Abstract
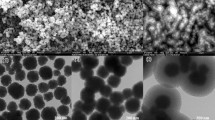
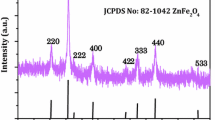
Magnetite hollow submicrospheres and mesoporous nanoparticles have been synthesized by a solvothermal approach with assistant of hexamethylenetetramine (HMT) and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP). Experimental results showed that the morphology of magnetite was transformed from hollow to solid submicrospheres with increasing amount of HMT. Moreover, without addition of PVP or appropriate addition of external water, mesoporous nanoparticles were obtained. A probable gaseous bubble template mechanism was proposed for the formation of magnetite hollow and mesoporous nanostructures based on experimental observations. Magnetic measurement results revealed that all of the samples were ferromagnetic at room temperature.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Terranova ML, Orlanducci S, Tamburri E, Guglielmotti V (2014) Si/C hybrid nanostructures for Li-ion anodes: an overview. J Power Sources 246:167–177. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.07.065
Song Q, John Zhang Z (2012) Controlled synthesis and magnetic properties of bimagnetic spinel ferrite CoFe2O4 and MnFe2O4 nanocrystals with core–shell architecture. J Am Chem Soc 134:10182–10190. doi:10.1021/ja302856z
Wang XL, Cui TY, Cui F, Zhang YJ, Li D, Zhang ZD (2011) Facile access to ultrasmall Eu2O3 nanoparticle-functionalized hollow silica nanospheres based on the spontaneous formation and decomposition of a cross-linked organic/inorganic hybrid core. Chem Commun 47:6329–6331. doi:10.1039/c0cc05510g
Liu Q, Zi Z, Zhang M, Zhang P, Pang A, Dai J, Sun Y (2013) Solvothermal synthesis of hollow glass microspheres/Fe3O4composites as a lightweight microwave absorber. J Mater Sci 48:6048–6055. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7401-y
Wang XL, Li D, Cui TY, Zhang ZD (2010) Magnetic and optical properties of multiferroic GdMnO3 nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 107:09B510. doi:10.1063/1.3358007
Sun S, Murry CB, Weller D, Folks L, Moster A (2000) Monodisperse FePt nanoparticles and ferromagnetic FePt nanocrystal superlattices. Science 287:1989–1992. doi:10.1126/science.287.5460.1989
Hu M, Jiang Y, Yan M (2014) Scalable synthesis of Fe3O4/C composites with enhanced electrochemical performance as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J Alloys Compd 582:563–568. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.08.098
Ye QL, Kozuka Y, Yoshikawa H, Awaga K, Bandow S, Iijima S (2007) Effects of the unique shape of submicron magnetite hollow spheres on magnetic properties and domain states. Phys Rev B 75:224404. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.75.224404
Ge L, He L, Goebl J, Yin Y (2009) Assembly of magnetically tunable photonic crystals in nonpolar solvents. J Am Chem Soc 131:3484–3486. doi:10.1021/ja809772v
Lu AH, Salabas EL, Schüth F (2007) Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:1222–1244. doi:10.1002/anie.200602866
Qu XF, Zhou GT, Yao QZ, Fu SQ (2010) Aspartic-acid-assisted hydrothermal growth and properties of magnetite octahedrons. J Phys Chem C 114:284–289. doi:10.1021/jp909175s
Li XH, Zhang DH, Chen JS (2006) Synthesis of amphiphilic superparamagnetic ferrite/block copolymer hollow submicrospheres. J Am Chem Soc 128:8382–8383. doi:10.1021/ja061460g
Liu Z, Zhang D, Han S, Li C, Lei B, Lu W, Fang J, Zhou C (2005) Single crystalline magnetite nanotubes. J Am Chem Soc 127:6–7. doi:10.1021/ja0445239
Wang J, Chen Q, Zeng C, Hou B (2004) Magnetic-field-induced growth of single-crystalline Fe3O4 nanowires. Adv Mater 16:137–140. doi:10.1002/adma.200306136
Wu H, Du N, Wang J, Zhang H, Yang D (2014) Three-dimensionally porous Fe3O4 as high-performance anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 246:198–203. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.07.063
Cao SW, Zhu YJ (2008) Surfactant-free preparation and drug release property of magnetic hollow core/shell hierarchical nanostructures. J Phys Chem C 112:12149–12156. doi:10.1021/jp803131u
Huang Z, Tang F (2005) Preparation, structure, and magnetic properties of mesoporous magnetite hollow spheres. J Colloid Interface Sci 281:432–436. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2004.08.121
Xia H, Wan Y, Yuan G, Fu Y, Wang X (2013) Fe3O4/carbon core–shell nanotubes as promising anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 241:486–493. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.04.126
Lim HS, Jung BY, Sun YK, Suh KD (2012) Hollow Fe3O4 microspheres as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 75:123–130. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2012.04.082
Wang F, Liu J, Kong J, Zhang Z, Wang X, Itoh M, Machida K (2011) Template free synthesis and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of monodispersed hollow magnetite nano-spheres. J Mater Chem 21:4314–4320. doi:10.1039/C0JM02894K
Cheng K, Peng S, Xu C, Sun S (2009) Porous hollow Fe3O4 nanoparticles for targeted delivery and controlled release of cisplatin. J Am Chem Soc 131:10637–10644. doi:10.1021/ja903300f
Yu B, Kwak SY (2010) Assembly of magnetite nanocrystals into spherical mesoporous aggregates with a 3-D wormhole-like pore structure. J Mater Chem 20:8320–8328. doi:10.1039/C0JM01274B
Liu Y, Goebla J, Yin Y (2013) Templated synthesis of nanostructured materials. Chem Soc Rev 42:2610–2653. doi:10.1039/C2CS35369E
Liu J, Liu F, Gao K, Wu J, Xue D (2009) Recent developments in the chemical synthesis of inorganic porous capsules. J Mater Chem 19:6073–6084. doi:10.1039/B900116F
Lou XW, Archer LA, Yang Z (2008) Hollow micro-/nanostructures: synthesis and applications. Adv Mater 20:3987–4019. doi:10.1002/adma.200800854
Dong F, Guo W, Ha CS (2012) Monodisperse single-crystal mesoporous magnetite nanoparticles induced by nanoscale gas bubbles. J Nanopart Res 14:1303. doi:10.1007/s11051-012-1303-9
Craig VSJ (2011) Very small bubbles at surfaces—the nanobubble puzzle. Soft Matter 7:40–48. doi:10.1039/C0SM00558D
Lynch J, Zhuang J, Wang T, LaMontagne D, Wu H, Cao Y (2011) Gas- bubble effects on the formation of colloidal iron oxide nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 133:12664–12674. doi:10.1021/ja2032597
Feng Y, Zhang M, Guo M, Wang X (2010) Studies on the PEG-assisted hydrothermal synthesis and growth mechanism of ZnO microrod and mesoporous microsphere arrays on the substrate. Cryst Growth Des 10:1500–1507. doi:10.1021/cg900327v
Ohnishi M, Kozuka Y, Ye QL, Yoshikawa H, Awaga K, Matsuno R, Kobayashi M, Takahara A, Yokoyama T, Bandowd S, Iijima S (2006) Phase selective preparations and surface modifications of spherical hollow nanomagnets. J Mater Chem 16:3215–3220. doi:10.1039/B605472B
Deng H, Li X, Peng Q, Wang X, Chen J, Li Y (2005) Monodisperse magnetic single-crystal ferrite microspheres. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:2782–2785. doi:10.1002/anie.200462551
Guo L, Liang F, Wen X, Yang S, He L, Zheng W, Chen C, Zhong Q (2007) Uniform magnetic chains of hollow cobalt mesospheres from one-pot synthesis and their assembly in solution. Adv Funct Mater 17:425–430. doi:10.1002/adfm.200600415
Hu P, Yu L, Zuo A, Guo C, Yuan F (2009) Fabrication of monodisperse magnetite hollow spheres. J Phys Chem C 113:900–906. doi:10.1021/jp806406c
Peng Q, Dong Y, Li Y (2003) ZnSe semiconductor hollow microspheres. Angew Chem Int Ed 42:3027–3030. doi:10.1002/anie.200250695
Wang N, Cao X, Kong D, Chen W, Guo L, Chen C (2008) Nickel chains assembled by hollow microspheres and their magnetic properties. J Phys Chem C 112:6613–6619. doi:10.1021/jp710850n
Zhu LP, Xiao HM, Zhang WD, Yang G, Fu SY (2008) One-pot template-free synthesis of monodisperse and single-crystal magnetite hollow spheres by a simple solvothermal route. Cryst Growth Des 8:957–963. doi:10.1021/cg700861a
Vinogradoff V, Rimola A, Duvernay F, Danger G, Theulé P, Chiavassa T (2012) The mechanism of hexamethylenetetramine (HMT) formation in the solid state at low temperature. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:12309–12320. doi:10.1039/C2CP41963G
Singh H, Bhagwat S, Jouen S, Lefez B, Athawale A, Hannoyer B, Ogale S (2010) Elucidation of the role of hexamine and other precursors in the formation of magnetite nanorods and their stoichiometry. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:3246–3253. doi:10.1039/B917407A
Cai W, Wan J (2007) Facile synthesis of superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles in liquid polyols. J Colloid Interface Sci 305:366–370. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2006.10.023
Millan A, Urtizberea A, Silva NJO, Palacio F, Amaral VS, Snoeck E, Serin V (2007) Surface effects in maghemite nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 312:L5–L9. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.09.011
Zhang YJ, Yao Q, Zhang Y, Cui TY, Li D, Liu W, Lawrence W, Zhang ZD (2008) Solvothermal synthesis of magnetic chains self-assembled by flowerlike cobalt submicrospheres. Cryst Growth Des 8:3206–3212. doi:10.1021/cg7010452
Srivastava AK, Madhavi S, White TJ, Ramanujan RV (2007) Cobalt–ferrite nanobowl arrays: curved magnetic nanostructures. J Mater Res 22:1250–1254. doi:10.1557/jmr.2007.0149
Duan G, Cai W, Li Y, Li Z, Cao B, Luo Y (2006) Transferable ordered Ni hollow sphere arrays induced by electrodeposition on colloidal monolayer. J Phys Chem B 110:7184–7188. doi:10.1021/jp057421t
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by Doctoral Science Foundation of Shenyang University of Technology (2012) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 51331006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Yu, J., Shi, G. et al. Solvothermal synthesis of magnetite hollow submicrospheres and mesoporous nanoparticles. J Mater Sci 49, 6029–6038 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8323-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8323-z