Abstract
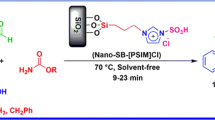
The catalytic activities of chlorosulfonyl-calix[4]arene-bonded silica gel (CSC[4]A-SG) as a novel heterogeneous catalyst was illustrated by efficient reduction of various ketones to their corresponding alcohols. To illustrate the promoting effect of the catalyst in the reaction, two more series of parallel experiments were also carried out using bare silica gel and no catalyst. The study suggests that this newly synthesized solid catalyst has high binding tendency toward sodium cations through ion- pair interactions and is consequently effective for the reduction of ketones to alcohols using NaBH4 as a hydrogen donor. Also to demonstrate the high affinity and strong trap capacity of CSC[4]A-SG toward sodium cation, atomic absorption spectrometric measurements were performed. As a result, quantitative reduction of ketones was observed in short time periods, while the catalyst shows high thermal stability (up to 300 °C) and can be recovered and reused for at least five times in a row without loss of its catalytic performance. This is the first report about the application of CSC[4]A-SG as a catalyst in the chemical reactions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ertl, G., Knözinger, H., Weitkamp, J.: Handbook of heterogeneous catalysis. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim (1997)
Sheldon, R.A., Downing, R.S.: Heterogeneous catalytic transformations for environmentally friendly production. Appl. Catal. A 189, 163–183 (1999)
Lucarelli, C., Vaccari, A.: Examples of heterogeneous catalytic processes for fine chemistry. Green Chem. 13, 1941–1949 (2011)
Hashmi, A., Stephen, K., Toste, F.D.: Modern gold catalyzed synthesis. John Wiley-VCH, Weinheim (2012)
Gutsche, C.D.: Calixarenes: an introduction. Royal Society of Chemistry, Tucson (2008)
Shinkai, S.: Calixarenes-the third generation of supramolecules. Tetrahedron 49, 8933–8968 (1993)
Sgarlata, C., Zito, V., Arena, G., Consoli, G.M.L., Galante, E., Geraci, C.: A sinapic acid–calix[4]arene hybrid selectively binds Pb2+ over Hg2+ and Cd2+. Polyhedron 28, 343–348 (2009)
Huang, H., Zhao, C., Ji, Y., Nie, R., Zhou, P., Zhang, H.: Preparation, characterization and application of p-tert-butyl-calix [4] arene-SBA-15 mesoporous silica molecular sieves. J. Hazard. Mater. 178, 680–685 (2010)
Tabakchi, M.: Immobilization of calix[4]arene bearing carboxylic acid and amid groups on aminopropyl silica gel and its sorption properties for Cr(VI). J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 61, 53–60 (2008)
Gutsche, C.D.: Calixarenes revisited, monografs in supramolecular chemistry. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge (1998)
Asfari, Z., Böhmer, V., Harrowfield, J., Vicens, J.: Calixarenes 2001. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (2001)
Bozkurt, S., Kocabas, E., Durmaz, M., Yilmaz, M., Sirit, A.: Synthesis and dichromate anion sorption of silica gel-immobilized calix [4] arenes. J. Hazard. Mater. 165, 974–979 (2009)
Arnaud-Neu, F., Barrett, G., Harris, S.J., Owens, M., McKervey, M.A., Schwing-Weill, M.J., Schwinte, P.: Cation complexation by chemically modified calixarenes. 5. Protonation constants for calixarene carboxylates and stability constants of their alkali and alkaline-earth complexes. Inorg. Chem. 32, 2644–2650 (1993)
Ghidini, E., Ugozzoli, F., Ungaro, R., Harkema, S., Abu El-Fadl, A., Reinhoudt, D.N.: Complexation of alkali metal cations by conformationally rigid, stereoisomeric calix [4] arene crown ethers: a quantitative evaluation of preorganization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 112, 6979–6985 (1990)
Shinkai, S., Otsuka, T., Fujimoto, K., Matsuda, T.: Metal selectivity of conformational isomers derived from p-t-Butylcalix [4] arene. Chem. Lett. 19, 835–838 (1990)
ávan Duynhoven, J.P.: Cavity effect of calix [4] arenes in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Chem. Commun. 13, 1517–1518 (1996)
Katz, A., Da Costa, P., Lam., A.C.P., Notestein, J.M.: The first single-step immobilization of a calix-[4]-arene onto the surface of silica. Chem. Mater. 14, 3364 (2002)
Ludwig, R.: Calixarenes in analytical and separation chemistry. Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. 367, 103–128 (2000)
Katz, A., Da Costa, P., Lam, A.C.P., Notestein, J.M.: The first single-step immobilization of a calix-[4]-arene onto the surface of silica. Chem. Mater. 14, 3364–3368 (2002)
Tabakci, M.: Immobilization of calix [6] arene bearing carboxylic acid and amide groups on aminopropyl silica gel and its sorption properties for Cr (VI). J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocyl. Chem. 61, 53–60 (2008)
Gübbük, I.H., Hatay, I., Coşkun, A., Ersöz, M.: Immobilization of oxime derivative on silica gel for the preparation of new adsorbent. J. Hazard. Materi. 172, 1532–1537 (2009)
Arena, G., Casnati, A., Contino, A., Mirone, L., Sciotto, D., Ungaro, R.: Synthesis of new calixcrowns and their anchoring to silica gel for the selective separation of Cs+ and K+. Chem. Commun. 19, 2277–2278 (1996)
Ohto, K., Tanaka, Y., Inoue, K.: Adsorptive separation of lead and zinc ions by novel type of calix [4] arene carboxylate resin immobilized with polyallylamine. Chem. Lett. 26, 647–648 (1997)
Xiao, X.Z., Feng, Y.Q., Da, S.L., Zhang, Y.: Preparation and evaluation of p-tert-butyl-calix [8] arene-bonded silica stationary phase for high performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Lett. 33, 3355–3372 (2000)
Sokoließ, T., Menyes, U., Roth, U., Jira, T.: Separation of cis-and trans-isomers of thioxanthene and dibenz [b, e] oxepin derivatives on calixarene-and resorcinarene-bonded high-performance liquid chromatography stationary phases. J. Chromatogr. A 948, 309–319 (2002)
Sokoließ, T., Schönherr, J., Menyes, U., Roth, U., Jira, T.: Characterization of calixarene-and resorcinarene-bonded stationary phases: I. Hydrophobic interactions. J. Chromatogr. A 1021, 71–82 (2003)
Li, L.S., Liu, M., Da, S.L., Feng, Y.Q.: Studies on the chromatographic behavior of nucleosides and bases on p-tert-butyl-calix [8] arene-bonded silica gel stationary phase by HPLC. Talanta 63, 433–441 (2004)
Li, L.S., Da, S.L., Feng, Y.Q., Liu, M.: Preparation and characterization of a p-tert-butyl-calix [6]-1, 4-benzocrown-4-bonded silica gel stationary phase for liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1040, 53–61 (2004)
Śliwka-Kaszyńska, M., Jaszczołt, K., Witt, D., Rachoń, J.: High-performance liquid chromatography of di-and trisubstituted aromatic positional isomers on 1, 3-alternate 25, 27-dipropoxy-26, 28-bis-[3-propyloxy]-calix [4] arene-bonded silica gel stationary phase. J. Chromatogr. A 1055, 21–28 (2004)
Liu, M., Li, L.S., Da, S.L., Feng, Y.Q.: High performance liquid chromatography with cyclodextrin and calixarene macrocycle bonded silica stationary phases for separation of steroids. Talanta 66, 479–486 (2005)
Śliwka-Kaszyńska, M., Jaszczołt, K., Hoczyk, A., Rachoń, J.: Preparation and evaluation of 1, 3-alternate 25, 27-dibenzyloxy-26, 28-bis-[3-propyloxy]-calix [4] arene-bonded silica stationary phase for high performance liquid chromatography. Chemia analityczna 51, 123–133 (2006)
Śliwka-Kaszyńska, M., Jaszczołt, K., Kołodziejczyk, A., Rachoń, J.: 1, 3-Alternate 25, 27-dibenzoiloxy-26, 28-bis-[3-propyloxy]-calix [4] arene-bonded silica gel as a new type of HPLC stationary phase. Talanta 68, 1560–1566 (2006)
Huai, Q.Y., Zuo, Y.M.: Study of the retention characteristics of calix [4] arene-bonded silica stationary phase and comparison with common phases for HPLC using linear solvation energy relationships. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 29, 801–814 (2006)
Nabok, A.V., Hassan, A.K., Ray, A.K., Omar, O., Kalchenko, V.I.: Study of adsorption of some organic molecules in calix [4] resorcinolarene LB films by surface plasmon resonance. Sens. Actuator B 45, 115–121 (1997)
Yang, X., Johnson, S., Shi, J., Holesinger, T., Swanson, B.: Polyelectrolyte and molecular host ion self-assembly to multilayer thin films: an approach to thin film chemical sensors. Sens. Actuator B 45, 87–92 (1997)
Hayashida, O., Shimizu, C., Fujimoto, T., Aoyama, Y.: Surface plasmon resonance study on the interaction of immobilized macrocyclic sugar clusters with lectins and water-soluble polymers. Chem. Lett. 27, 13–14 (1998)
Hassan, A.K., Ray, A.K., Nabok, A.V., Davis, F.: Spun films of novel calix [4] resorcinarene derivatives for benzene vapour sensing. Sens. Actuator B 77, 638–641 (2001) (2001)
Khalil, K.M., Elsamahy, A.A., Elanany, M.S.: Formation and characterization of high surface area thermally stabilized titania/silica composite materials via hydrolysis of titanium (IV) tetra-isopropoxide in sols of spherical silica particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 249, 359–365 (2002)
Kamboh, M.A., Solangi, I.B., Sherazi, S.T.H., Memon, S.: A highly efficient calix [4] arene based resin for the removal of azo dyes. Desalination 268, 83–89 (2011)
Gao, B., He, S., Guo, J., Wang, R.: Preparation and antibacterial character of a water-insoluble antibacterial material of grafting polyvinylpyridinium on silica gel. Mater. Lett. 61, 877–883 (2007)
Tabakci, M., Yilmaz, M.: Sorption characteristics of Cu (II) ions onto silica gel-immobilized calix [4] arene polymer in aqueous solutions: batch and column studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 151, 331–338 (2008)
Yilmaz, M., Memon, S., Tabakci, M., Bartsch, R.A.: New frontiers in polymer research. Nova Science Publishers, New York (2006)
Memon, S., Yilmaz, M.: Synthesis and complexation studies of 1, 3-dialkylated p-tert-butylcalix [4] arene telomers. React. Funct. Polym. 44, 227–233 (2000)
Taghvaei-Ganjali, S., Zadmard, R., Saber-Tehrani, M.: Immobilization of chlorosulfonyl-calix [4] arene onto the surface of silica gel through the directly estrification. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 5925–5932 (2012)
Servati, Z., Saber-Tehrani, M., Taghvaei-Ganjali, S., Zadmard, R.: Silica bonded calix [4] arene as an efficient, selective and reusable sorbent for rubber chemical additives. J. Porous Mater. 25, 1463–1474 (2018)
Ruiz, J.R., Jiménez-Sanchidrián, C., Hidalgo, J.M., Marinas, J.M.: Reduction of ketones and aldehydes to alcohols with magnesium–aluminium mixed oxide and 2-propanol. J. Mol. Catal. A 246, 190–194 (2006) (2006)
Hongbing, J.I., Huang, Y., Yu, Q., Tingting, W., Zhang, M.: Ni-mediated liquid phase reduction of carbonyl compounds in the presence of atmospheric hydrogen. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 14, 118–121 (2006)
Rahman, A., Jonnalagadda, S.B.: Rapid and selective reduction of adehydes, ketones, phenol, and alkenes with Ni–boride–silica catalysts system at low temperature. J. Mol. Catal. A 299, 98–101 (2009)
Cook, P.L.: The reduction of aldehydes and ketones with nickel—aluminum alloy in aqueous alkaline solution1. J. Org. Chem. 27, 3873–3875 (1962)
Yakabe, S., Hirano, M., Morimoto, T.: Alumina-assisted reduction of carbonyl compounds with sodium borohydride in hexane. Can. J. chem. 76, 1916–1921 (1998)
Zhang, Y., Liao, S., Xu, Y., Yu, D.: Catalytic selective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde to hydrocinnamaldehyde. Appl. Catal. A 192, 247–251 (2000)
Choudary, B.M., Kantam, M.L., Rahman, A., Reddy, C.R.V.: Selective reduction of aldehydes to alcohols by calcined Ni–Al hydrotalcite. J. Mol. Catal. A 206, 145–151 (2003)
Vayner, G., Houk, K.N., Sun, Y.K.: Origins of enantioselectivity in reductions of ketones on cinchona alkaloid modified platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 199–203 (2004)
Hu, A., Ngo, H.L., Lin, W.: Chiral porous hybrid solids for practical heterogeneous asymmetric hydrogenation of aromatic ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 11490–11491 (2003)
Maillet, C., Janvier, P., Bertrand, M.J., Praveen, T., Bujoli, B.: (2002) Phosphonate-based hybrid materials for catalysis? Supported rhodium/2, 2′-bipyridine complexes as reduction catalysts under hydrogen pressure. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 1685–1689 (2002)
Milone, C., Ingoglia, R., Tropeano, M.L., Neri, G., Galvagno, S.: First example of selective hydrogenation of unconstrained α, β-unsaturated ketone to α, β-unsaturated alcohol by molecular hydrogen. Chem. Commun. 7, 868–869 (2003)
De Bruyn, M., Coman, S., Bota, R., Parvulescu, V.I., De Vos, D.E., Jacobs, P.A.: Chemoselective reduction of complex α, β-unsaturated ketones to allylic alcohols over Ir-Metal particles on β zeolites. Angew. Chem. 115, 5491–5494 (2003)
Selvam, P., Sonavane, S.U., Mohapatra, S.K., Jayaram, R.V.: Chemoselective reduction of α, β-unsaturated carbonyls over novel mesoporous CoHMA molecular sieves under hydrogen transfer conditions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 346, 542–544 (2004)
Johnstone, R.A., Wilby, A.H., Entwistle, I.D.: Heterogeneous catalytic transfer hydrogenation and its relation to other methods for reduction of organic compounds. Chem. Rev. 85, 129–170 (1985)
Cho, B.T., Kang, S.K., Kim, M.S., Ryu, S.R., An, D.K.: Solvent-free reduction of aldehydes and ketones using solid acid-activated sodium borohydride. Tetrahedron 62, 8164–8168 (2006)
Kimura, K., Miura, T., Matsuo, M., Shono, T.: Polymeric membrane sodium-selective electrodes based on lipophilic calix [4] arene derivatives. Anal. Chem. 62, 1510–1513 (1990)
Kivlehan, F., Mace, W.J., Moynihan, H.A., Arrigan, D.W.: Potentiometric evaluation of calix [4] arene anion receptors in membrane electrodes: phosphate detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 585, 154–160 (2007)
Buie, N.M., Talanov, V.S., Butcher, R.J., Talanova, G.G.: New fluorogenic dansyl-containing calix [4] arene in the partial cone conformation for highly sensitive and selective recognition of lead (II). Inorg. Chem. 47, 3549–3558 (2008)
Coquière, D., Cadeau, H., Rondelez, Y., Giorgi, M., Reinaud, O.: Ipso-chlorosulfonylation of calixarenes: A powerful tool for the selective functionalization of the large rim. J. Org. Chem. 71, 4059–4065 (2006)
O’Connor, K.M., Arrigan, D.W., Svehla, G.: Calixarenes in electroanalysis. Electroanalysis 7, 205–215 (1995)
Tikhomirova, T.I., Fadeeva, V.I., Kudryavtsev, G.V., Nesterenko, P.N., Ivanov, V.M., Savitchev, A.T., Smirnova, N.S.: Sorption of noble-metal ions on silica with chemically bonded nitrogen-containing ligands. Talanta 38, 267–274 (1991)
Acknowledgements
The authors highly acknowledge the IAU, North Tehran Branch for financial supporting of this project. Also they are very grateful to Professor Saeed Taghvaei-Ganjali for his continuous and appreciable comments and supports of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chenari, A.B., Saber-Tehrani, M., Mamaghani, M. et al. Covalently anchored chlorosulfonyl-calix[4]arene onto silica gel as an efficient and reusable heterogeneous system for reduction of ketones using NaBH4. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 94, 45–53 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-019-00894-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-019-00894-x