Abstract
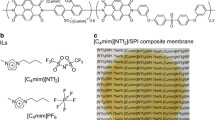
Six types of PILs were designed and synthesized by radical polymerization reaction and ion exchange reaction and the 1H NMR analysis and TG-MS analysis proved the successful procedure and their CO2 permeation properties were evaluated. 1-butyl 3-methylimidazole double trifluoromethane sulfonate ([bmim][Tf2N])-based facilitated transport membrane, with 10 wt% poly([ViEtIm] Tf2N), showed an excellent CO2 permeability of 920 Barrer, similar to that of the others investigated. PILs were distributed in the SILM using the “like dissolves like” theory to investigate the gas permeation separation performance before and after doping of the PILs in SILM. Owing to the reversible interaction between the CO2 molecules and electropositive PIL chains, this supported ionic liquid membrane selectively transfer CO2 more rapidly. The polymer chains play the role of mobile CO2 carrier in the SLM, and introduce facilitated transport mechanism. This concept may provide a means for fabricating a highly permeable and selective membrane to break through Robeson’s upper bound.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li P, Pramoda KP, Chung TS (2011) CO2 separation from flue gas using polyvinyl-(room temperature ionic liquid)room temperature ionic liquid composite membranes. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:9344–9353
Standing TH (2001) Climate change projections hinge on global CO2, temperature data. Oil Gas J 99:20–21
Yang H, Xu Z, Fan M, Gupta R, Slimane RB, Bland AE, Wright I (2008) Progress in carbon dioxide separation and capture: a review. J Environ Sci 20:14–27
Yeo ZY, Chew TL, Zhu PW et al (2012) Conventional processes and membrane technology for carbon dioxide removal from natural gas: a review. J Nat Gas Chem 3:282–298
Xiao YC, Low BT, Hosseini SS et al (2009) The strategy of molecular designand modification of polyimide-based membranes for CO2 removal from natural gas—a review. Prog Polym Sci 34:561–580
Drioli E, Brunetti A, Di Profio G et al (2012) Process intensification strategies and membrane engineering. Green Chem 14:1561–1572
Shao L, Low BT, Chung TS et al (2009) Polymeric membranes for the hydrogen economy: contemporary approaches and prospects for the future. J Membr Sci 327:18–31
Scholes CA, Smith KH, Kentish SE, Stevens GW (2010) CO2 capture from pre-combustion processes—strategies for membrane gas separation. Int J Greenhouse Gas Control 4:739–755
Plasynski SI, Chen Z (2000) Review of CO2 capture technologies and some improvement opportunities. ACS Div Fuel Chem Prepr 45:644–649
Stern SA (1994) Polymers for gas separations: the next decade. J Membr Sci 94:1–65
Fortunato R, Afonso CAM, Reis MAM, Crespo JG (2004) Supported liquid membranes using ionic liquid: study of stability and transport mechanisms. J Membr Sci 242:197–209
Iiconich J, Myers C, Pennline H, Luebke D (2007) Experimental investigation of the permeability and selectivity of supported ionic liquid membranes for CO2/He separation at temperatures up to 125°C. J Membr Sci 298:41–47
Ferguson L, Scovazzo P (2007) Solubility, diffusivity, and permeability of gases in phosphonium-based room temperature ionic liquids: data and correlations. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:1369–1374
Yokozeki A, Shiflett MB (2007) Hydrogen purification using room-temperature ionic liquids. Appl Energy 84:351–361
Scovazzo P, Kieft J, Finan DA, Koval C, DuBois D, Noble RD (2004) Gas separation using non-hexafluorophosphate [PF6] anion supported ionic liquid membranes. J Membr Sci 238:57–63
Scovazzo P, Havard D, McShea M, Mixon S, Morgan D (2009) Long-term, continuous mixed-gas dry fed CO2/CH4 and CO2/N2 separation performance and selectivities for room temperature ionic liquid membranes. J Membr Sci 327:41–48
Bara JE, Gabrel CJ, Carlisle TK, Camper DE, Finotello A, Gin DL, Noble RD (2009) Gas separation in fluoroalkyl-functionalized room-temperature ionic liquids using supported liquid membranes. Chem Eng J 47:43–50
Hu X, Tang J, Blasig A, Shen Y, Radosz M (2006) CO2 permeability, diffusivity and solubility in polyethylene glycol-grafted polyionic membranes and their CO2 selectivity relative to methane and nitrogen. J Membr Sci 281:130–138
Bara JE, Lessmann S, Gabriel CJ, Hatakeyama ES, Noble RD, Gin DL (2007) Synthesis and performance of polymerizable room-temperature ionic liquids as gas separation membranes. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:5397–5404
Bara JE, Gabriel CJ, Hatakeyama ES, Carlisle TK, Lessmann S, Noble RD, Gin DL (2008) Improving CO2 selectivity in polymerized room-temperature ionic liquid gas separation membranes through incorporation of polar substituents. J Membr Sci 321:3–7
Min GH, Yim T, Lee HY (2006) Synthesis and properties of ionic liquids: imidazolium tetrafluoroborates with unsaturated side chains. Bull Korean Chem Soc 27:847–852
Placido GM, Letizia L, Sandra LS et al (2012) Fast and reversible CO2 quartz crystal microbalance response of vinylimidazolium based poly(ionic liquid)s. Polym Adv Technol 23:1511–1519
Iz´ak P, Ruth W, Fei Z et al (2008) Selective removal of acetone and butan-1-ol from water with supported ionic liquid–polydimethylsiloxane membrane by pervaporation. Chem Eng J 139:318–321
Yuan S, Deng Q, Fang G et al (2012) A novel ionic liquid polymer material with high binding capacity for proteins. J Mater Chem 22:3965–3972
Bara JE, Hatakeyama ES, Gin DL, Noble RD (2008) Improving CO2 permeability in polymerized room-temperature ionic liquid gas separation membranes through the formation of a solid composite with a room-temperature ionic liquid. Polym Adv Technol 19:1415–1420
Bara JE, Noble RD, Gin DL (2009) Effect of “Free” cation substituent on gas separation performance of polymer-room-temperature ionic liquid composite membranes. Ind Eng Chem Res 48:4607–4610
Bara JE, Camper DE, Gin DL, Noble RD (2010) Room-temperature ionic liquids and composite materials: platform technologies for CO2 capture. Acc Chem Res 43:152–159
Lee JH, Hong J, Kim JH, Kang YS, Kang SW (2012) Facilitated CO2 transport membranes utilizing positively polarized copper nanoparticles. Chem Commun 48:5298–5300
Hudiono YC, Carlisle TK, LaFrate AL, Gin DL, Noble RD (2011) Novel mixed matrix membranes based on polymerizable room-temperature ionic liquids and SAPO-34 particles to improve CO2 separation. J Membr Sci 370:141–148
Sun X, Zhang M, Luo J, Li J (2014) Constructing CO2-facilitated transport highway in supported ionic liquid membranes. Funct Mater Lett 7:1450012
Tang J, Tang H, Sun W, Plancher H, Radosz M, Shen Y (2005) Poly(ionic liquid)s: a new material with enhanced and fast CO2 absorption. Chem Commun 3325–3327
Tang J, Sun W, Tang H, Radosz M, Shen Y (2005) Enhanced CO2 absorption of poly(ionic liquid)s. Macromolecules 38:2037–2039
Blasig A, Tang J, Hu X, Tan S, Shen Y, Radosz M (2007) Carbon dioxide solubility in polymerized ionic liquids containing ammonium and imidazolium cations from magnetic suspension balance: P[VBTMA][BF4] and P[VBMI][BF4]. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:5542–5547
Blasig A, Tang J, Hu X (2007) Magnetic suspension balance study of carbon dioxide solubility in ammonium-based polymerized ionic liquids: poly(p-vinyl-benzyltrimethyl ammonium tetrafluoroborate) and poly([2-(methacryl oyloxy)ethyl] trimethyl ammonium tetrafluoroborate). Fluid Phase Equilib 256:75–80
Marcilia R, Blazquez JA, Rodriguez J (2004) Tuning the solubility of polymerized ionic liquids by simple anion-exchange reactions. J Polym Sci Pol Chem 42:208–212
Jiang YY, Zhou Z, Jiao Z, Li L, Wu YT, Zhang ZB (2007) SO2 gas separation using supported ionic liquid membranes. J Phys Chem B 111:5058–5061
Kasahara S, Kamio E, Ishigami T, Matsuyama H (2012) Amino acid ionic liquid-based facilitated transport membranes for CO2 separation. Chem Commun 48:6903
Kasahara S, Kamio E, Ishigami T, Matsuyama H (2012) Effect of water in ionic liquids on CO2 permeability in amino acid ionic liquid-based facilitated transport membranes. J Membr Sci 415–416:168–175
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 21136007) and the authors express their gratitude to Prof. Wu you-ting of the Nanjing University in Jiangsu Province for his kind assistance with the setting up of the permeability tester and the beneficial academic communication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Zhang, M., Guo, R. et al. CO2-facilitated transport performance of poly(ionic liquids) in supported liquid membranes. J Mater Sci 50, 104–111 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8570-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8570-z