Abstract
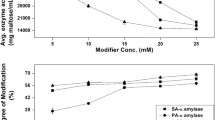
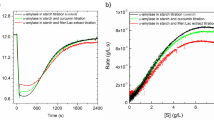
A growing interest has been shown regarding the impact of α-amylase on the quality of fermented foods. Therefore, the interaction between γ-cyclodextrin and α-amylase was investigated in this article. The results showed that γ-cyclodextrin had an inhibitory effect on the activity of α-amylase under certain conditions, obtaining the strongest inhibitory effect when the concentration of γ-cyclodextrin was 10 mmol/L, the reaction temperature was 45 °C, pH = 5.9 and reaction time of 120 min. The results also showed important changes in the secondary structure of α-amylase induced by γ-cyclodextrin, including the transformation of α-helix, β-fold and random coil. Moreover, the addition of γ-cyclodextrin could induce the change of endogenous fluorescence intensity by changing the microenvironment of the α-amylase. According to the results of NMR, a part of the α-amylase molecule enters the cavity of the γ-cyclodextrin, and the other part forms a hydrogen bond with the outer cavity, forming a complex. The experimental results provide references for the application of γ-cyclodextrin and α-amylase.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Szetjli, J.: Introduction and general overview of cyclodextrin chemistry. Chem. Rev. 29(39), 1743–1753 (1998)
Ali, S.M., Upadhyay, S.K., Maheshwari, A., Koketsu, M.: Complexation of fluvastatin sodium with β-cyclodextrin: NMR spectroscopic study in solution. J. Incl. Phenom. Macro. 55(3–4), 394–398 (2006)
Li, S.Y., Xing, P.Y., Zhang, L., Xin, F.F., Nie, J.H., Wang, H.L., Ma, M.F., Wu, Y.R., Hao, A.Y.: Controllable self-assembly of an amphiphilic drug with β-cyclodextrin and α-amylase. Colloid Surfaces A. 445, 67–74 (2014)
Lumholdt, L.R., Holm, R., Jorgensen, E.B., Larsen, K.L.: In vitro investigations of α-amylase mediated hydrolysis of cyclodextrins in the presence of ibuprofen, flurbiprofen, or benzo[α]pyrene. Carbohyd. Res. 362, 56–61 (2012)
Toda, J., Misaki, M., Konna, A., Wada, T., Yasumatsu, K.: Interaction of cyclodextrin with taste substances. Qual. Food Bever. 1, 19–34 (1985)
Rao, P., Suresh, C., Rao, D.N., Kumar, S.U., Divakar, S.: Digestion of residual β-cyclodextrin in treated egg using glucoamylase from a mutant strain of Aspergillus niger. Food Chem. 65(3), 97–301 (1999)
Sherje, A.P., Dravyakar, B.R., Kadam, D., Jadhav, M.: Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges: a critical review. Carbohydr. Chem. 173, 37 (2017)
Wang, Z., Zhang, P., Hu, F., Zhao, Y., Zhu, L.: A crosslinked β-cyclodextrin polymer used for rapid removal of a broad-spectrum of organic micropollutants from water. Carbohyd. Polym. 177, 224–231 (2017)
Yao, D., Zhu, Z.Z., Cai, H.Y., Chen, X., Sun, W., Barba, F.J., Li, F., Shen, W.Y., Ding, W.P.: Inhibition of cyclodextrins on α-galactosidase. Food Chem. 217, 59–64 (2017)
Trubst, A.A.L., Cristianini, M.: High pressure homogenization of a fungi α-amylase. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 13(13), 107–111 (2012)
Muralikrishna, G., Nirmala, M.: Cereal α-amylase–an overview. Carbohyd. Polym. 60(2), 163–173 (2005)
Lin, S.C., Lin, W.T., Liu, S.H., Chou, W.I., Hsiung, B.K., Lin, I.P., Sheu, C.C., Chang, M.D.: Role of the linker region in the expression of Rhizopus oryzae glucoamylase. BMC Biochem. 8(3), 21–27 (2007)
Lillienberg, L., Baur, X., Doekes, G., Belin, L., Raulf-Heimsoth, M., Sander, I., Ståhl, A., Thissen, J., Heederik, D.: Comparison of four methods to assess fungal alpha-amylase in flour dust. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 44(6), 427–433 (2000)
Hamilton, L.M., Kelly, C.T., Fogarty, W.M.: Review: cyclodextrins and their interaction with amylolytic enzymes. Enzyme Microb Tech. 26, 561–567 (2000)
Li, Y.X., Wang, J.P., Jin, Z.Y., Jiao, A.Q., Xu, X.M.: A study on the potential interaction between cyclodextrin and lipoxygenase. J. Incl. Phenom. Macro. 76(2), 107–111 (2013)
Yu, B., Tian, Y.Q., Yang, N., Xu, X.M., Jin, Z.Y.: A study on the inhibition mechanism of β-cyclodextrin on pillulanase. J. Incl. Phenom. Macro. 70, 161–165 (2011)
Yang, J.Y., Wu, C.S., Martinez, H.M.: Calculation of protein conformation from circular dichroism. Methods Enzymol. 130(4), 208–269 (1986)
Yu, B., Wang, J., Zhang, H., Jin, Z.Y.: Investigation of the interactions between the hydrophobic cavities of cyclodextrins and pullulanase. Molecules 16(4), 3010–3017 (2011)
Rodrigues, E., Vaz, S., Gil, S., Caldeira, M.M., Silva, A.M.D.: Inclusion of polyphenol oxidase substrates in β-Cyclodextrin: a H-NMR study. J. Incl. Phenom. Macro. 44, 395–397 (2002)
He, W.Y., Li, Y., Tang, J.H., Luan, F., Jin, J., Hu, Z.D.: Comparison of the characterization on binding of alpinetin and cardamonin to lysozyme by spectroscopic methods. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 39(4–5), 165–173 (2006)
Babu, K.R., Douglas, D.J.: Methanol-induced conformations of myoglobin at pH 4.0. Biochemistry 39(47), 14702–14710 (2000)
Yang, S.J., Lee, H.S., Park, C.S., Kim, Y.R., Moon, T., Park, K.H.: Enzymatic analysis of an amylolytic enzyme from the hyperthermophilic archaeon pyrococcus furious reveals its novel catalytic properties as both an α-amylase and a cyclodextrin-hydrolyzing enzyme. Appl Environ Microb. 70(10), 5988–5995 (2004)
Ballschmiter, M., Armbrecht, M., Ivanova, K., Antranikian, G., Garabed, L., Liebl, W.: AmyA, an α-amylase with β-cyclodextrin-forming activity, and AmyB from the thermoalkaliphilic organism Anaer- obranca gottschalkii: two α-amylases adapted to their di erent cellular localizations. Appl Environ Microb. 71(7), 3709–3715 (2005)
Herale, R., Sukumaren, U.K., Kadeppagari, R.K.: Evidence for the improvement of thermostability of the maltogenic α-amylase of Aspergillus niger by negative pressure. Starch. 64(8), 646–651 (2012)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Number 31301415), Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2017CFB308) and Foundation of Wuhan Polytechnic University (2016RZ21).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Yang, P., Shen, W. et al. Investigation on the interaction between γ-cyclodextrin and α-amylase. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 94, 103–109 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-019-00913-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-019-00913-x