kishi H, Tamura H, Tomikawa Y, Hirose S (2007) Miniature cantilever-type ultrasonic motor using Pb-free multilayer piezoelectric ceramics. Jpn J Appl Phys 46:4921–4925
Nagata H, Hiruma Y, Suzuki M, Takenaka T (2008) Bismuth layer-structured ferroelectric ceramics with high mechanical quality factor. Electron Commun Jpn 91:39–45
Smolenskii GA, Isupov VA, Agranovskaya AI, Krainik NN (1961) New ferroelectrics of complex composition. J Sov Phys Solid State 2:2651–2654
Aksel E, Forrester JS, Jones JL, Thomas PA, Page K, Suchomel MR (2011) Monoclinic crystal structure of polycrystalline Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3. Appl Phys Lett 98:152901
Anton EM, Jo W, Damjanovic D, Rödel J (2011) Determination of depolarization temperature of (Bi1/2Na1/2)TiO3-based lead-free piezoceramics. J Appl Phys 110:094108
Siny IG, Tu CS, Schmidt VH (1995) Critical acoustic behavior of the relaxor ferroelectric Na1/2Bi1/2TiO3 in the inter transition region. Phys Rev B 51:5659–5665
Sasaki A, Chiba T, Mamiya Y, Otsuki E (1999) Dielectric and piezoelectric properties of (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3-(Bi0.5K0.5)TiO3 systems. Jpn J Appl Phys 38:5564–5567
Otoničar M, Škapin SD, Spreitzer M, Suvorov D (2010) Compositional range and electrical properties of the morphotropic phase boundary in the Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3–K0.5Bi0.5TiO3 system. J Eur Ceram Soc 30:971–979
Moosavi A, Bahrevar MA, Aghaei A, Ramos P, Algueró M, Amorín H (2014) High field electromechanical response of Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-Bi0.5K0.5TiO3 across its morphotropic phase boundary. J Phys D 47:055304
Tani T, Kimura T (2012) Processing and properties of textured BNT-based piezoelectrics. In: Priya S, Nahm S (eds) Lead-free piezoelectrics. Springer, New York, pp 311–335
Su S, Zuo R (2012) Fabrication and electrical properties of 0.94Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3–0.06BaTiO3 textured ceramics by RTGG method using micrometer sized BaTiO3 plate-like templates. J Alloys Comp 525:133–136
Saito Y, Takao H, Tani T, Nonoyama T, Takatori K, Homma T et al (2004) Lead-free piezoceramics. Nature 432:84–87
Lv D, Zuo R (2013) Evolution of crystallographic grain orientation and anisotropic properties of (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3 ceramics using BaTiO3 templates by reactive templated grain growth. J Alloys Comp 560:62–66
Messing GL, Trolier-Mckinstry S, Sabolsky EM, Duran C, Kwon S, Brahmaroutu B et al (2004) Templated grain growth of textured piezoelectric ceramics. Crit Rev Solid State Mater Sci 29:45–96
Tani T, Kimura T (2006) Reactive-templated grain growth processing for lead free piezoelectric ceramics. Adv Appl Ceram 105:55–63
Kimura T, Takahashi T, Tani T, Saito Y (2004) Crystallographic texture development in bismuth sodium titanate prepared by reactive-templated grain growth method. J Am Ceram Soc 87:1424–1429
Kaneko S, Dong D, Murakami K (1998) Effect of simultaneous addition of BiFeO3 and Ba(Cu0.5W0.5)O3 on lowering of sintering temperature of Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 81:1013–1018
Chao X, Yang Z, Kang C, Chang Y (2008) Effects of BiFeO3 addition on electrical properties and temperature stability of low temperature sintered PZT–PFW–PMN ceramics. Sens Actuators A 141:482–488
Kimura T, Yamaguchi T (1983) Fused salt synthesis of Bi4Ti3O12. Ceram Int 9:13–17
Amorín H, Santacruz I, Holc J, Thi MP, Kosec M, Moreno R et al (2009) Tape-casting performance of ethanol slurries for the processing of textured PMN–PT ceramics from nanocrystalline powder. J Am Ceram Soc 92:996–1001
Khomskii DI (2006) Multiferroics: different ways to combine magnetism and ferroelectricity. J Magn Magn Mater 306:1–8
Catalan G, Scott JF (2009) Physics and applications of bismuth ferrite. Adv Mater 21:2463–2485
Ni F, Luo L, Pan X, Li W, Zhu J (2012) Effects of A-site vacancy on the electrical properties in lead-free non-stoichiometric ceramics Bi0.5+x(Na0.82K0.18)0.5−3xTiO3 and Bi0.5+y(Na0.82K0.18)0.5TiO3. J Alloys Comp 541:150–156
Wang B, Luo L, Ni F, Du P, Li W, Chen H (2012) Piezoelectric and ferroelectric properties of (Bi1−xNa0.8K0.2Lax)0.5TiO3 lead-free ceramics. J Alloys Comp 526:79–84
Levin I, Reaney IM, Anton EM, Jo W, Rödel J, Pokorny J et al (2013) Local structure, pseudosymmetry, and phase transitions in Na1/2Bi1/2TiO3-K1/2Bi1/2TiO3 ceramics. Phys Rev B 87:024113
Robels U, Arlt G (1993) Domain wall clamping in ferroelectrics by orientation of defects. J Appl Phys 73:3454–3460
Jaita P, Watcharapasorn A, Cann DP, Jiansirisomboon S (2014) Dielectric, ferroelectric and electric field-induced strain behavior of Ba(Ti0.90Sn0.10)O3-modified Bi0.5(Na0.80K0.20)0.5TiO3 lead-free piezoelectrics. J Alloys Comp 596:98–106
Zhang ST, Kounga AB, Aulbach E, Jo W, Granzow T, Ehrenberg H et al (2008) Lead-free piezoceramics with giant strain in the system Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-BaTiO3-K0.5Na0.5NbO3. II. Temperature dependent properties. J Appl Phys 103:034108
Zhang MS, Scott JF, Zvirgzds JA (1986) Raman spectroscopy of Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3. Ferroelectr Lett 6:147–152
Jin L, He Z, Damjanovic D (2009) Nanodomains in Fe+3-doped lead zirconate titanate ceramics at the morphotropic phase boundary do not correlate with high properties. Appl Phys Lett 95:012905
Wang H, Xu H, Luo H, Yin Z, Bokov AA, Ye ZG (2005) Dielectric anomalies of the relaxor-based 0.9Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-0.1PbTiO3 single crystals. Appl Phys Lett 87:012904
Jo W, Granzow T, Aulbach E, Rödel J, Damjanovic D (2009) Origin of the large strain response in (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3-modified (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3-BaTiO3 lead-free piezoceramics. J Appl Phys 105:094102
Park SE, Shrout TR (1997) Ultrahigh strain and piezoelectric behavior in relaxor based ferroelectric single crystals. J Appl Phys 82:1804–1811
Hao J, Shen B, Zhai J, Chen H (2014) Effect of BiMeO3 on the phase structure, ferroelectric stability, and properties of lead-free Bi0.5(Na0.80K0.20)0.5TiO3 ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 97:1776–1784
Sumang R, Vittayakorn N, Bongkarn T (2013) Crystal structure, microstructure and electrical properties of (1-x-y)Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-xBi0.5K0.5TiO3-yBiFeO3 ceramics near MPB prepared via the combustion technique. Ceram Int 39:S409–S413
Zou M, Fan H, Chen L, Yang W (2010) Microstructure and electrical properties of (1−x) [0.82Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-0.18Bi0.5K0.5TiO3]-xBiFeO3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. J Alloys Comp 495:280–283
Ramana EV, Suryanarayana SV, Sankaram TB (2010) Synthesis and magnetoelectric studies on Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3-BiFeO3 solid solution ceramics. Solid State Sci 12:956–962
Matsuo H, Noguchi Y, Miyayama M, Suzuki M, Watanabe A, Sasabe S, Ozaki T, Mori S, Torii S, Kamiyama T (2010) Structural and piezoelectric properties of high-density Bi0.5K0.5TiO3-BiFeO3 ceramics. J Appl Phys 108:104103
Acknowledgements
Research was funded by Materials and Energy Research Center (MERC) (PhD. Project Grant No. 488973) and the Spanish MINECO through project MAT2011-23709. A. M. acknowledges support from MERC to go to Spain, and the Spanish CSIC for the 6-month period spent at the Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Madrid.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moosavi, A., Bahrevar, M.A., Aghaei, A.R. et al. Effects of nano-sized BiFeO3 addition on the properties of high piezoelectric response (1 − x)Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3–xBi0.5K0.5TiO3 ceramics. J Mater Sci 50, 2093–2102 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8771-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8771-5